Case 107: 43-Year-Old Lady with Severe Upper Abdominal Pain.
The problem of upper abdominal pain
-
Upload
ahmed-bahnassy -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
944 -
download
1
description
Transcript of The problem of upper abdominal pain

The problem of Upper Abdominal
painDr/Ahmed a. Bahnassy
Consultant Radiologist RMH
MBCHB-MSc-FRCR

Anatomical orientation

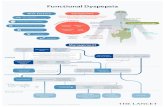
Aetiology: Pancreatic: Acute or chronic Pancreatitis. Hepatic: hepatitis, hepatic abscess. Gastric:gastritis Duodenal :Duodenal ulcer,duodenitis. Biliary :Cholecystitis,choledocholithiasis. Renal : stones,pyelonephritis. Aortic :Dissecting aortic aneurysm. Splenic: Infarction (Sickle cell crisis) Large bowel: Colitis. Referred pain :e.g.pneumonia,spondylosis.

Methods of Examination Plain x-ray Barium studies. Ultrasonography Computed tomography. Isotopic scan (e.g.: Cholecystitis) MRI :MRCP Arteriography.

Rationale of imaging Clinical data of the patient.
Biliary colic Epigastric pain with high serum amylase Flank pain with haematuria jaundice
Ultrasound
CT
US NECT/IVP
ERCP/MRCP
US Focal hepatic lesion
Triphasic CT/MRIBiliary dilatation
ERCP/MRCP
No biliary duct dilatation
Pre/hepatic haundice

Plain abdominal films Stones detection. Calcifications. Air under diaphragm.

Gall Stones and chronic Pancreatitis

Gall stones

Pneumoperitoneum -Free air

Subphrenic Abscess

Contrast studies Evaluation of gastroesophageal junction
abnormalities. Gastric ulcers and masses. Duodenal pathology.

Hiatal Hernia.

Giant Gastric ulcer

Duodenal ulcer

Ultrasonography. Gall bladder disease. Biliary radicle dilatation. Renal problems.

Acute Calcular Cholecystitis

Biliary dilatation

Hydronephrosis

Computed Tomography Pancreatitis evaluation. Focal hepatic lesions. Renal diseases. Aortic lesions. Bony lesions Trauma evaluation.

Acute Pancreatitis .

CT severity index

Acute pseudocyst

Pancreatic necrosis

The Focal Hepatic Lesion:Radiologic Assessment

Hepatic VenousPortal Venous
Triple Phase Helical CT
Axial C+ CT Arterial Phase
Axial C+ CT Portal Venous
Phase
Axial C+ CT Hepatic Venous
Phase
Contrast Injection
Arterial
0 15 30 45 60 75Time (sec)

Liver Metastasis.Axial C+ CT
Film Findings:
Multiple hypoenhancing heterogenous lesions

Liver AbscessAxial C+ CT
Film Findings:
Well demaracated hypoenhancing lesion
Rim of increased Rim of increased enhancement relative to enhancement relative to central regioncentral region

Complicated Hydatid cyst .water lilly sign

NECT
Right chronic pyelo-nephritis
Left renal stones

Renal Abscess

Aortic Dissection Type B

Bony lesions :Lytic lesion in upper lumbar vertebra .

Abdominal trauma On evaluation, urgent life-threatening injuries,
such as a large hemoperitoneum, a large or tension pneumothorax, or active arterial extravasation, should be sought out first.
This should be followed by a thorough interrogation for injury of the abdomen and pelvis: liver and right paracolic gutter; spleen and left paracolic gutter; upper abdominal organs, arterial tree; retroperitoneum; small bowel, colon, and mesentery.

liver trauma 4-cm-thick
subcapsular hematoma associated with parenchymal hematoma

Renal injury
Subcapsular and perinephric haematoma.

Splenic trauma
Splenic lacerations with perisplenic haematoma

Clinical evaluation of the patient is the first step in the diagnosis.
Choose the appropriate imaging modality.