The Structure and Function of Cells Cell Theory Parts of a cell Organelles Cell Diversity Crossing...
-
Upload
joleen-grant -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
0
Transcript of The Structure and Function of Cells Cell Theory Parts of a cell Organelles Cell Diversity Crossing...

The Structure and Function The Structure and Function of Cellsof Cells
Cell TheoryCell TheoryParts of a cellParts of a cellOrganellesOrganellesCell DiversityCell DiversityCrossing the MembraneCrossing the Membrane
Unit 5

The Cell TheoryThe Cell Theory
4 Parts4 Parts–Cells are the basic unit of lifeCells are the basic unit of life–All organisms are made up of All organisms are made up of
one or more cellsone or more cells–All cells carry out life processesAll cells carry out life processes–All cells arise from pre-existing All cells arise from pre-existing
cellscells

Who is Responsible for this cell Who is Responsible for this cell theory????theory????
A whole bunch of dead A whole bunch of dead scientists…..scientists…..– Anton Von LeeuwenhoekAnton Von Leeuwenhoek
– Robert HookeRobert Hooke
– Matthais Schleiden Matthais Schleiden
– Theodor SchwannTheodor Schwann
– Carolis LinnaeusCarolis Linnaeus

The Parts of a Cell The Parts of a Cell (organelles) (organelles)
Organelle = Little organsOrganelle = Little organs

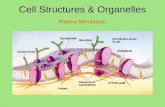
Cell membraneCell membraneFound in plant and animal cellsFound in plant and animal cells
Outside of cellOutside of cell
Controls what enters Controls what enters and leaves the cell.and leaves the cell.
Holds the cell Holds the cell together and keeps together and keeps the organelles the organelles inside.inside.

Cell Wall (Plant cell only)Cell Wall (Plant cell only)
Cell Wall

Cell wallCell wall - What is it? - What is it?
Found only in plant Found only in plant cells outside of the cells outside of the cell membranecell membrane
Composed mainly of Composed mainly of cellulose (type of cellulose (type of carbohydrate)carbohydrate)

What is the Cell Wall for?What is the Cell Wall for?
Helps to maintain the shape of the plant Helps to maintain the shape of the plant and keep the structure of the plant.and keep the structure of the plant.

The NucleusThe NucleusBrainBrain of the cell of the cell
It tells every part of the It tells every part of the cell what to do.cell what to do.
Prokaryotes-do not Prokaryotes-do not have a nucleushave a nucleus
Eukaryotes-have a Eukaryotes-have a nucleusnucleus

What’s inside the nucleus?What’s inside the nucleus?
DNADNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) (deoxyribonucleic acid)
DNA tells the cell what proteins to make DNA tells the cell what proteins to make and what the cell needs to do.and what the cell needs to do.

TheThe Nuclear MembraneNuclear Membrane
The nuclear membrane is a membrane The nuclear membrane is a membrane around the nucleus that holds it together around the nucleus that holds it together and helps keep DNA insideand helps keep DNA inside

NucleolusNucleolus
Looks like a small, Looks like a small, dark area inside the dark area inside the nucleus.nucleus.
This contains This contains protein and RNA…protein and RNA…

RibosomesRibosomesProtein builders of the Protein builders of the cellcell
Found either free floating Found either free floating in the cytoplasm (fluid in the cytoplasm (fluid that fills a cell) or that fills a cell) or attached to the attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.endoplasmic reticulum.
Proteins made are used Proteins made are used inside and outside of the inside and outside of the cell for growth and cell for growth and repair.repair.

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
2 Types - Rough and 2 Types - Rough and Smooth ERSmooth ER
Used for transport in Used for transport in the cellthe cell

No Ribosomes on its surface Has Ribosomes on its surface

Golgi ApparatusGolgi ApparatusMade out of a bunch of Made out of a bunch of flattened sacs. Think of flattened sacs. Think of a stack of pancakes.a stack of pancakes.
It is the packaging center It is the packaging center of the cell.of the cell.
Like a mailroomLike a mailroom
It takes simple molecules It takes simple molecules and combines them to and combines them to form more complex form more complex molecules.molecules.

MitochondriaMitochondriaPOWERHOUSE OF POWERHOUSE OF THE CELLTHE CELL
Where cells use Where cells use glucose to make glucose to make energy (ATP)energy (ATP)
Site of Site of respirationrespiration in in a cella cell

ChloroplastChloroplast (Plant cells only) (Plant cells only)
Carry out Carry out photosynthesisphotosynthesis - - take energy from the take energy from the sun and make food.sun and make food.
This food comes in This food comes in the form of sugars the form of sugars and starches and starches (glucose)(glucose)

Photosynthesis

VacuoleVacuoleStorage compartments Storage compartments in cellsin cells
Some contain food, Some contain food, others hold oil, some others hold oil, some hold wasteshold wastes
They are huge in plant They are huge in plant cells and much smaller cells and much smaller in animal cellsin animal cells
The vacuole basically The vacuole basically holds things that the holds things that the cell might need, like a cell might need, like a backpackbackpack

LysosomesLysosomes
Have enzymes that break Have enzymes that break down waste and down waste and unwanted cellular unwanted cellular material.material.

CentriolesCentrioles
Only in animal Only in animal cellscells
Where Where chromosomes chromosomes attach during attach during cellular cellular reproduction.reproduction.

Lets put ‘em all togetherLets put ‘em all together
Animal Cells Plant Cells

Animal CellAnimal Cell
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosome
Mitochondria Vacuole
Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus
NucleolusFlagella
Cell Membrane

Animal Cells-DrawingAnimal Cells-Drawing

Plant CellsPlant Cells
Where do they come from?Where do they come from?
Plants of course……DUH!!Plants of course……DUH!!
All plant cells have the same characteristicsAll plant cells have the same characteristics

Plant cellPlant cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Chloroplast
Cell membrane
Cell wall
Vacuole
Mitochondria
Golgi
Nucleus

Major Differences between Major Differences between Plant and Animal CellsPlant and Animal Cells
Plant CellsPlant CellsPlants have a cell Plants have a cell wallwall
Contain Contain chloroplastschloroplasts
Have a large Have a large vacuolevacuole
Do NOT have Do NOT have centriolescentrioles
Animal CellsAnimal CellsNo cell wallNo cell wall
No ChloroplastsNo Chloroplasts
Small vacuolesSmall vacuoles
Have centriolesHave centrioles

One more thing to worry One more thing to worry about…about…
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic cellsProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic cellsProkaryotesProkaryotes
NO NUCLEUSNO NUCLEUSHave a cell Have a cell membrane and membrane and cytoplasm…but no cytoplasm…but no organellesorganellesCarry out life Carry out life processesprocesses
EXP: EXP: BacteriaBacteria
EukaryotesEukaryotesHAVE NUCLEUSHAVE NUCLEUSHave organelles Have organelles contained within the contained within the cytoplasmcytoplasmCarry out life Carry out life processesprocesses
EXP: EXP: PlantPlant and and animalanimal cellscells