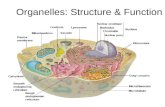
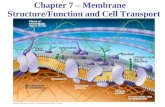
The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5
-
Upload
zephr-chan -
Category
Documents
-
view
40 -
download
1
description
Transcript of The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5
The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5
• Membrane Function
• Passive Transport
• Osmosis and Water Balance
• Active Transport
• Bulk Transport
–Exo- and Endocytosis
• Cell Signaling
Membrane Function
• Working cells must control the flow of materials to and from the environment.
Membrane Selectivity
• A cell membrane or wrapper made of phospholipids is relatively impermeable
• Proteins embedded in the membrane provide for selective permeability and transport of materials into and out of the cell, among other things
The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5
• Membrane Function
• Passive Transport
• Osmosis and Water Balance
• Active Transport
• Bulk Transport
–Exo- and Endocytosis
• Cell Signaling
Passive Transport: Diffusion Across Membranes
• Molecules contain heat energy.
– They vibrate and wander randomly.
• Diffusion is movement of molecules from regions of high concentration to low concentration
– Molecules tend to spread into the available space.
Diffusion
• Diffusion Across A Membrane
– Passive transport of small or hydrophobic molecules
– Facilitated diffusion of larger and polar molecules
The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5
• Membrane Function
• Passive Transport
• Osmosis and Water Balance
• Active Transport
• Bulk Transport
–Exo- and Endocytosis
• Cell Signaling
Osmosis and Water Balance in Cells
• Osmosis is the passive transport of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
• Water moves across a membrane from high concentration (high purity) to low concentration (low purity)
• A hypertonic solution
– Has a higher concentration of dissolved substances (solute)
Terms Used to Compare the Purity of Water Solutions
• A hypotonic solution
– Has a lower concentration of dissolved substances (solute)
• An isotonic solution
– Has an equal concentration of dissolved substances (solute).
5% salt
1% salt
1% salt
1% salt
1% salt
5% salt
The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5
• Membrane Function
• Passive Transport
• Osmosis and Water Balance
• Active Transport
• Bulk Transport
–Exo- and Endocytosis
• Cell Signaling
Active Transport: The Pumping of Molecules Across Membranes
• Active transport requires energy to pump molecules across a membrane, into more a more crowded space
Active Transport
• Active transport is the movement of molecules from low concentration to high concentration
The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5
• Membrane Function
• Passive Transport
• Osmosis and Water Balance
• Active Transport
• Bulk Transport
–Exo- and Endocytosis
• Cell Signaling
Bulk Transport: Exocytosis and Endocytosis
• Exocytosis
– Dumping molecules out of the cell (export)
Exocytosis and Endocytosis Introduction
• Endocytosis
– Bringing molecules into the cell (import)
– Includes pinocytosis, phagocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis
Bulk Transport: Exocytosis and Endocytosis
Pinocytosis: cell “drinking”
Phagocytosis: cell “eating”
The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5The Working Cell: Membrane Function CHAPTER 5
• Membrane Function
• Passive Transport
• Osmosis and Water Balance
• Active Transport
• Bulk Transport
–Exo- and Endocytosis
• Cell Signaling
The Role of Membranes in Cell Signaling
• Cellular communication
1. Begins with the reception of an extracellular signal.
3. A response is elicited from the transduced signal
2. The signal is transduced or passed across the membrane