Muscle Contraction and Relaxation
description
Transcript of Muscle Contraction and Relaxation

Muscle Contraction and Relaxation

Important Muscle Fibres:
• Thin Filaments – Actin
• Thick Filaments - Myosin

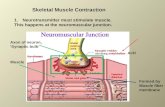
Contraction:• Myosin grabs onto the actin filaments• Forms “CROSSBRIDGES”
• ATP (energy) and Ca++ ions are needed for contraction
Myosin Fibre Actin Fibre

Relaxation:• ATP now pumps Ca++ out of muscle cell• Myosin releases actin filaments

Sliding Filament Theory
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0kFmbrRJq4w

Forensics Again!

Rigor Mortis (stiffness of death)
• ATP has been used to contract the muscles
• Actin and myosin remained linked = WHY?
• Relax when the muscles start to decompose

Order of Rigor
Facial muscles, eyelids, neck and jaw
Trunk and internal organs
Extremities
(Disappears in the same order from head down)
*also starts first in muscles that were exercising



Cadaveric Spasm

Timeline of Rigor• Becomes apparent at 2-4 hours after death.
• Complete at 12-18 hours after death.
• Begins to go away 18-36 hours after death.
• Usually disappeared 48-60 hours after death.

Algor Mortis (coldness of death)• Reduction of body temperature after death• Temperature taken under armpit, in the ear or
rectally (most accurate)• First 12 hours bodies lose 1.4⁰C per hour• After 12 hours bodies lose 0.7⁰C per hour
• General Formula: • hours dead = (37 ⁰ C – body temp)/1.4 ⁰C • Affected by clothing, body fat, illness, age, etc.

Pallor Mortis (paleness of death)
• Occurs 15 – 30 minutes after death• Blood sinks to lower parts of the body• Not much use to determine time of death

Livor Mortis (blueness of death)
• AKA Lividity
• Blood settles in the body at the lowest point
• Doesn’t settle in spots with pressure

Timeline of Livor Mortis
• Starts 20 min – 3 hr after death• Maximizes at 6 – 12 hours• Blood is congealed after 12 hours• Can help determine if body has been moved• Can help determine time of death– Press skin – pale – colour returns < 12 h






Other Ways to Estimate Time of Death:
• Stomach Contents – calculate the degree of digestion of food
• Insect activity – observe lifecycle of flies (including eggs and larvae)