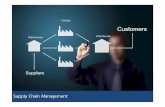
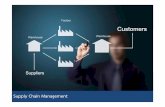
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
-
Upload
fatima-byrd -
Category
Documents
-
view
18 -
download
0
description
Transcript of SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT

Next End

Supply Chain Management – Definitions
Supply chain management is the management of a network of
interconnected businesses involved in the ultimate provision of
product and service packages required by end customers
(Harland, 1996).
Importance of Supply Chain Management
To compete in the global market and networked economy.
Inter-organizational supply network can be acknowledged as
a new form of organization.
The network structure fits neither "market" nor "hierarchy"
categories
Previous Next End
Introduction

• Evolution of Supply Chain Management Studies:
Six major movements can be observed in the evolution of supply
chain management studies:
1. Creation era
Supply chain management was first coined by a U.S. industry
consultant in the early 1980s.
Supply chain management include the need for large-scale
changes, re-engineering, downsizing driven by cost reduction
programs.
Previous Next End

2. Integration era
Development of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) systems in
the 1960s and developed through the 1990s by the
introduction of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems.
3. Globalization era
The third movement of supply chain management
development, the globalization era, can be characterized by
the attention given to global systems of supplier relationships
and the expansion of supply chains over national boundaries
and into other continents.
Previous Next End

4. Specialization era
Phase I: Outsourced Manufacturing and Distribution
In the 1990s, industries began to focus on “core
competencies” and adopted a specialization model.
Companies abandoned vertical integration, sold off non-core
operations, and outsourced those functions to other
companies.
Previous Next End

5. Specialization Era
Phase II - Supply Chain Management as a service
Specialization within the supply chain began in the 1980s with
the inception of transportation brokerages, warehouse
management, and non-asset-based carriers and has matured
beyond transportation and logistics into aspects of supply
planning, collaboration, execution and performance
management
Previous Next End

Supply Chain Management Activities
1. Determine channel strategy and level of distribution
intensity
2. Manage relationships in the supply chain
3. Manage the logistical components of the supply chain
4. Balance the costs of the supply chain with the service level
demanded by customer
Previous Next End

Components of Supply Chain Management Integration
Planning and control
Work structure
Organization structure
Product flow facility structure
Information flow facility structure
Management methods
Power and leadership structure
Risk and reward structure
Culture and attitude
Previous Next End

Role of Supply Chain Management• Communicator of Customer demand from point of sale to
supplier• Physical flow process that engineers the movement of
goods
Supply Chain Management and its Benefits• Reduction of product losses in transportation and storage.• Increasing of sales.• Dissemination of technology, advanced techniques, capital
and knowledge among the chain partners.
Previous Next End

Better information about the flow of products, markets and
technologies.
Transparency of the supply chain.
Tracking & tracing to the source.
Better control of product safety and quality.
Large investments and risks are shared among partners in the
chain.
Previous Next End
Contd……

Supply Chain Modeling Approaches Network Design Methods Rough Cut Methods Simulation methods
Critical drivers in a Supply Chain
1.Inventory
2.Transportation
3. Facilities
4. Information
Previous Next End

Agricultural Supply Chain Management at global level Cross-border Supply Chain
INPUT SUPPPLIERINPUT SUPPPLIER FARMERFARMER
FOOD INDUSTRY
FOOD INDUSTRY
AGRI INDUSTRYAGRI INDUSTRY
RETAILERRETAILERCONSUMERCONSUMER
Previous Next End

Cycle for supply chain development
AWARENESS AND RISING ACTIVITIES
AWARENESS AND RISING ACTIVITIES
TOOL AND CASE DESCRIPTIONS
TOOL AND CASE DESCRIPTIONS INSTITUTION
BUILDINGINSTITUTION
BUILDING
CHAIN PILOT PROJECTSCHAIN PILOT PROJECTS
Previous Next End

Infra Structure For Horticultural Supply Chain Management
Cold Chain Facilities Industrial cold stores in the Production zones Refrigerated vehicles for long distance transport Refrigerated room in wholesale markets
Field Heat facilities Product temperature upon harvest Major fraction of the heat load to be removed Influences the rate of reactions during storage
Previous Next End

Pre-Cooling facilities
1.Necessary for removal of field heat
2.Slow down the temperature dependent metabolic processes
3.Ensures longer storage and better product quality
Refrigerated Cooling
Hydro Cooling
Vacuum Cooling
Previous Next End

Supply Chain Umbrella
i. Purchasing
ii. Quality control
iii. Demand and supply planning
iv. Material or inventory control
v. Order processing
vi. Production planning, scheduling and control
vii. Warehousing / distribution
viii. Customer service
Previous Next End

Previous
• India is going through a retail revolution. Food being perishable item, for the retailer to be successful the key is proper supply chain management.• Planning and control, Work structure, Organization structure, Product flow facility structure, Information flow facility structure Management methods, Power and leadership structure, Risk and reward structure Culture and attitude are the main components of supply chain management.• Awareness and rising activities, Institution building, Chain pilot projects, Tool and case descriptions are the main cycle for supply chain development.• Supply chain management help to effective utilization of inputs and improve distribution of output.
Let us sum Up