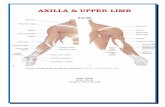
The upper limb
description
Transcript of The upper limb

The upper limb

Muscles That Move the Pectoral Girdle Originate on the axial skeleton and insert on the clavicle and
scapula. Stabilize the scapula and move it to increase the arm’s angle of
movements. Some of the superficial muscles of the thorax are grouped
together according to the scapular movement they direct. elevation, depression, protraction, or retraction

The muscles of backSuperficial group Trapezius Latissimus dorsi Levator scapulae Rhomboideus
Deep group Erector spinae Splenius Thoracolumbar fascia

4

The muscles of thoraxExtrinsic muscles Pectoralis major Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior
Intrinsic muscles Intercostales externi Intercostales interni Intercostales intimi

6

The Muscles of Upper Limb
Muscles of shoulder Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Teres major Subscapularis

Major muscles of shoulder
Deltoid Origin: lateral third of
clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula
Insertion: deltoid tuberosity of humerus
Action: abduction, flexion and extension, medial and lateral rotation of arm

Major muscles of shoulderTeres major Origin: dorsal surface
of inferior angle of scapula
Insertion: crest of lesser tubercle of humerus
Action: medially rotates and adducts arm

Arm and Forearm Muscles That Move the Elbow Joint/Forearm Anterior (flexor) compartment Posterior (extensor) compartment Anterior compartment
primarily contains elbow flexors Posterior compartment contains elbow extensors
the principal flexors biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis
muscles that extend the elbow joint triceps brachii and anconeus


Muscles of arm Antererior group
Biceps brachii Coracobrachialis Brachialis
Posterior group triceps brachii anconeus

Muscles of armBiceps brachii Origin: long head,
supraglenoid tubercle; short head, coracoid process
Insertion: radial tuberosity Action: supinator of forearm,
flexor of elbow joint, weak flexor of should joint

Muscles of armTriceps brachii Origin:
long head, infraglenoid tubercle lateral head, above groove for
radial nerve medical head, below groove for
radial nerve Insertion: olecranon of ulna Action: extends elbow joint,
long head extends and adducts shoulder joint

Triceps brachii

Forearm Muscles Supinate and Pronate Supinator muscle supinates the forearm. Biceps brachii supinates the forearm. Pronator teres and pronator quadratus pronate the forearm.
Move the Wrist Joint, Hand, and Fingers Muscles in the forearm move the hand at the wrist and/or the fingers. Extrinsic muscles of the wrist and hand originate on the forearm, not
the wrist or hand.
Tendons of forearm muscles typically are surrounded by tendon (synovial) sheaths and held adjacent to the skeletal elements by strong fascial structures.
At the wrist, the deep fascia of the forearm forms thickened, fibrous bands termed retinacula.


Muscles of forearm
Superficial layer Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus Flexor carpi ulnaris

Muscles of forearmPronator teres Origin: medical epicondyle of
humerus and deep fascia of forearm
Insertion: middle of lateral surface of radius
Action: pronation of forearm and flexion of elbow

Second layer Flexor digitorum superficials

Third layer Flexor digitorum
profundus Flexor pollicis longus
Fourth layer Pronator quadratus
Action: flex radiocarpal joint and fingers, pronate forearm

Lateral group (3)
Brachioradialis Extensor carpi radialis
longus Extensor carpi radialis
brevis

Posterior group (8) Superficial layer (3)
Extensor digitorum Extensor digiti minimi
Extensor carpi ulnaris Action: extension at
wrist joint

Deep layer (5) Supinator Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis Extensor pollicis longus Extensor indicis Action: extend at wrist
joint and fingers, and supinate forearm
Posterior group (8)

Muscles of hand Lateral group thenar (4)
Abductor pollicis brevis Flexor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Adductor pollicis
Action: flex, abduct, adduct and oppose thumb
Medial group hypothenar (3) Abductor digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi brevis Opponens digiti minimi
Action: flex, abduct , and oppose little finger

Muscles of handIntermedial group Lumbricales (4) flex
fingers at MP joints; extend fingers at IP joints
Palmar interossei (3) adduct fingers towards middle finger at MP joints
Dorsal interossei (3) abduct fingers away from middle finger at MP joints

Arteries of upper limbAxillary artery Continuation of subclavian artery at
lateral border of first rib Becomes brachial artery at lower
border of teres major Divided into three parts by overlying
pectoralis minor First portion, above muscle - gives
rise to thoracoacromial a. Second portion, behind muscle -
gives rise to lateral thoracic a. Third portion, below muscle - gives
rise to subscapular a., anterior and posterior humeral circumflex a.; the former then divides into throcodorsal a. and circumflex scapular a.


Brachial artery Continuation of axillary
artery Divides into radial and
ulnar arteries at level of neck of radius
Branches Deep brachial a.
accompanies with radial nerve
Superior ulnar collaeral a. accompanies with ulnar nerve
Inferior ulnar collateral a.
Arteries of upper limb

Radial artery and branches Radial recurrent a. Superfical palmar branch Principal artery of thumb Ulnar artery and branches Ulnar recurrent a. Common interosseous artery
Anterior interossous a. Posterior interosseous a.
Deep palmar branch
Arteries of upper limb

Superficial palmar arch Formed by ulnar artery
and superficial palmar branch of radial artery
Curve of arch lies across the palm, level with the distal border of fully extended thumb
Gives rise to three common palmar digital arteries each then divides into two proper palmar digital arteries
Arteries of upper limb

Deep palmar arch Formed by radial artery
and deep palmar branch of ulnar artery
Curve of arch lies across upper part of palmar at level with proximal border of extended thumb
Gives rise to three palmar metacarpal arteries
Arteries of upper limb

Veins of the upper limbDeep veins: accompany the
arteries of the same region and bear similar names
Superficial veins Cephalic vein
Arises from the lateral side of the dorsal venous rete of hand
Ascends on radial side of the forearm to the elbow and then in the lateral side of biceps brachii furrow, continues up the arm in the deltopectoral groove and then to the infraclavicular fossa, where it pierces clavipectoral fascia to drain into axillary vein

Basilic vein Arises from the medial side of
the dorsal venous rete of hand
Ascends on the ulnar side of forearm to the elbow and then in the medial bicepital brachii furrow to middle of the arm where it pierces the deep fascia and joins the brachial vein or axillary vein
Median cubital vein links cephalic vein and basilic
vein in the cubital fossa. It is a frequent site for venipuncture to remove a sample of blood or add fluid to the blood

The lymphatic drainage of upper limbLymphatic vessels
Superficial - follow the superficial veins, drain into supratrochlear and axillary lymph nodes
Deep - accompany main vessels, end in axillary lymph nodes
lymph nodes Cubital lymph node: lies above
medial epicondyle of humerus Axillary lymph node - arranged
in five groups

Axillary lymph nodesArranged in five groups Lateral lymph nodes lie around
the distal end of axillary vein , receiving drainage from the arm, forearm, and hand
Pectoral lymph nodes lie along lateral thoracic vessels, receive afferents from anterior thoracic wall including central and lateral portion of mamma
Subscapular lymph node along subscapular vessels, receive lymph from nape and scapular region
Efferents above three groups pass to central lymph node

Central lymph node lie in fat of axillary fossa,
receive drainage from all the above nodes, efferents pass to apical lymph node
Apical lymph node Lie in the apex of the axilla,
along the proximal end of axillary vessels
Receive drainage chiefly from central lymph node , upper portion of mamma
Efferents form subclavian trunk, the right subclavian trunk joints the right lymphatic duct; left usually drains directly into thoracic duct

Brachial plexus Formation: Five roots: formed by anterior
rami of C5-C8 and T1 spinal nerves, roots C5-C7give rise to long thoracic n.
Three trunks The upper trunk is formed by the
joining of root C4,C5,C6. The middle trunk is the
continuation of root C7. The lower trunk is formed by the
joining of root C8 and T1. Six divisions: above clavicle,
trunks form anterior and posterior divisions
Three cords: below clavicle, divisions form three cords that surround the second portion of axillary a.

Position: passes through the scalene fissure to
posterosuperior of subclavian artery, then enters the axilla to form lateral, medial and posterior cords
Main branches Lateral cord
Musculocutaneous n. Lateral root to median n.
Medial cord Medial root to median n. Ulnar n. Medial brachial cutaneous n. Medial antebrachial cutaneous n.

Posterior cord radial n. axillary n. thoracodorsal n.

Musculocutaneous Distribution: Biceps
brachii, brachalis and coracobrachialis ‘BBC nerve’; skin on anterior aspect of forearm

Distribution: Flexors of forearm except brachioradialis, flexor carpi ulnaris and ulnar half of flexor digitorum profundus, thenar except adductor pollicis, first two lumbricals; skin of thenar, central part of palm, palmar aspect of radial three and one-half fingers, including middle and distal fingers on dorsum.
Injury: Apehand produces sign of benediction,
in which the index and middle fingers cannot be flexed and the thumb cannot be opposed
Median nerve

Distribution: Flexor carpi ulnaris, ulnar half of flexor digitorum profundus, hypothenar muscles, interossei, 3rd and 4th lumbricals and adductor pollicis; skin of hypothenar, palmar surface of ulnar one and one-half fingers, ulnar half of dorsum of hand, posterior aspect of ulnar two and one-half fingers
Injury: clawhand
Ulnar nerve

Distribution: Extensor muscles of arm and forearm, brachioradialis; skin on back of arm, forearm, and radial side of dorsum of hand and radial two and one-half fingers
Injury: Wristdrop
Radial nerve

Axillary Distribution: Deltoid
and teres minor muscle; skin over deltoid and upper posterior aspect of arm
Injury: results in deltoid and teres minor paralysis (loss of shoulder abdution and weel external rotation) with loss of sensation over the deltoid