Structure and Function of Cells Chapter 2. Looking at cells Living cells can be classified into 2...
-
Upload
elisabeth-parker -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of Structure and Function of Cells Chapter 2. Looking at cells Living cells can be classified into 2...
Chapter 2
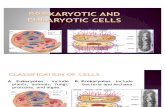
Structure and Function of CellsChapter 2Looking at cellsLiving cells can be classified into 2 different kinds:Prokaryotic cellsEukaryotic cells
All cells have an outer boundary known as the plasma membrane (or cell membrane)Prokaryotic cells have very little defined internal structures. They are very simple cells.This includes bacteria Eukaryotic cells are much more complex. They contain membrane bound organelles. Organelles are structures that perform the tasks that a cell needs to do.This includes all animals, plants, fungi, other single celled organismsThe plasma membrane boundaryControls entry and exit of substancesIs very thin (0.01m)Present in prokaryotes and eukaryotesIs partially permeable meaning it is selective about which dissolved substances are allowed in or out.Consists of a phospholipid bilayerFluid mosaic model describes the form it takes
Free passage: DiffusionDiffusion is the net movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. It is a passive process (does not require energy)
See simulation on scootleOsmosis: a special case of diffusionOsmosis is the movement of water from an area of low solute concentration (high in water, low in dissolved substances) to an area of high solute concentration (low in water, high in dissolved substances) UNTIL the concentration is equal
See simulation on scootleFacilitated diffusionIn some cases, movement of substances across the membrane is assisted by carrier protein molecules (think back to the fluid mosaic model)This occurs when the substances are unable to move through the lipid bilayer.It is a passive process (does not require energy)
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_facilitated_diffusion_works.html
Paid passage: active transportActive transport is the movement of dissolved substances against a concentration gradient (the OPPOSITE of diffusion)It is an energy requiring processhttp://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_the_sodium_potassium_pump_works.html
Bulk transportEndocytosis and exocytosis are two methods for moving large particles into and out of cells.Endocytosis involves the cell membrane engulfing a foreign object and moving it into the cytosol. Eg white blood cellsExocytosis involves a vesicle (containing whatever is to be released) fusing with the cell membrane and release its contents into the environment surrounding the cell See figure 2.12 pg 30Phagocytosis: solid materialPinocytosis: fluid material Surface area to Volume ratio SA:VCells are smallSome cells have folded membranes
Cells must maintain a favourable SA:V which means that their surface area is sufficient to take up materials essential for cell functioning.
Refer to biozone activity- pg 79See pg 44 of text
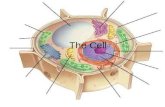
Cell wallsNot found in ANIMAL cellsIn plants, fungi & bacteria, a cell wall exists outside the plasma membraneCell walls provide organisms with a rigid support structureCell organellesThe nucleus: control centreMitochondrion: energy supplying organelleNuclei are present in eukaryotic cellsThe nucleus contains the genetic material (DNA) of the cell, which provides instructions for performing all of the tasks that a cell needs to do.
Mitochondria complete cellular respiration in order to provide ATP for cellular activities.They are the powerhouse of the cellCell Organelles (cont)Ribosomes: protein factoriesLysosomes: controlled destructionRibosomes makes proteins for use in the cell or for export outside the cell (eg hormones)Programmed cell death: apoptosisLysosomes contain digestive enzymes, which can be released to cause the self destruction of the cell
Transport, storage and exportEndoplasmic reticulumGolgi complexTransports proteins within the cell.Can be called rough ER or smooth ERRough ER is surrounded by ribosomes.Transports substances made in the cell to outside the cellChloroplastsFlagella & cilia: whipping around.Found in PLANT cells onlySite of photosynthesis: the trapping of sunlight and conversion to chemical energy in the form of glucose.Contain the substance chlorophyll, a green, light trapping pigmentAre found in cells where movement is required.Flagella are a tail structure, where its movement cause the cell to move. Cilia are hair like structures- movement of cilia may cause the cell to move, or may cause things outside the cell to move past it. (Eg trachea) Cells in multicellular organisms: levels of organisationCells tissues organs systems HomeworkBiozone pgs 73, 75,76-77, 81, 83
Plant and animal cells pgs 67- 70
Practical report from last weeks prac