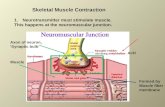
Topics –Role of calcium –Muscle fiber membrane potential & contraction –Neural control of...
-
Upload
kelley-carr -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of Topics –Role of calcium –Muscle fiber membrane potential & contraction –Neural control of...

• Topics– Role of calcium– Muscle fiber membrane potential & contraction– Neural control of muscle & reflexes– Whole muscle physiology

Role of calcium
Troponin complex
Tropomyosin
•Troponin and Tropomyosin bind to actinblock the actin – myosin binding sites
•Troponin is a calcium binding protein

• When Troponin binds calcium it moves Tropomyosin away from the actin-myosin binding site
CaCa

Where does Calcium come from?
• Intracellular storage called Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
• Surround each myofibril of the whole muscle• Contains high concentration of calcium
• Transverse Tubules connects plasma membrane to deep inside muscle

Myofibril
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Transverse tubules
Transverse tubules

• So far:– Actin and myosin will bind to each other– Troponin / tropomyosin inhibit this– Calcium removes inhibition

What controls muscle calcium?
• What else do we know?– Neurons initiate muscle contraction at NMJs
by generating postsynaptic potentials
(some muscle fibers have APs)
• Maybe muscle membrane potential is important

Muscle fiber
Tension
VmStimulate nerve
Te
nsio
n
Vm
Time
Muscle AP
Force Transducer
Excitation-Contraction coupling:1
‘twitch’

Vm
Tension
Force TransducerVary [K+] outside
Vm (mV)
Ten
sion
1.0
0-70 -60 -50 -40 -30
Conclusion: Muscle contraction occurs with Vm depolarization
Muscle fiber
Excitation-Contraction coupling:2

Why T-tubules important?Stimulate near T-tubule see contractionof adjoining sarcomeres
No contractions
T-tubule ‘Local stimulation’

Motor nerve
Neurotransmitter receptors
Membrane depolarization or APs carried deep into the muscle by T-tubules
+
T-tubule
SR

Text Fig 10-21Myofibril
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Transverse tubules
Transverse tubules

MyT-tubule
SR
SR
Ryanodine Receptor
Dihydropyridine receptor
myoplasm

T-tubule(extracellular)
SR
Myoplasm(intracellular)
++
++++
Ca++Ca++Ca++
_ _ _
+++
_ _ _+++
Ca++ pump

1. Synaptic Depolarization of the plasma membrane is carried into the muscle by T-Tubules
2. Conformational change of dihydropyridine receptor directly opens the ryanodine receptor calcium channel
3. Calcium flows into myoplasm where it binds troponin
4. Calcium pumped back into SR
Summary of events

• Neural Control of Muscle– Voluntary– Reflex

Neural control of muscle contraction
Motor Pool: all of the motor neurons that innervate a single muscle
Motor Unit: single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates– a few fibers 1000s of fibers

• Size of the motor units determines precision of movementFingers have small motor units, legs have big
motor units
• Recruitment of twitch fibers• Smallest motor units to a single muscle are
recruited first• Why?
Allow smooth generation of movement

First
Little force
Second
More force Even more force
Third
1+2+3 = maximum force
Whole muscle
Individual myofibrils
Motor neurons

Reflex control of muscle contraction
Two sensory receptors
1. Muscle Spindle• Monitors muscle length
2. Golgi Tendon Organ• Monitors muscle tension

Muscle Spindle
Motorneurons
Group I and IISensory fibers
IntrafusalMuscle fibers
ExtrafusalMuscle fibers
Muscle Spindle
Motor neurons

Muscle spindle
Extrafusal muscle fibers
nerve

motor neurons innervate extrafusal muscle fibers and cause the muscle to contract
motor neurons innervate only the intrafusal muscle fibers and cause them to contract
• The sensory endings in the muscle spindle are activated by muscle lengthening

Isolated muscleIa sensoryneuron
Motor neurons
Muscle stretch
Muscle length
APs insensory
APs inmotor
Spinal cord
Longer
AP
AP

Effect of muscle spindle
• When muscle stretches, spindle stretches1. Increase APs in 1a sensory neuron
2. Increase APs in motor neuron
3. Muscle contracts and returns to original length (almost)

• When muscle contracts, spindle shortens– Might expect activity of spindle to decrease
• BUT– To maintain sensitivity of the spindle, the
intrafusal fibers also contract– Controlled by motor neurons

Muscle Spindle
Motor neurons
ExtrafusalMuscle fibers
Motorneurons
Group I and IISensory fibers
IntrafusalMuscle fibers

Muscle length
longer
shorter
Motor neuron
Ia sensoryneuronstimulate
record
APs in sensory - Motor neuron only

Muscle length
longer
shorter
Motor neuron
Ia sensoryneuronstimulate
record
Motor neuron
APs in sensory - Motor neuron only
APs in sensory - and Motor neurons

Muscle Spindle motor neurons
• permit muscle spindle to function at all muscle lengths
• Maintains sensitivity of the spindle

Ia sensoryneuron
Muscle spindle
Motor neurons
Inhibitory interneuron
Spinal cord

Golgi Tendon Organ
• Operates like muscle spindle, but monitors muscle tension (force)
• Negative feedback because they inhibit the muscle they are located in

APs from GTO
Muscle length
longer
shorter
Increased APs during contraction
Very little at rest
Golgi Tendon Organ

Ib sensoryneuron
Golgi tendon organ
Motor neurons
Inhibitory
interneuron
Spinal cord

Muscle Spindle Response Tendon Organ Response
Passive Stretch Increase APs Decrease APs
Active Contraction No change Increase APs

Summary
• Muscle Spindles– Monitor muscle length– When activated cause contraction
• Golgi Tendon Organ– Monitor muscle tension– When activated reduce contraction

Whole muscle physiology
• Types of skeletal muscle fibers
• Neural control of muscle contraction
• Production of force

Classification of muscle fiber types
1. Electrical properties of muscle membrane – do muscles have APs?
2. Maximal rate of contraction (Vmax) • determined by myosin ATPase activity
3. Density of SR calcium pumps
4. Density of mitochondria and blood supply

Vertebrate Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types:
1. Tonic
2. Twitch (or Phasic)a. Slow oxidative (Type I)
b. Fast oxidative (Type IIa)
c. Fast glycolytic (Type IIb)

• Tonic fibers– Very slow contractions– Do not produce APs do not twitch– Postural muscles

Twitch muscles• Slow oxidative (Type I)
– Contract slowly– Resist fatigue – Postural
• Fast Oxidative– High rate of contraction– Moderately resistant to fatigue– Rapid, repetitive motion (flight muscles migratory
birds)
• Fast Glycolytic– Rapid contraction– Rapid fatigue

Non-twitch fibers
• Many arthropods (crayfish, insects) do not have muscle APs
• Rather they have graded synaptic potentials
• Calcium released from SR in graded manner
• Degree of contraction depends on summation and facilitation of neural input

Te
nsio
n
Vm
Time
Muscle AP
Te
nsio
n
Vm
Time
Summation of Synaptic Potential

Non-twitch fibers
• Graded potential graded contraction
• Even large motor units can have precise contraction

Twitches and Tetanus
• The amount of force generated varies with frequency of neural APs
• Under low frequency neural AP, muscle will contract and relax – Single twitches
• If neural APs arrive before muscle can relax, the forces generated are additive
• At highest frequencies the muscle does not relax– tetanus

Twitches and Tetanus
Temporal Summation (20Hz)
Single twitches (5 Hz)
Unfused Tetanus (80Hz)
Fused Tetanus (100 Hz)
Ten
sion
Time

Te
nsio
n
Vm
‘twitch’Muscle AP
Timelatency
• Why latency?– In part due to time for all biochemical
reactions– Also due to elastic components of the muscle
• Tendons, connective tissue, cross-bridge links

Contractile component
Series elasticcomponent
Parallel ElasticComponent

Rest Contraction initiated
•Sarcomere shortens•Series elastic component stretches •but no muscle shortening
Tension generation
•Sarcomere shortens further
•muscle shortens
Text fig 10-26

Whole muscle summary
• 4 types of skeletal muscle fibers
• Neural control of contraction– Twitches and tetanus– Motor units & size principal
• Generation of muscle force– Elastic components of muscle
• Non-twitch muscles– Graded contractions

Muscle Diseases
• Duchenne muscular dystrophy– Muscle wasting disease– Affects 1 in 3500 boys– Life expectancy ~20 years
• Genetic disease– Complete absence of the protein ‘dystrophin’

Muscle plasma membrane
Dystrophin
Actin cytoskeleton(not actin thin filaments)
Dystroglycan Dystroglycan
Grb2Acetylcholine receptor
Potential protein associations of dystrophinExtracellular matrix

• There are many effects of dystrophin absence including:– Altered calcium handling (too much)– Membrane destabilization (too permeable)– Susceptibility to mechanical damage

• Effects on neuromuscular physiology– Altered nACH receptor clusters– Reduced mepp size

Force is proportional to cross-sectional area