TAEM10: Acute Scrotal Pain
-
Upload
taem -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
3.861 -
download
8
description
Transcript of TAEM10: Acute Scrotal Pain

Acute Scrotal Pain13 Feb 2009
นพ.ประสิทธิ์ วุฒิสุทธิเมธาวี
หน่วยเวชศาสตร์ฉุกเฉิน
คณะแพทยศาสตร์
มหาวิทยาลัยสงขลานครินทร์

BackgroundNot uncommon presentation
Maybe cause from serious condition; rupture AAA,
Strangurated IIH, Fournier’s gangrene
Chalanging EP
Early diagnosis can prevent function loss
or complications

Anatomy

History & Clinical
Age (host.)
Pain characteristic
Sexual function
+/- Undescended testis

Pain Characteristic
Painless VS Painful
Sudden onset VS gradual onset
Location
Association symptoms: fever, dysuria

Age- Neonate
- Prepuberty
- Post puberty : Epididymitis
- Adult : STD
Torsion of testis

Physical ExaminationRelax
Reassure
Relate (compare) with other side


SignsScrotum
edema
erythema
size
tender
Testis
location / axis
size
tender
consistency
erythema

Transillumination testHydrocele
+/- Chronic hydrocele
Reactive hydrocele


Cremasteric ReflexPinch inner thigh, observe testis
Present : testis elevate > 0.5 cm.
Absent : testis not elevate or elevate < 0.5 cm.
Torsion of testis

Frehn’s SignScrotum elevation
Positive : pain relief
Negative : pain persist Torsion of testis

InvestigationsUrine analysis (UA.) +/- U/C
Complete blood count
Plain X-rays
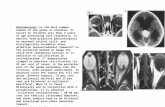
Color doppler USG
Nuclear scintigraphy

Color Doppler USGNo clinical strongly of testicular torsion
No pain free intervals
No clinical diagnosis of epididymitis
Scrotal trauma
No pathognomonic findings

Color Doppler USGIncrease blood flow
Epididymitis, Torsion of appendage
Decrease blood flow
Torsion of testis



Nuclear Scintigraphy
Radioisotope (Tc99m)
Uptake at 30 min
Negative : no radioisotope uptake
(Testicular Scan)
Positive : radioisotope uptake



Nuclear ScintigraphyAvailability
Can not identify anatomy if testicular rupture
Same result in epididymitis and
torsion of testicular appendage
Limitations
Can not detect spontaneous detorsion

Common diagnosis

Differential DiagnosisEmergent
Torsion of testis Rupture of testis
Fournier’s gangrene Peritonitis
AAA


Differential DiagnosisNon-emergent
Torsion of appendage Epididymitis
Orchitis Inguinal hernia
Scrotal hematoma / abscess

Differential DiagnosisNon-emergent
Testicular neoplasm Renal colic
Hydrocele / Varicocele
Venomous insect bite



Most common diagnosisTorsion of testis
Torsion of testicular appendage
Epididymitis
Orchitis

Torsion of testis

Incidence1/4,000 annual (men < 25 years old)
Dimorphic
Neonate : < 1 year
Pre-puberty : 12-18 years old (14 yrs)
Undescended testis

Pathophysiology“Bell-Clapper” deformity
Redundant spermatic cord
Right: clockwise
Left : counterclockwise
Medial rotation (aldolescence)




Signs & SymptomsSudden scrotal pain +/- N/V, fever
High riding testis
Transverse axis of testis

Suspicion Torsion of TestisHigh riding testis
Abnormal axis (upright position)
Abnormal position of the epididymis in
scrotumAbnormal axis in contralateral testis (bell
clapper” deformity) except in 180o rotation


InvestigationsUrine analysis
Complete Blood Count
Color doppler USG: decrease blood flow
Nuclear Scintigraphy: no isotope uptake
(Duration > 12 hrs immediate Sx.)


TreatmentGeneral treatment
Pain relief
Cold application
Correct Electrolyte imbalance
Pre-operative evaluation

TreatmentSpecific treatment
Manual detorsion (temporaly)
Early Urologist (Gen Sx.) consultation
Scrotal exploration, opened
detorsion and bilateral orchiopexy


History, Physical Examination and urine analysis
Short duration of symptoms
Negative urine analysis
High probability of torsion
Long duration of symptoms
Positive urine analysis
Low probability of torsion
Surgical exploration Color doppler USG
Nuclear scintigraphy
> 6 hr< 6 hr
+ / -

Color doppler USG
Nuclear scintigraphy
Decrease or absent blood flow
Equivocal
Increase or
Normal blood flow
Surgical exploration Non-operative management
Observation

Epididymitis

InfectionBacteria
STD :
TB :
UTI
Congenital anomaly
Retained foley catheter
Chlamydia trachomatis
N. gonorrhea, Syphilis
Cold abscess

SymptomsGradual onset
Scrotal pain
Fever (95%)
Dysuria, Urethral d/c (30-50%)
Scrotal edema

SignsScrotal swelling
Scrotal erythema
Tender at scrotal and groin

Difficult to differentiate
from torsion of testis.
Torsion of testis
Sudden onset
High riding
Abnormal axis
Tender at groin
abdomen
Epididymitis
Gradual onset
Normal position / axis
Tender at superior pole
of testis
Fever, dysuria

InvestigationsUrine analysis : pyuria (50%)
Complete Blood Count: leukocytosis (30-50%)
Color doppler USG: normal/increase blood flow
Nuclear Scintigraphy: normal isotope uptake


Criteria for DiagnosisGradual onset of pain
Dysuria, Urethral d/c
History of urinary tract infection
Fever ( BT > 38.3 oc)
Tenderness at epididymis
Abnormal Urine analysis

Treatment
General treatment
Rest
Scrotal support
Analgesia (NSAIDs)
Cold application
Specific treatment
Antibiotic
STD: partner

Orchitis


PathophysiologyHighly resistance to infection
Hematologic spread
Mump
Immunocompromise

SymptomsPyogenic orchitis
Fever
Malaise
Dysuria
Viral orchitis
- Post parotitis 4-6
days
- 70 % unilateral lesion


Signs
Gradual onset
Scrotal swelling / pain / edema
Prehn’s sign: positive

Investigations
Urine analysis : pyuria
Complete Blood Count: leukocytosis
Color doppler USG: normal/increase blood flow
Nuclear Scintigraphy: normal isotope uptake

Difficult to differentiate from epididymitis
Orchitis
tender at testis
Epididymitis
tender at superior pole
of testis

TreatmentGeneral treatment
Rest
Scrotal support
Analgesia (NSAIDs)
Cold application

TreatmentSpecific treatment
Pyogenic orchitis antibiotic
Viral orchitis supportive treatment
Usually improve in 3-5 days

Torsion of testicular appendage

Background
Pre aldolescence
Age 3- 13 years old (peak 7-12 yrs)
Another diagnosis is torsion of epididymal
appendage

Pathophysiology
Unknown
Increase estrogen level increase size of
appendage strangulation
Torsion obstruct venous flow decrease
arterial flow ischemia and necrosis



SymptomsAcute onset
Scrotal pain +/- swelling
Nausea / Vomiting
Fever
Dysuria / Urethral d/c

SignsPalpate mass at superior pole of testis
Tender at testis / swelling / Blue dot sign
+/- reactive hydrocele
Transillumination test Black dot sign
Dysuria / Urethral d/c

Torsion of testis
Sudden onset
High riding
Abnormal axis
Tender through testis
Torsion of appendage
Sudden onset
Normal position / axis
Tender at superior testis

InvestigationsUrine analysis
Complete Blood Count
Color doppler USG: normal/increase blood flow
Nuclear Scintigraphy: normal isotope uptake


TreatmentGeneral treatment
Rest
Scrotal support
Analgesia (NSAIDs)
Cold application
Usually improve in 7-10 days

Conclusion

Goal
To detect and exclude “Torsion of testis“

Thank you for your attention













![Scrotal Edema in a Patient with Liver Cirrhosis › gastroenterology › fulltext › downl… · The incidence of acute scrotal swellings is up to 20% in childhood [1]. The major](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5f2501575c9ddf4907735589/scrotal-edema-in-a-patient-with-liver-cirrhosis-a-gastroenterology-a-fulltext.jpg)