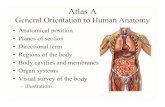
The Planes of the Body
description
Transcript of The Planes of the Body

The Planes of the Body• Anterior
• Posterior
• Midline
• Midclavicular line
• Midaxillary

Directional Terms• Right and left• Superior and inferior• Lateral and medial• Proximal and distal• Superficial and deep• Ventral and dorsal • Palmer and planter• Apices and bilateral

Movement Terms

Anatomic Positions (1 of 2)
• Prone
• Supine

Anatomic Positions (2 of 2)
• Shock position
• Trendelenburg’s position
• Fowler’s position

The Skeletal System• Gives form to the body
• Protects vital organs
• Consists of 206 bones
• Acts as a framework for attachment of muscles
• Designed to permit motion of the body

The Skull

The Neck

The Spinal Column

The Thorax

The Abdomen (1 of 2)
• The abdomen is the second major body cavity.
• It contains the major organs of digestion and excretion.

The Abdomen (2 of 2)

The Pelvis

The Lower Extremity• Hip• Thigh• Knee• Leg• Ankle• Foot

The Upper Extremity• Shoulder girdle• Arm• Elbow• Forearm• Wrist• Hand

Joints

Functions of theMusculoskeletal System • Gives the body shape• Protects internal organs• Provides for movement• Consists of more than 600
muscles

Types of Muscle (1 of 2)
• Skeletal (voluntary) muscle
– Attached to the bones of the body
• Smooth (involuntary) muscle
– Carries out the automatic muscular functions of the body

Types of Muscle (2 of 2)
• Cardiac muscle– Involuntary muscle– Has own blood supply and electrical system– Can tolerate interruptions of blood supply for
only very short periods

The Respiratory System

Diaphragm• Has characteristics of both voluntary and
involuntary muscles
• Dome-shaped muscle
• Divides thorax from abdomen
• Contracts during inhalation
• Relaxes during exhalation

Breathing Process: Inhalation• Diaphragm and intercostal muscles
contract, increasing the size of the thoracic cavity.
• Pressure in the lungs decreases.
• Air travels to the lungs.

Breathing Process: Exhalation• Diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax.
• As the muscles relax, all dimensions of the thorax decrease.
• Pressure in the lungs increases.
• Air flows out of the lungs.

Exchange of Oxygen andCarbon Dioxide
• Oxygen-rich air is delivered to alveoli with inspiration.• Oxygen diffuses into the blood.• The body does not use all the inhaled oxygen.

Control of Breathing• Brain stem controls breathing.
– Increases breathing rate if the carbon dioxide level in blood becomes too high
• Hypoxic drive is a “backup system.”
– Activates when oxygen levels fall to stimulate breathing

Normal Breathing Characteristics• Normal rate and depth• Regular rhythm• Good breath sounds in both lungs• Regular rise and fall movements in the
chest• Easy, not labored

Normal Breathing RatesAdults 12 to 20 breaths/min
Children 15 to 30 breaths/min
Infants 25 to 50 breaths/min

Recognizing Inadequate Breathing• Irregular rhythm
• Labored breathing
• Muscle retractions
• Pale or blue skin
• Cool, clammy skin
• Faster respiratory rate

Infant and Child Anatomy• Structures less rigid• Airway smaller• Tongue proportionally
larger• Dependent on diaphragm
for breathing

The Circulatory System

The Heart

Blood Flow Through the Heart

Electrical Conduction System• SA node
• AV node
• Purkinje fibers

Normal Heart RatesAdults 60 to 100 beats/min
Children 70 to 150 beats/min
Infants 100 to 160 beats/min

Major Arteries and Veins• Aorta
• Pulmonary
• Carotid
• Femoral
• Brachial
• Radial
• Superior vena cava
• Inferior vena cava
• Pulmonary

Components of Blood• Plasma
• Red blood cells
• White blood cells
• Platelets

Physiology of theCirculatory System (1 of 2)
• Pulse
– The wave of blood through the arteries formed when the left ventricle contracts
– Can be felt where an artery passes near the skin surface and over a bone

Physiology of theCirculatory System (2 of 2)
• Blood pressure– Amount of force exerted against walls of arteries– Systole: Left ventricle contracts– Diastole: Left ventricle relaxes
• Perfusion– Circulation of blood within an organ or tissue– If inadequate, the patient goes into shock.

The Nervous System• The nervous system controls the body’s voluntary
and involuntary actions.
• Somatic nervous system
– Regulates voluntary actions
• Autonomic nervous system
– Controls involuntary body functions

Central Nervous System (1 of 2)

Central Nervous System (2 of 2)

Peripheral Nervous System• Links the organs of the body to the central nervous
system.• Sensory nerves carry information from the body to
the central nervous system.• Motor nerves carry information from the central
nervous system to the muscles of the body.

The Skin (1 of 2)
• Protects the body from the environment
• Regulates body temperature
• Transmits information from environment to the brain

The Skin (2 of 2)

Endocrine System• Complex message and control system
• Made up of seven glands
• Glands produce and release hormones.

Endocrine Glands• Adrenal
• Ovary
• Pancreas
• Parathyroid
• Pituitary
• Testes
• Thyroid

Digestive System• Mouth
• Salivary glands
• Oropharynx
• Esophagus
• Stomach
• Pancreas
• Liver
• Bile ducts
• Small intestine
• Large intestine
• Appendix
• Rectum

Urinary System

Male Reproductive System

Female Reproductive System













![[A&P eBook] Planes and Positions | Visible Body](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5874dd9c1a28abd05f8b739f/ap-ebook-planes-and-positions-visible-body.jpg)




