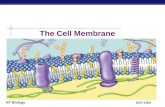
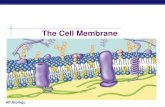
Cell Membrane Structure & Function Biology 11 Ms. Lowrie.
-
Upload
primrose-mcdaniel -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of Cell Membrane Structure & Function Biology 11 Ms. Lowrie.

Cell MembraneCell Membrane
Structure & FunctionStructure & Function
Biology 11Biology 11
Ms. LowrieMs. Lowrie

HomeostasisHomeostasis
Definition:Definition:– Constant state or balance within our Constant state or balance within our
internal environment even when the internal environment even when the external environment changesexternal environment changes
Required by each cell to continue lifeRequired by each cell to continue life
Maintained by cell membraneMaintained by cell membrane

Cell MembraneCell Membrane
Selectively permeableSelectively permeable– Allows some molecules to pass Allows some molecules to pass
through while stopping othersthrough while stopping others– a.k.a. semi-permeablea.k.a. semi-permeable
PermeabilityPermeability– Degree to which substances can Degree to which substances can
passpass

Parts of the Parts of the Cell Cell MembraneMembrane

extracellular fluid (outside cell)
cytoplasm (inside cell)
microfilamentsperipheral
protein
integral protein
cholesterol
glycolipid glycoprotein
carbohydrate chain
headtails
phospholipid bilayer

Fluid Mosaic ModelFluid Mosaic Model
FluidFluid– Phospholipids not Phospholipids not
attached & are attached & are able to moveable to move
MosaicMosaic Mixture, varietyMixture, variety
– Made of many Made of many partsparts
– Proteins floating Proteins floating throughout itthroughout it

Fluid Mosaic ModelFluid Mosaic Model

Phospholipid BilayerPhospholipid Bilayer
Two layer membrane Two layer membrane Phospholipids are NOT attached Phospholipids are NOT attached
togethertogether– FlexibleFlexible– Small holes willSmall holes will
seal quicklyseal quickly

PhospholipidsPhospholipids
Heads point outward Heads point outward – HydrophilicHydrophilic
Water attracting/lovingWater attracting/loving
Tails point inwardTails point inward– HydrophobicHydrophobic
Water repelling/Water repelling/
fearing fearing

Why are cells round?Why are cells round?
Because they are Because they are surrounded by surrounded by fluid...fluid...

Carbohydrate ChainCarbohydrate Chain
Chain of sugar moleculesChain of sugar molecules
Gives identity (unique marking)Gives identity (unique marking) for each type of cellfor each type of cell– Similar to a “fingerprint”Similar to a “fingerprint”
May be attached to a May be attached to a protein or a lipidprotein or a lipid

Cell IdentityCell Identity
DonationDonation– BloodBlood– OrgansOrgans
Immune Immune systemsystem

extracellular fluid (outside cell)
cytoplasm (inside cell)
glycolipid glycoprotein
carbohydrate chain

GlycoproteinGlycoprotein
Protein on outside of membrane Protein on outside of membrane – With carbohydrate chain attachedWith carbohydrate chain attached
Gives identityGives identity
glycoprotein

GlycolipidGlycolipid
Phospholipid on outside of Phospholipid on outside of membrane membrane – With carbohydrate chain attachedWith carbohydrate chain attached
Gives identityGives identity

Integral ProteinIntegral Protein
Protein extending through bilayerProtein extending through bilayer Contains channels Contains channels Moves molecules in/outMoves molecules in/out
a.k.a:a.k.a:– Carrier …Carrier …– Channel … Channel … – Gatekeeper …Gatekeeper …– Transport …Transport …– Membrane …Membrane …

Peripheral ProteinPeripheral Protein
Protein on inside layer of Protein on inside layer of membranemembrane
Attaches to microfilaments for Attaches to microfilaments for supportsupport

CholesterolCholesterol
Embedded in membraneEmbedded in membrane Allows membrane to function Allows membrane to function
in all temperaturesin all temperatures

Not all cholesterol is Not all cholesterol is bad!bad! In high temperaturesIn high temperatures
– Keeps membrane rigidKeeps membrane rigid
In low temperatures In low temperatures – Keeps membrane flexibleKeeps membrane flexible– Prevents cells from freezingPrevents cells from freezing

MicrofilamentsMicrofilaments
– a.k.a. “filaments of cytoskeleton”a.k.a. “filaments of cytoskeleton” Provides support for membraneProvides support for membrane

Other PartsOther Parts
Extracellular fluidExtracellular fluid– Fluid outside cellFluid outside cell
CytoplasmCytoplasm– Fluid inside cellFluid inside cell

What do you see?What do you see?

QuestionsQuestions
Answer:Answer:– #1, 2 & 5 (pg 49)#1, 2 & 5 (pg 49)
Hints:Hints:#1#1
““molecular structure” means what it is molecular structure” means what it is made ofmade of
#5#5 Look for 3 functions in the textLook for 3 functions in the text

#1 – Molecular #1 – Molecular StructureStructure Phospholipid bilayer
– Hydrophilic heads facing out– Hydrophobic tails facing in
Embedded with:– Proteins (peripheral & integral)– Glycoproteins– Glycolipids– Cholesterol

#2 – Fluid Mosaic #2 – Fluid Mosaic ModelModel Fluid:
– Phospholipids that are not attached to each other
Can easily move around and reposition
– Flexible Mosaic:
– Embedded with proteins mixed throughout

#5 – Protein Functions#5 – Protein Functions
1. Allow materials to move into and out of cell (integral)
2. Cell recognition/identity (glycoprotein)
3. Support (peripheral)4. Receptor sites for hormones

Extra QuestionsExtra Questions
A.A. Why is it important for the cell Why is it important for the cell membrane to be fluid?membrane to be fluid?
B.B. Define: selectively permeable, Define: selectively permeable, impermeable, permeable. Which term impermeable, permeable. Which term applies to the cell membrane? Why?applies to the cell membrane? Why?
C.C. Why do cells need an ‘identity’?Why do cells need an ‘identity’?
D.D. Why is cholesterol important?Why is cholesterol important?
E.E. List 3 materials that move into or out of List 3 materials that move into or out of cells.cells.
F.F. Contrast a cell membrane & cell wall.Contrast a cell membrane & cell wall.

A – Fluid MembraneA – Fluid Membrane
Allows for some movement without damage
Phospholipids rejoin quickly if a small hole is made

B – PermeabilityB – Permeability
Selectively/Semi – some things are allowed in or out
Impermeable – nothing … Permeable – everything …
Cell membrane = selectively permeable– Protects the cells

C – Cell C – Cell IdentityIdentity Blood donationBlood donation Organ Organ
transplanttransplant Immune Immune
systemsystem– Detects invaders Detects invaders
Allows cells to Allows cells to function in all function in all temperaturestemperatures
High temperatures:High temperatures:– Keeps membrane rigidKeeps membrane rigid
Low temperatures: Low temperatures: – Keeps membrane Keeps membrane
flexibleflexible– Prevents cells from Prevents cells from
freezingfreezing
D – D – CholesterolCholesterol

E – What Moves?E – What Moves?
In:In: WaterWater OxygenOxygen Carbon dioxideCarbon dioxide Glucose (sugar)Glucose (sugar) MineralsMinerals NutrientsNutrients
Out:Out: WaterWater OxygenOxygen Carbon DioxideCarbon Dioxide WastesWastes

F – Membrane vs. WallF – Membrane vs. Wall
Cell Membrane Living Made of proteins &
phospholipids Materials pass
between phospholipids
Found in plant and animal cells
Cell Wall Nonliving Made of
cellulose Materials pass
through small pores
Found in plant cells only

Any QuestionsAny Questions