Green supply chain management practices and supply chain ...
Supply chain management. Chapter outline Introduction Basic terms and concepts of supply chain...
-
Upload
ferdinand-crawford -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
7
Transcript of Supply chain management. Chapter outline Introduction Basic terms and concepts of supply chain...

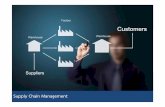
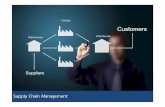
Supply chain management

Chapter outline Introduction
Basic terms and concepts of supply chain management
Principles of supply chain management
Tools and techniques used in supply chain management
The Importance of Supply Chain Management

Introduction
What is supply chain management?We have three main definition
The design and management of seamless, value-added process across organizational boundaries to meet the real needs of the end customer Institute for Supply Management
Managing supply and demand, sourcing raw materials and parts, manufacturing and assembly, warehousing and inventory tracking, order entry and order management, distribution across all channels, and delivery to the customer The Supply Chain Council
The planning and management of all activities involved in sourcing and procurement, conversion, and all logistics management activities … also includes coordination with channel partners, which can be suppliers, intermediaries, third party service providers, and customers. Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals

Basic terms of supply chain management
Production- this is the capacity of a supply chain to make and storeproducts
Inventory-it refers to raw material, work in process to finished goods that areheld by the manufacturers, distributors, and retailers in a supply chain
Transportation-This refers to the movement of raw material and finishedgoods between different facilities in a supply chain
Warehouse-this refers to commercial building to store raw material work in process and finished goods
Location-Location refers to the geographical siting of supply chain facilities

Principles of supply chain management
Principle 1: Segment customers based on the ser vice needs of distinct groups and adapt the supply chain to serve customer needs profitably. Both business people and supply chain professionals are trained to focus on the customer's needs. In order to understand customer better, we divide customers into a different group and we call it "segmentation". The most primitive way to segment customer is ABC analysis that groups customer based on the sales volume or profitability(Ross, 2013). Segmentation can also be done by product, industry and trade channel.
Principle 2: Customize logistics network to the service requirements and profitability of customer segments.This is whereby the business is made to tailor different logistics network to serve different segment(Fawcett, Ellram and Ogaden, 2014)

Principles of supply chain management (cont.)
Principle 3: align demand planning accordingly across the supply chain, ensuring consistent forecasts and optimal resource allocation Supply chain experts are taught to share the demand data with trading partners so nobody has to keep the unnecessary stock.
Principle 4: Differentiate product closer to the customer and amass them when customer places an order .
Principle 5: Manage sources of supply strategically to reduce outsource.
Principle 6: Develop a supply chain-wide technology strategy that supports multiple levels of decision making and gives a clear view of the flow of products, services, and information.
Principle 7: Adopt channel-spanning performance measures to gauge collective success in reaching the end-user effectively and efficiently.

Tools and techniques supply chain
1. BenchmarkingBenchmarking improves performance by identifying and applying best demonstrated practices to operations and sales (Handfield and Nicholas, 1999). Managers compare the performance of their products or processes externally with those of competitors and best-in-class companies, and internally with other operations that perform similar activities in their own fi rms. The objective of Benchmarking is to find examples of superior performance and understand the processes and practices driving that performance. Companies then improve their performance by tailoring and incorporating these best practices into their own operations
Benchmarking involves the following steps:• Select a product, service or process to benchmark• Identify the key performance of supply chain metric. • Choose companies or internal areas to benchmark• Collect data on performance and practicesCompanies use Benchmarking to:• Improve performance. Benchmarking identifies methods of improving operational efficiency and product design.• Understand relative cost position. Benchmarking reveals a company’s relative cost position and identifies opportunitiesfor improvement.

Tools and techniques supply chain(cont.)
2. Integrated logistic process with supplierThis offers the supply chain rapid extraction, transformation, loading, search, analysis and sharing of massive data sets. Byanalyzing a large, integrated, real-time database rather than smaller, independent, batch-processed data sets, integrated logistic process seeks to quickly identify previously unseen correlations and patterns to improve decision making. The results help managers better measure and manage the most critical functions of their business. Companies start by identifying significant business opportunities that may be enhanced by superior data and then determinehow the supply chain is to be carried out. If they are, the business will need to develop the hardware, software and talentrequired to capitalize on Integrated logistic process with supplier. That often requires the addition of data scientists who are skilled in asking the right questions, identifying cost-effective information sources, findingtrue patterns of causality and translating analytic insights into actionable business information.Common uses• Decide whether to purchase or rent the system• Establish guiding principles such as data privacy and security policies• Test, learn, share and refine• Develop repeatable models and expand applications to additional business areas

Tools and techniques supply chain(cont.)3. Complexity reduction
Complexity Reduction helps companies simplify their strategy, organization, products, processes and information technology.Reduction in any of these areas opens up opportunities for simplification supply chain. Unwieldy complexity often results frombusiness expansions or bureaucracies that unnecessarily complicate a company’s operating model, leading to sluggish growth,higher costs and poor returns. Complexity Reduction finds inflection points where products or services fully meet customerneeds at the lowest costs. By streamlining product lines, for example, companies may be able to simplify organization structures and decision making to serve their core customers betterwhile also reducing demands on business processes and information systems.Complexity Reduction requires supply chain managers to:to simplify products, organizationstructures, business Understand the sources of complexity and examine trade-offsbetween operations and variety or customization for customers• Identify opportunities processes and information systems tosave costs while strengthening core capabilities and increasing the focus on customers• Take steps to stem the return of complexity by reexamining thehurdle rates for new products and other expansion activities

Importance of supply chain management
Boosts Customer ServiceSCM impacts customer service by making sure the right product assortment and quantity are delivered in a timely fashion. Additionally, those products must be available in the location that customers expect. Customers should also receive quality after-sale customer support.
Improves financial position Increases Profit Leverage. Firms value supply chain management because it helps control and reduce supply chain costs. This can result in dramatic increases in firm profits.it also decrease fixed assets used by the company

Importance of supply chain management(cont.)
Reduce operating cost.
Decreases Purchasing Cost. Retailers depend on supply chains to quickly deliver expensive products to avoid holding costly inventories in stores any longer than necessary. Decreases Production Cost. Manufacturers depend on supply chains to reliably deliver materials to assembly plants to avoid material shortages that would shutdown production. Supply chain management leads to reduced supply chain cost to manufactures, supplier and the consumer.
Ensure human survival.
Human survival depends on the supply chain to provide necessities. The supply chain also helps in supply of medicines and healthcare. this leads to improve human care.
Improves human life
Supply chain leads to improvement in standard of living.it also the foundation of economic growth as people are able to exchange goods and services. Creation of employment by the supply chain also improves life as people can afford to pay for goods and services

reference
Handfield, R. B., & Nichols, E. L. (1999). Introduction to supply chain management (Vol. 999). Upper Saddle River, NJ: prentice Hall.
Christopher, M. (1998). Logistics and supply chain management: Strategies for reducing cost and improving service.
Fawcett, S. E., Ellram, L. M., & Ogden, J. A. (2014). Supply chain management: from vision to implementation. London: Pearson.
Wisner, J., Tan, K. C., & Leong, G. (2015). Principles of supply chain management: a balanced approach. Cengage Learning.
Ross, D. F. (2013). Competing through supply chain management: creating market-winning strategies through supply chain partnerships. Springer Science & Business Media.