THE ANALYSIS OF HUMAN BEHAVIOUR AND EVACUATION IN A FIRE...
-
Upload
duonghuong -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of THE ANALYSIS OF HUMAN BEHAVIOUR AND EVACUATION IN A FIRE...

THE ANALYSIS OF HUMAN BEHAVIOUR AND EVACUATION IN A FIRE THE ANALYSIS OF HUMAN BEHAVIOUR AND EVACUATION IN A FIRE
SITUATION IN A BUILDING FOR HIGHER EDUCATION
Technical University Faculty of Civil
SITUATION IN A BUILDING FOR HIGHER EDUCATION
Technical University
“Gheorghe Asachi”
Iassy, Romania
Faculty of Civil
Engineering and
Building ServicesDan Diaconu-Şotropa, Zeno Cosmin GrigoraşTechnical University “Gheorghe Asachi” from, Iassy, RomaniaTechnical University “Gheorghe Asachi” from, Iassy, Romania
Abstract Content and method of research Main tenability criteriaAbstract
• The paper presents the analysis of a human evacuation
from a higher education building located in Iassy,
Content and method of research
• The case study analyzes the safe evacuation of people in
the building (positioned as specified above) for two
Main tenability criteria
- the visibility through smoke layer, quantified by
minimum visible distance which is 10 m (for large rooms);from a higher education building located in Iassy,
Romania, by means of engineering techniques to
approach fire safety.
• This paper is based on the assumption of starting a fire in
the building (positioned as specified above) for two
possible situations:
- S1, human evacuation through both primary and
secondary access;
minimum visible distance which is 10 m (for large rooms);
- Fractional Effective Dose (FED), quantified by the
maximum value of 1 (a non-lethal environment for
adults).• This paper is based on the assumption of starting a fire in
the space of a hall for festivities, located on the ground
floor of the building, near two human evacuation routes.
secondary access;
- S2, human evacuation through the main access
(secondary access being accidentally locked).
adults).
floor of the building, near two human evacuation routes. (secondary access being accidentally locked).
• The supposed fire start in the festivity hall, located on the
ground floor and close to the main exit of the building. The
interior furniture is specific to the office type spaces andinterior furniture is specific to the office type spaces and
predominantly cellulosic/wood, HRR = 250 kW/m2..
• We analyzed, by means of the finite volume method, fire
The research instrument
Results
Image from “Tenability criteria for design of smoke hazard management systems” by Dr. Weng Poh
Building presentation
Analyzed building: Faculty of Civil Engineering and
• We analyzed, by means of the finite volume method, fire
development and human evacuation inside the building in
both S1 and S2 situations. The types of analysis involved
by the case study requires the use of a virtual discreteGraphical variation of the temperature (left) and the
visibility (right) at the ground floor (red line–critical values):
Results
Analyzed building: Faculty of Civil Engineering and
Building Services
Location: Iassy, Romania
Height: ground floor + 4 floors
by the case study requires the use of a virtual discrete
model, with finite volumes.
FDS 5.5.3 - based on Fluid Dynamics (Computational Fluid
Dynamics, CFD) and applied to Fire Dynamics; designed
visibility (right) at the ground floor (red line–critical values):
Height: ground floor + 4 floors
Ground area: 826 m2
Usable floor area: 3340 m2
Built volume:
Dynamics, CFD) and applied to Fire Dynamics; designed
by NIST U.S.A.
FDS+Evac 2.2.1 - analyzing the human evacuation in fireBuilt volume: 12820 m3
People accommodated: over 700
FDS+Evac 2.2.1 - analyzing the human evacuation in fire
situation; developed by VTT Finland.
SmokeView 5.6 - postprocessor software used for
overview of the results.• The main features of the building are:
- on the ground floor, three halls for teaching activities
(accommodating, at the time of the fire, 50 persons each)
overview of the results.
Discrete model for fire development and human evacuation(accommodating, at the time of the fire, 50 persons each)
and a hall for festivities (without people at the time of the
fire);• The numerical simulation of the spread of smoke and hot
gases inside the building used a virtual model with 2- on the 1st floor ... 3rd floor, three lecture halls
(accommodating, at the time of the fire, 50 persons each)
and a laboratory (with 20 computer workplaces each);
gases inside the building used a virtual model with 2
meshes.
• The numerical simulation for human evacuation of the
building was performed on a virtual model with 6 mainand a laboratory (with 20 computer workplaces each);
- on the 4th floor, a lecture hall (accommodating, at the
time of the fire, 50 persons);.
• The access to the floors is done through two staircases,
building was performed on a virtual model with 6 main
meshes corresponding to each level, and 7 secondary
meshes corresponding to stair landings.
• A finite volume size is 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.38 m.• The access to the floors is done through two staircases,
with two ramps and intermediate landing:
- the main staircase, centrally located, allows access from
• A finite volume size is 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.38 m.
• The authors used the following data for analysis:
- the movement speed for an adult person model is has athe ground floor to the second floor; further, the access to
the next floors is allowed through other staircase located at
the edge of the hall;
- the movement speed for an adult person model is has a
uniform distribution with the values : minimum 0.95 m/s and
maximum 1.55 m/s;
- the detection time (the time interval between the alarmFED =0,04 (S1) FED =0,06 (S2)
the edge of the hall;
- the secondary staircase, located in the outer limit of the
main hall, provides the access from the ground floor to the
top floor of the building.
- the detection time (the time interval between the alarm
activation and the moment when the occupants of the
building are aware of the danger) is establish to 120 s ...
180 s with a uniform distribution;Conclusions
FEDmax=0,04 (S1) FEDmax=0,06 (S2)
top floor of the building. 180 s with a uniform distribution;
- the reaction time is set to 5 s and a triangular distribution,
with were specified a minimum value of 1s and maximumThe current case study, following the performed
numerical simulations, shows that the travel time for
Conclusions
with were specified a minimum value of 1s and maximum
of 9 s its assumed.numerical simulations, shows that the travel time for
evacuation (the time for occupants to travel to a place
of safety - the exterior of the building) is higher than
the norm prescriptive time and it is possible that thethe norm prescriptive time and it is possible that the
engineering approach to human evacuation in case of
fire to be closer to reality.fire to be closer to reality.
Situation
Numerical
simulation
The Romanian specific
prescriptive regulation Situation simulation
FDS+Evac
prescriptive regulation
P118-99
S1 340 s 125 s
Main tenability criteria
S1 340 s 125 s
S2 406 s 63 s
Contact information
The main tenability criteria in the interaction of occupants-
Main tenability criteria
Dan Diaconu-Şotropa, Professor PhD. Eng., Tehnical
Contact information
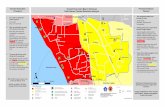
The ground floor plan
The main tenability criteria in the interaction of occupants-
effluents, considered in the analysis for safe evacuation
during the supposed fire, are:
-the radiant heat is 2.5 kW/m2 and/or the maximum
University, Iassy, Romania
[email protected] 00-40-744-505857
The ground floor planME - main exit; MSC - main staircase; SSC - secondary staircase;
SSCE - secondary staircase entrance;
-the radiant heat is 2.5 kW/m2 and/or the maximum
permissible temperature at the bottom of the top layer of
smoke is 2000C;
Zeno Cosmin Grigoraş, Eng. MSc student, Tehnical
University, Iassy, Romania
[email protected] [email protected] 00-40-742-961328