The Integumentary System The body’s largest organ is the skin ~ 9-11 pounds (7% total body wt) An...
-
Upload
judith-kurk -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of The Integumentary System The body’s largest organ is the skin ~ 9-11 pounds (7% total body wt) An...

The Integumentary SystemThe body’s largest organ is the skin ~ 9-11 pounds (7% total body wt)
An average adult male covers 20 square feetAn average adult female covers 17 square feet
Skin is constantly flaking away and replaced completely every 4 weeksOn average, every person sheds 40 pounds of skin in a lifetime
Everything you see when you look at someone is dead!

The Integumentary SystemWould you be enticed by an advertisement for a coat that is waterproof, stretchable, washable, and permanent-press, that automatically repairs small cuts, rips and burns, and that is guaranteed to last a lifetime with
reasonable care?

Integumentary System· Integument means “covering”
· Structures
· Skin (cutaneous membrane)· Cut- or cutis- = the true skin; -ous = possessing, full of
· Covers 15 to 20 square feet
· Average weight is 9 pounds (7% of body weight)
· Composed of two layers
· Epidermis (epithelial) and dermis (fibrous CT)
· Skin derivatives· Sweat glands, oil glands, hairs and nails

Skin (Integument) Functions• Mechanical (physical) protection
(barrier)
• Hardness of keratinized cells (intact epidermis)
• Chemical protection (barrier)
• Melanin produced by melanocytes provides shield to prevent UV damage
• “Acid mantle”
• Acidic secretions that inhibits bacteria
• Desiccation
• Prevention of drying out (keratin waterproofs)

Skin (Integument) Functions• Biological protection (barrier)
• Langerhans’ cells in epidermis and macrophages (phagocytes) in dermis ingest foreign substances and pathogens

Skin (Integument) Functions
• Temperature Regulation
• Normal conditions sweat glands produce ~ 500 mL of sweat a day
• If body temperature rises, nervous system stimulates blood vessels to dilate and sweat glands to secrete sweat
• Heat loss
• Activate sweat glands produce sweat
which evaporate and cool the body
• Allow blood to flush in skin capillary beds
and radiate from surface of the skin
• Heat retention
• Not allowing blood to flush into skin capillary beds

Skin Functions· Cutaneous sensation
· Cutaneous sensory receptors (nervous system)
· Exteroceptors (respond to external stimuli)
· Detect pain, light pressure, deep pressure, and temperature (hot and cold)· Meissner’s corpuscles (dermal papillae)
· Light pressure and touch
· Pacinian corpuscles (deep dermis)
· Deep pressure
· Free nerve endings
· Painful stimuli like chemicals, temperature change, or pain

Skin (Integument) Functions· Metabolic functions (chemical reactions)
· Modified cholesterol molecules in skin are converted to vitamin D by sunlight
· Without vitamin D calcium cannot be absorbed in the intestines
· Blood reservoir· Dermal vascular supply is extensive and can hold large volumes of blood
(about 5% of entire blood volume)

Skin (Integument) Functions· Excretion
· Nitrogen-containing wastes, water and salts are eliminated in sweat

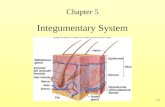
Skin Structure

Skin Structure· Epidermis (outer layer) (Epi - = upon, on)
· Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
· Avascular (without blood vessels)
· Oxygen and nutrients diffuse from dermis
· Dermis (inner layer)· Dense fibrous CT with collagen and elastic fibers
· Much thicker
· Contains blood vessels, nerve fibers, etc.
· Hypodermis (underlying layer or subcutaneous)· Adipose tissue
· Anchors skin to the underlying structures
· Shock absorber and insulator to reduce heat loss


Cells of the Epidermis
· Keratinocytes (most)
· Melanocytes
· Langerhans’ (dendritic) cells
· Tactile (Merkel) cells

· Keratinocytes · Primary cell type of epidermis
· Produces keratin · Protein that gives epidermis its protective
function
· Arise in deepest layer (stratum basale)
· New cells push old cells upward and by the time they reach the surface they are dead cells filled with keratin
· Millions of cells rub off each day
· Completely new epidermis every 25-45 days
· Persistent friction causes a thickening of the epidermis called a callus
Cells of the Epidermis

Cells of the Epidermis· Melanocytes
· Spider-shaped epithelial cells
· Produce the pigment melanin
· Found in the deepest layer of epidermis (stratum basale)
· keratinization
· In keratinocytes the melanin accumulate on ‘sunny side’ or superficial side of nucleus and forms a shield that protects it from UV radiation – natural sunscreen

Cells of the Epidermis
· Langerhans’ (dendritic) cells· White blood cells that arise from
bone marrow and migrate to epidermis
· Ingest foreign substances
· Key activators of immune system
· Tactile (Merkel) cells· Shaped like a spiky hemisphere
· Rarely found and associated with sensory nerve ending
· Sensory receptor for touch

Layers of Epidermis· Variation of thickness depends on
location in body
· Four or five structurally different layers called strata
· Thick skin – palms, fingertips, soles of feet consists of all five layers
· Thin skin – rest of the body the stratum lucidum is not present
· Deep to superficial
· Stratum basale
· Stratum spinosum
· Stratum granulosum
· Stratum lucidum (thick skin only)
· Stratum corneum

Layers of Epidermis· Stratum basale
· Deepest layer – closest to dermis
· Cells rest on underlying dermis
· Basal cells · 90% are keratinocytes
· 10% are melanocytes and other types
· Stratum spinosum (prickly cell layer)· Several cell layers thick of flattened cells
with bundles of keratin
· Langerhans’ (dendritic) cells are most abundant in this layer

Layers of Epidermis
· Stratum granulosum· Very thin region (3-5 layers)
· Last layer that can obtain nutrients from diffusion
· Process of keratinization begins here and cells die
· Cells flatten and ‘toughen’ up
· Stratum lucidum (clear layer)· 2-3 rows of clear, flat, dead cells
· Translucent layer that looks like a band
· Visible only in thick skin

Layers of Epidermis· Stratum corneum
· Outermost layer
· 20 to 30 cells thick of dead cells
· High levels of keratin
· Protection against abrasion and penetration, water repellant (prevents water loss)
· Average person sheds 8 lb of dead skin cells in a year

Epidermis Check-up
• While walking barefoot in the barn, Jeremy stepped on a rusty nail that penetrated the depth of the epidermis on the sole of his foot. Name the layers the nail pierced from the superficial skin surface to the junction with the dermis.
• What is the stratum basale’s function?
• Given that epithelia are avascular, what layer would be expected to have the best-nourished cells?
Stratum basale stratum spinosum stratum granulosum stratum lucidum stratum corneum
To produce new keratinocytes and keratin
Stratum basale

Dermis (Derm = skin)· Second major skin region· It is your “hide”· Strong, flexible connective
tissue layer· Cells
· Fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells and white blood cells
· Matrix · Embedded with
collagen, elastic and reticular fibers
· Rich in nerve fibers, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
· Major portions of hair follicles, sweat and oil glands reside in dermis

· Two major layers of dermis· Papillary layer · Reticular layer
Dermis (Derma = skin)

· Papillary layer· Papilla = any nipple-like
projection· Thin superficial layer· Areolar connective tissue· Superior surface is called
the dermal papillae · Projections that protrude
into epidermis · Some contain capillary
loops, free nerve endings, and Meissner’s corpuscles
· Where we get our fingerprint
Dermis (Derma = skin)

Dermis – your ‘hide’· Reticular layer
· Deepest layer· Dense connective tissue· 80% of the thickness of the dermis· Highly vascular - lots of blood
vessels· Matrix contains thick bundles of
collagen fibers (strength and resiliency) and elastic fibers (stretch-recoil)
· Wrinkling of the skin is caused by loss of the elasticity of the skin
· Many appendages are located here: sweat glands, oil glands and nerve receptors

Skin Structure
Figure 4.4

Dermis Check Up
· What layer of the dermis is responsible for producing finger-print patterns?
· What cell component of the hypodermis makes it a good shock absorber?
· You have just gotten a paper cut. It is very painful, but it doesn’t bleed. Has the cut penetrated into the dermis or just the epidermis? What component of the layer was affected?
Papillary layer – dermal papillae
Adipocytes
Epidermis – tactile cells

Normal Skin Color
Skin Color Variations
Skin Appendages

Normal Skin Color· Three pigments contribute to skin color
· Melanin (only one made in skin)· Carotene· Hemoglobin

Normal Skin Color· Melanin (Melan - = black)
· Pigment found in eyes, skin and hair
· Function is to protect cells from UV radiation – a natural sunscreen
· Range in color from yellow to tan to reddish-brown to black
· Produced by melanocytes and phagocytized by keratinocytes

Normal Skin Color· Melanin
· Exposure to sun = increase in melanin production
· Darker-skinned people tend to live near the equator and those with lighter skin live near the poles
· Freckles and moles are local accumulation of melanin
· Albinism (albin- = white)· No melanin produced; eyes, skin
and hair are white

Normal Skin Color
· Carotene· Yellow-orange pigment
found in certain plant products such as carrots
· Found predominantly in the stratum corneum
· Can be changed by altering diet and it is not dangerous to health
· Carotene can be converted to Vitamin A in the liver· Essential for normal
vision and protection of epithelial tissues

Normal Skin Color· Hemoglobin
· Oxygen carrying pigment found in red blood cells and gives them their red color
· Produces a pinkish hue of fair skin · Caucasian skin contains small amounts of
melanin, so the color can show through easier· Oxygen content determines the extent of
red coloring· When capillaries are open the blood is
rushed to the surface causing redness

Skin Color Variations· Cyanosis (Blue color disorder)
· Hemoglobin is poorly oxygenated· The skin and blood appear blue· Occurs during heart failure and
respiratory disorders· In darker skinned individuals, the skin
does not appear cyanotic because of so much melanin· Apparent in mucous membranes
and nail beds
· Redness (Erythema)· Capillaries dilate and open up to bring
blood to the surface· Caused by irritation or injury· Other causes are embarrassment,
fever, hypertension or allergy

Skin Color Variations· Pallor or blanching (Paleness or white)
· Blood is either shunted or directed away from surface· Fear, anger, anemia or low blood pressure.
· Jaundice (yellow cast)· Caused by the buildup of yellow bile pigments from the liver called bilirubin· They accumulate in the blood and are deposited in body tissues like the skin
or whites of eyes

Skin Color Variations· Hematomas (Bruises)
· Collection of blood, usually clotted, in a tissue or organ, usually caused by a break in a blood vessel
· Black and blue bruises· Hema- = blood and -oma =
tumor


Appendages of the Skin
· Derivatives of the epidermis called skin appendages
· Nails, sweat glands, sebaceous (oil) glands and hair
· Each appendage plays a unique role in maintaining homeostasis

· Distributed over the entire skin except nipples, lips, and some genitalia
· Most numerous gland ~2.5 million/person
· Two types
· Eccrine and apocrine
· Simple, coiled tubular glands
· Sweat is secreted into and through the gland’s duct system to the surface of the skin
· Sudor = sweat
Sudoriferous (sweat) glands

Eccrine glands
·Found almost everywhere and most numerous
·Abundant on palms, soles and forehead
·Secretory part lies coiled in dermis
·Duct extends to open in a pore
·Eccrine gland secretion (sweat)
·Sweat· 99% water with some salts,
vitamin C, antibodies and traces of wastes
· Composition of sweat depends on genetics and diet
· Acidic with pH between 4-6

Apocrine Glands
·Found in axillary and genital areas (about 2000 of them)
·Found deeper in dermis and larger than eccrine glands
·Ducts empty into hair follicles
·Apocrine gland sweat composition· Same as eccrine sweat plus fatty
substances and proteins
· Odorless and appears milky or white
· Bacteria eats organic molecules in the sweat and causes body odor
·Begin functioning at puberty

Functions of Sweat · Controlled by the nervous system· Can be heat-induced or emotionally induced (cold sweat)
· Heat-induced begins on forehead and spreads inferiorly· Emotionally induced begins on the palms, soles and then spreads
· Excretes waste products· Acidic nature inhibits bacteria growth

Sudoriferous glands
· Ceruminous glands
· Modified apocrine glands
· Found in lining of external ear canal
· Produce cerumen (ear wax)
· Functions to deter insects and block entry of foreign materials.
· Mammary glands
· Specialized sweat glands
· Secretes milk

Sebaceous (Oil) Glands
· Found all over the body except on palms and soles of feet
· Secrete an oily substance called sebum
· Softens and lubricates hair and skin
· Bactericidal (bacteria-killing) action
· Develop and secrete into hair follicles
· Stimulated by hormones and activated at puberty

Sebaceous (Oil) Glands
· Blackheads
· Appears on surface of skin when a sebaceous gland duct is blocked and the sebum accumulates
· Acne
· An active inflammation of the sebaceous glands accompanied by ‘pimples’ (pustules)
· Usually caused by bacterial infection

Hair· Millions of hairs are distributed all over the body
except on the palms, soles, lips, nipples, and parts of external genitalia
· Flexible strands produced by hair follicles
· Consist largely of dead, keratinized cells
· Melanocytes provide pigment for hair color
· Hair Functions· Not really used for warmth anymore
· Sense insects on the skin before they bite us
· Hair on scalp guards the head from physical trauma, heat loss and sunlight
· Eyelashes shield the eyes
· Nose hairs filter large particles from the air

Hair· Regions of a hair
· Hair Shaft
· Projects from the skin
· Extends halfway down the embedded portion
· Hair Root
· Remainder of hair deep in the follicle

Hair Anatomy· Hair has 3 concentric layers of keratinized cells
· Medulla - central core
· Consists of large cells and open spaces
· Cortex – surrounds medulla
· Several layers of flattened cells
· Cuticle - outside of cortex
· Single layer of cells that overlap each other
· Looks like shingles on a roof
· Most heavily keratinized and provides strength
· “Split ends” occurs when the cuticle wears away

Hair Follicle· Epithelial tissue folds down from the
epidermis into the dermis
· Deep end of the follicle forms a hair bulb
· Hair follicle is the wall around the hair
· Two sheaths
· Outer connective tissue root sheath derived from the dermis
· Inner epithelial root sheath derived from the epidermis
Figure 4.7a

Hair Follicle· Hair papilla
· Dermal connective tissue protrudes into the hair bulb
· Contains capillaries that supplies the nutrients to the hair
· Hair matrix (growth zone)· Actively dividing area of the hair bulb
· Produces the hair
Figure 4.7a

Hair Follicle· Arrector pili
· Each hair follicle has a smooth muscle attached to it
· Hair follicles approach surface of the skin at a slight angle
· Muscle contraction pulls the hair follicle to an upright position
· Causes a dimple in the skin – goosebumps
· Response to fear or cold temperatures

Hair Growth
· Hair growth is influenced by many factors
· Nutrition and hormones
· Hirsutism (excessive hairiness)· Results from an adrenal gland or ovarian
tumor that secretes an abnormally high amount of androgens
· Androgens control the growth of hair and are produced by ovaries and adrenal glands
· These tumors are usually removed as soon as possible

Hirsuitism

Hair Thinning and Baldness
· A hair follicle only has a limited number of cycles in it
· Hair grows fastest from the teen years to the 40s and then it slows
· Alopecia (scientific term for baldness)· When the hairs are not replaced as they are shed leads to hair thinning or
baldness due to age
· True Baldness· Male pattern baldness that is genetically determined, sex-influenced condition
· Hair thinning can occur because of high fever, surgery, emotional trauma, certain drugs, and protein-deficient diets · If the cause is removed or corrected, the hair will grow back
· Hair loss due to severe burns or follicular damage is permanent


Skin Homeostatic Imbalances· Homeostatic Imbalance
· A disease or condition as a result of a disturbance in homeostasis
· Skin Homeostatic Imbalances· Cancer· Burns· Bacterial, viral or yeast infections

Skin Cancer· Cancer
· When cells fail to follow normal controls of cell division and multiply excessively it results in a tumor
· Two types of tumors· Benign (most tumors like warts)
· Does not spread and grows slowly· Malignant (mal = ‘bad’)
· Grow relentlessly and may become killers· Metastasis
· Cells tend to break away from the mass and travel via blood or lymph to other body organs where they can grow into new masses

Skin Cancer Types· 1 in 5 Americans will develop skin cancer at some point· Huge risk factor is too much UV radiation which damages DNA bases· Three types of skin cancer
· Basal cell carcinoma· Squamous cell carcinoma· Melanoma

Skin Cancer Types· Basal cell carcinoma
· Least malignant but most common skin cancer (80%)· Stratum basal cells proliferate and invade the dermis and hypodermis· Occur most often on sun-exposed areas of face · Appear as shiny, dome-shaped nodules that develop a central ulcer
with a pearly, beaded edge – sore that doesn’t heal

Skin Cancer Types· Basal cell carcinoma

Skin Cancer Types· Squamous cell carcinoma
· Second most common skin cancer · Affects men more than women· Arises from keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum· Lesion appears as a scaly reddened papule that
arises usually on head and hands· Grows and metastasizes to lymph nodes quickly· Early removal allows a good chance of cure

Skin Cancer TypesBasal Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cell type Stratum basale (basal layer) keratinocytes
Stratum spinosum keratinocytes
Rank them by how common they are to get
1st 2nd
Seriousness and metastasis
Least malignant Grows and metastasizes quickly
Appearance Shiny, dome-shaped nodules with a central ulcer and a pearly edge
Scaly, reddened papule

Skin Cancer Types

Skin Cancer Types
· Malignant melanoma· Most deadly of skin cancers· Highly metastatic and resistant to chemotherapy· Rare (2-3% of all skin cancers)· Cancer of melanocytes and can begin wherever there is pigment· Appears as a spreading brown to black patch · Early detection is key to survival· Detection uses ABCD rule

ABCD Rule
· A = Asymmetry· Two sides of pigmented mole do not match
· B = Border irregularity· Borders of mole are not smooth
· C = Color· Different colors in pigmented area
· D = Diameter· Spot is larger then 6 mm in diameter
(pencil eraser)· Skin Cancer Video

Skin Homeostatic Imbalances· Burns
· Tissue damage inflicted by intense heat (fire or materials), electricity, radiation (sunlight), or certain chemicals
· Denature cell proteins and cause cell death
· Immediate threat to life is loss of body fluids containing proteins and electrolytes
· Results in dehydration and electrolyte imbalance
· After initial crises, infection and sepsis becomes the main threat

Extent of Burn - Rules of Nines
· Volume of fluid lost can be estimated by computing the percentage of body surface burned
· Tool to approximate the extent of burns using the rule of nines
· Body is divided into 11 areas
· Each area represents about 9% of total body area
· Head and neck = 9 %
· Upper limbs = 18%
· Trunk = 36%
· Lower limbs = 36%
· Genitals =1%

Severity of Burns· Burns are classified according to their
severity (depth)· First-degree burns (epidermis)
· Skin is red and swollen· Second degree burns (epidermis and
upper dermis)· Skin is red with blisters
· Third-degree burns (entire skin layer)· High risk for fluid loss· Burn is gray-white, cherry red or
black· Nerve endings are destroyed so it
is not painful at first· Skin regeneration may occur but
will take too long· Usually skin grafting is required

Critical Burns· Burns are considered critical if:
1. Over 25% of body has second degree burns
2. Over 10% of the body has third degree burns
3. There are third degree burns of the face, hands, or feet
• Most third degree burns will never heal and may require a skin graft
• Skin Grafting
• Removal and transplanting of healthy skin from one area to another

Infections & Allergies· Psoriasis
· A chronic condition characterized by reddened epidermal lesions covered with dry, silvery scales.
· Athlete’s Foot
· An itchy, red, peeling condition of the skin between the toes resulting from a fungal infection.
· Cold Sores
· Small fluid filled blistered that itch and sting, caused by a herpes simplex infection.

Infections & Allergies· Contact Dermatitis
· Itching, redness, and swelling of the skin, progressing to blistering. Caused by the exposure of skin to chemicals that provoke allergic responses. (it is = swelling)
· Impetigo
· Pink, water-filled, raised lesions that develop (mouth and nose) a yellow crust and eventually rupture . Caused by staphylococcus infection.