Skull D.Rania Gabr D.Sama. Objectives Identify the different bones forming the skull with important...
-
Upload
joshua-maxwell -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Skull D.Rania Gabr D.Sama. Objectives Identify the different bones forming the skull with important...
Objectives
• Identify the different bones forming the skull with important foramina.
• Differentiate between the bony features of the skull of an adult and infant.
The Skull• It consists of flat and irregular bones• Divides into: Cranial bones which encase the brain Facial bones which form the bones of the face• The following must be identified: Nasion Inion Bregma Lambda External occipital protuberance Parietal eminence Zygomatic arch
• Cranial bones include: (Neurocranium) Frontal Ethmoid Sphenoidal Occipital
ParietalTemporal
• Facial bones include: (Viscerocranium)
MaxillaZygomaticNazalPalatine
Lacrimal Inferior concha
VomerMandible
The Skull
The Skull
• Parietal• Temporal
SquamousMastoidStyloidTympanicPetrous
• SphenoidGreater wingLesser wingPterygoid processBody
• Occipital
The Skull
• Petrous part of temporal• Lesser wing of sphenoid• Body of sphenoid• Pterygoid process• Ethmoid bone
Crista galliCribriform platePerpendicular plate
• Vomer • Palatine bone
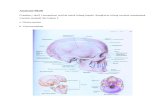
Cranial Fossa
• It is the cavity of the skull
• Divides into: Anterior cranial fossa Middle cranial fossa Posterior cranial fossa
Anterior Cranial Fossa
• Formed of: Orbital plate of frontal bone Cribriform plate of ethmoid Crista galli Lesser wing of sphenoid• Occupies: Frontal lobe of the cerebrum Optic nerves Olfactory bulb and tract
Middle Cranial Fossa
• Formed of: Greater wing of sphenoid Body of sphenoid Squamous part of temporal bone Anterior part of petrous bone• It occupies: Temporal lobe of the cerebrum
Posterior Cranial Fossa
• Formed of: Sphenoid part of clivus Posterior part of petrous bone Occipital bone• It shows the following land marks: Groove for transverse sinus Groove for segmoid sinus Internal occipital protuberance• It occupies: Cerebellum Brain stem
Foramina of the Skull
• Foramina are found within the skull bones• They vary in size and shape• They transmit nerves, blood vessels and dura matter
Sutures of the Skull
• Sutures are fibrous joints articulating the skull bones
• They include: Coronal Sagittal Lambdoid Pterion
Skull Fontanel
• Fontanels are spaces between some of the skull bones of infants
• They permit easy growth of the brain
• They permit overlapping of skull bones during labor
• They are anterior, posterior, anterolateral, and postero- lateral• They close later in life at 6-18 months
The Mandible
• It is a flat bone• Identify the following: Head(condylar process) Mandibular notch Coronoid process Ramus Angle Body Mylohyoid line Submandibular fossa Digastric fossa Mandibular foramen Mental foramen