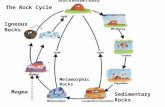
Rocks and the Rock Cycle Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic varieties.
The Rock Cycle Thinking about relationships among the major rock groups (Igneous, Sedimentary, and...
-
Upload
jaime-woollen -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
1
Transcript of The Rock Cycle Thinking about relationships among the major rock groups (Igneous, Sedimentary, and...
The Rock CycleThinking about relationships among the
major rock groups (Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic)
3
Major Rock Groups• Igneous
– Formed from a melt (i.e. molten rock)– Plutonic (i.e. intrusive): slow cooling and crystallization
from a magma.– Volcanic (i.e. extrusion): quick cooling at the surface (lava).
• Sedimentary– Formed at the Earth’s surface.– Clastic (mineral fragments or grains, clays)– Chemical (crystalline chemical/biochemical precipitates)
• Metamorphic– Changed by pressure, temperature and hot chemical fluids.
10
MAGMA
Volcanic
IGNEOUS
Plutonic
SEDIMENT
SEDIMENTARY
Uplift
Crystallization
WeatheringErosion
Transport
Deposition
11
MAGMA
Volcanic
IGNEOUS
Plutonic
SEDIMENT
SEDIMENTARY
Uplift
Crystallization
WeatheringErosion
Transport
Deposition
Lithification
Remember
• Lithification =– Sediment turns to sedimentary rock by the processes of
compaction and cementation.
13
MAGMA
Volcanic
IGNEOUS
Plutonic
SEDIMENT
SEDIMENTARY
METAMORPHIC
UpliftBurial
Increased P&T
Crystallization
WeatheringErosion
Transport
Deposition
Lithification
Remember
• Note that the process of melting is not involved or associated with metamorphism.
• Note that the grade of metamorphism could be increased (e.g., low-grade metamorphic rocks to high-grade metamorphic rocks) as the conditions of metamorphism are increased.
15
MAGMA
Volcanic
IGNEOUS
Plutonic
SEDIMENT
SEDIMENTARY
METAMORPHIC
UpliftBurial
Increased P&T
MeltingCrystallization
WeatheringErosion
Transport
Deposition
Can you see
any shortcuts?
Lithification
16
MAGMA
Volcanic
IGNEOUS
Plutonic
SEDIMENT
SEDIMENTARY
METAMORPHIC
UpliftBurial
Increased P&T
MeltingCrystallization
WeatheringErosion
Transport
Deposition
Lithification
• The rock cycle demonstrates the relationships among the three major rock groups.
• It is powered by the interior heat of the Earth as well as Earth’s momentum and the energy from the sun.
• It involves processes on Earth’s surface as well as the Earth’s interior.
• It connects the “hydrologic cycle” with the “tectonic cycle”.
In Conclusion…