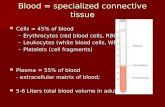
Lab 3 Blood Cells & Blood Typing. Blood Contents Plasma = 55% Blood Cells = 45% Centrifuged blood.
SKELETAL SYSTEM NOTES. 4 Major Functions Framework Protection Storage Blood cells.
-
Upload
lindsey-watson -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
5
Transcript of SKELETAL SYSTEM NOTES. 4 Major Functions Framework Protection Storage Blood cells.
Generic Parts• Periosteum• Endosteum• Epiphysis• Diaphysis• Epiphyseal
Cartilage• Yellow Marrow• Red Marrow• Foramen
Chest• Clavicle – 2• Scapula – 2 (glenoid
cavity, acromion process)• Ribs – 12• Sternum (manubrium,
body, xiphoid process)
Leg• Femur – head, neck, greater and lesser
trochanter• Patella• Tibia – medial ankle “bone”• Fibula – lateral ankle “bone”• Tarsals – talus, calcaneus• Metatarsals• Phlanges
Joint Types
• Synarthroses – immovable
• Amphiarthroses – slightly moveable
• Diathroses – freely moveable
Diathroses Joints
• Hinge – atlas, elbow, knee, fingers, toes
• Pivot – axis, forearm• Saddle – thumb• Condyloid – wrist, ankle• Ball and Socket – shoulder, hip• Gliding - vertebrae
Movement Terms
• Flexion – decreasing angle
• Extension – increasing angle
• Abduction – moving away
• Adduction – moving towards
• Rotation – turning on an axis
Movement Terms• Pronation – turning palm down
• Supination – turning palm up
• Inversion – turning sole inward
• Eversion – turning sole outward
• Dorsal Flexion – toes towards nose
• Plantar Flexion – toes away from nose
Major Diseases/Disorders• Sprain – stretched ligament/tendon• Arthritis – inflamed joint• Osteomyelitis – inflamed bone• Osteoporosis – loss of bone density• Osteosarcoma – bone cancer• Leukemia – white blood cell cancer• Fracture – break or crack in a bone
Types of Fractures
• Simple – break thru bone
• Compound – bone end thru skin
• Greenstick – bent bone
• Comminuted – splintered bone
Types of Fractures• Compressed – bone pieces
pressed together• Spiral – break caused by twist• Incomplete – crack in bone• Avulsion – process broken off
bone
Complete Blood Count• Erythrocytes (RBC): carry o2
and co2, 4 million• Leukocytes (WBC): fight
invaders, 5-10 thousand• Thrombocytes (platelets): clot
blood, 250-400 thousand