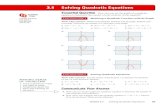
Section 7.5 – Graphing Quadratic Functions Using Properties.
-
Upload
vivien-pierce -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
1
Transcript of Section 7.5 – Graphing Quadratic Functions Using Properties.
f(x)=(x-3)(x+1)
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
A function that can be written in the form , where is a quadratic function.
Quadratic Function
cbxaxxf 2)(0a
The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola.
vertexy-intercept
x-intercept
opens upConcave Up
f(x)=(x-3)(x+1)
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y f(x)=-x^2 + 2x + 3
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
Quadratic Function - Concavity32)( 2 xxxf32)( 2 xxxf
f(x)=x^2 - 2x + 3
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
32)( 2 xxxf
Quadratic Function - Concavity
cbxaxxf 2)( If a > 0, concave upIf a < 0, concave down
f(x)=x^2 - 5x + 1
f(x)=-2x^2 + 5
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
15)( 2 xxxf 52)( 2 xxfMatching
15)( 2 xxxf
52)( 2 xxf
f(x)=(x-3)(x+1)
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y f(x)=-x^2 + 2x + 3
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
Quadratic Function – y-intercept32)( 2 xxxf32)( 2 xxxf
f(x)=x^2 - 2x + 3
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
32)( 2 xxxf
f(x)=2x^2 - 6x + 4
f(x)=x^2 - 2x - 6
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
Quadratic Function – y-intercept
cbxaxxf 2)( y-intercept: (0, c)
62)( 2 xxxf 462)( 2 xxxfMatching
462)( 2 xxxf
62)( 2 xxxf
f(x)=(x-3)(x+1)
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y f(x)=-x^2 + 2x + 3
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
Quadratic Function – x-intercepts32)( 2 xxxf32)( 2 xxxf
f(x)=x^2 -6x + 9
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
96)( 2 xxxff(x)=x^2 - 2x + 3
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
32)( 2 xxxf
)1)(3()( xxxf 32)( 2 xxxf )1)(3()( xxxf
)3)(3()( xxxf
Can’t be factored using real numbers
The x-intercepts of are the REAL solutions to the quadratic equation.
Quadratic Function – x-interceptscbxaxxf 2)(
f(x)=-x^2 + 2x + 3
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
f(x)=x^2 - 2x + 3
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
yf(x)=x^2 -6x + 9
-9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
x
y
Two Real Solutions
One Real Solution No Real Solutions
Quadratic Function – x-intercepts
86)( 2 xxxf 8)( 2 xxxf8168)( 2 xxxff(x)=x^2 - 6x + 8
f(x)=x^2 + x + 8
f(x)=8x^2 - 16x + 8
-2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
x
y
)2)(4()( xxxf
)1)(1(8)(
128)( 2
xxxf
xxxf
cbxaxxf 2)(
The vertex of the parabola is an ordered pair, (h, k). It can be found by finding the x value first:
a
bh
2
Once you have found the x value, substitute that value in to the function and simplify to find the y value.
Finding the Vertex – Standard Form
842 xxy
Finding the Vertex - Standard Form
Vertex:
22
4
)1(2
)4(2
a
bh
4
884
8)2(4)2( 2
k
)4,2(
f(x)=x^2 - 4x + 8
-7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
x
y