SD308 · Web viewWord Choice: Axon Axon Terminal Cell Body Dendrite Node of Ranvier Nucleus Schwann...
9
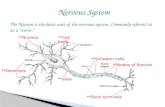
Station 1 Number your paper 1-7 and name the parts. Word choices are given. Then place the letter of the corresponding function next to the name. Answer questions 8 and 9. 1 2 7 3 4 5 6 Functions: A. Metabolic center of the cell B. Protects and insulates the cell C. Picks up messages from other nerve cells D. Releases neurotransmitters E. Allows for faster pathway of an impulse F. Transports electrical messages away from the cell body G. Contains the cell’s DNA 8. Is this cell part of the CNS or PNS? How do you know? 9. What is the difference between white matter and grey matter in terms of composition? Word Choice: Axon Axon Terminal Cell Body Dendrite Node of Ranvier Nucleus Schwann Cell
Transcript of SD308 · Web viewWord Choice: Axon Axon Terminal Cell Body Dendrite Node of Ranvier Nucleus Schwann...
Station 1
Number your paper 1-7 and name the parts. Word choices are given. Then place the letter of the corresponding function next to the name. Answer questions 8 and 9.
Word Choice:
C. Picks up messages from other nerve cells
D. Releases neurotransmitters
F. Transports electrical messages away from the cell body
G. Contains the cell’s DNA
8. Is this cell part of the CNS or PNS? How do you know?
9. What is the difference between white matter and grey matter in terms of composition?
Station 2
1. Name the 3 main functions of the nervous system.
2. Use the terms below to create a flow chart of the nervous system. Place the letter of the description next to each name.
Afferent
Autonomic
Station 3
Number your paper 1- 6 and match the cell to its function. There may be multiple answers.
1. Astrocyte
2. Microglia
3. Ependymal
4. Oligodendrocytes
B. Form Myelin
D. Produce cerebrospinal fluid
F. Clean up dead cells and bacteria
G. General name for all supporting cells
H. Connect neurons to a blood supply
I. Main messaging cell of the nervous system
Station 4
Number your paper 1-6 and name the parts. Answer question 7 and 8.
Terms:
Effector
Q8. What is the purpose of this within our body?
Station 5
Number your paper 1-15 and name the parts shown. Then place the letter of each function next to the name.
15
Terms:
Spinal cord Epithalamus
A. Balance and Coordination of the body
B. Involuntary control center ex. Blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate
C. Connects the two cerebral hemispheres to allow for communication
D. Stimulates and controls various muscles and glands for sex drive, thirst, pleasure, pain
E. Relay center for sensory impulses from spinal cord to cerebral cortex for interpretation
F. Reflex center for vision and hearing
G. Controls breathing
I. Circulates cerebrospinal fluid through the cerebral hemispheres
J. Location of the pineal gland
K. Produces melatonin
Station 6
Number your paper 1-11 and use the terms to name the parts. Place the letter of the description or function next to the answer. Answer questions 12-13.
1 2 3
Occipital lobe
Temporal lobe
Precentral gyrus
Postcentral gyrus
Central sulcus
D. Divides the frontal and the parietal lobes
E. Planning, behavior, intellect
G. New memories and short-term memories
H. Auditory area found here
I. Stores sequenced activities
Q12. What is the cerebral cortex?
Q13. Is this the left or the right side of the brain?
Station 7
Number your paper 1-14. Put the following in the correct order.
A. A stimuli excites the neuron.
B. Potassium channels on the neuron's membrane open.
C. Potassium rushes out of the neuron.
D. Resting potential is restored.
E. Sodium channels in the membrane open.
F. Sodium is pumped back to the outside of the neuron and potassium is pumped back to the inside of the neuron.
G. Sodium rushes into the neuron down the concentration gradient.
H. Some ions sneak through the neuron's membrane to the other side, however, the sodium potassium pump returns ions to their original positions.
I. The inside of the neuron's membrane becomes positive for a period of time.
J. The major positive ions inside the cell are potassium, whereas the major positive ions outside the cell are sodium.
K. The neuron is depolarized.
L. The neuron is repolarized.
M. The outside of the neuron's membrane has more positive ions than the inside of the neurons membrane.
N. This is known as resting potential; the neuron is inactive.
Station 8
Match the neurotransmitter with its function.
1. Dopamine
2. Serotonin
3. GABA
4. Glutamate
A. Inhibitory neurotransmitter, natural tranquilizer
B. Regulates movement and emotional responses, involved in the rewards pathway of the brain
C. Mood, emotion, sleep and appetite
D. Excitory neurotransmitter, important for learning and memory
5. Name six ways that drugs and/or toxins can alter the transmission of a nerve impulse at synapse.
Station 9
Station 10
Number your paper 1-7 and name the parts. Word choices are given. Then place the letter of the corresponding function next to the name. Answer questions 8 and 9.
Word Choice:
C. Picks up messages from other nerve cells
D. Releases neurotransmitters
F. Transports electrical messages away from the cell body
G. Contains the cell’s DNA
8. Is this cell part of the CNS or PNS? How do you know?
9. What is the difference between white matter and grey matter in terms of composition?
Station 2
1. Name the 3 main functions of the nervous system.
2. Use the terms below to create a flow chart of the nervous system. Place the letter of the description next to each name.
Afferent
Autonomic
Station 3
Number your paper 1- 6 and match the cell to its function. There may be multiple answers.
1. Astrocyte
2. Microglia
3. Ependymal
4. Oligodendrocytes
B. Form Myelin
D. Produce cerebrospinal fluid
F. Clean up dead cells and bacteria
G. General name for all supporting cells
H. Connect neurons to a blood supply
I. Main messaging cell of the nervous system
Station 4
Number your paper 1-6 and name the parts. Answer question 7 and 8.
Terms:
Effector
Q8. What is the purpose of this within our body?
Station 5
Number your paper 1-15 and name the parts shown. Then place the letter of each function next to the name.
15
Terms:
Spinal cord Epithalamus
A. Balance and Coordination of the body
B. Involuntary control center ex. Blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate
C. Connects the two cerebral hemispheres to allow for communication
D. Stimulates and controls various muscles and glands for sex drive, thirst, pleasure, pain
E. Relay center for sensory impulses from spinal cord to cerebral cortex for interpretation
F. Reflex center for vision and hearing
G. Controls breathing
I. Circulates cerebrospinal fluid through the cerebral hemispheres
J. Location of the pineal gland
K. Produces melatonin
Station 6
Number your paper 1-11 and use the terms to name the parts. Place the letter of the description or function next to the answer. Answer questions 12-13.
1 2 3
Occipital lobe
Temporal lobe
Precentral gyrus
Postcentral gyrus
Central sulcus
D. Divides the frontal and the parietal lobes
E. Planning, behavior, intellect
G. New memories and short-term memories
H. Auditory area found here
I. Stores sequenced activities
Q12. What is the cerebral cortex?
Q13. Is this the left or the right side of the brain?
Station 7
Number your paper 1-14. Put the following in the correct order.
A. A stimuli excites the neuron.
B. Potassium channels on the neuron's membrane open.
C. Potassium rushes out of the neuron.
D. Resting potential is restored.
E. Sodium channels in the membrane open.
F. Sodium is pumped back to the outside of the neuron and potassium is pumped back to the inside of the neuron.
G. Sodium rushes into the neuron down the concentration gradient.
H. Some ions sneak through the neuron's membrane to the other side, however, the sodium potassium pump returns ions to their original positions.
I. The inside of the neuron's membrane becomes positive for a period of time.
J. The major positive ions inside the cell are potassium, whereas the major positive ions outside the cell are sodium.
K. The neuron is depolarized.
L. The neuron is repolarized.
M. The outside of the neuron's membrane has more positive ions than the inside of the neurons membrane.
N. This is known as resting potential; the neuron is inactive.
Station 8
Match the neurotransmitter with its function.
1. Dopamine
2. Serotonin
3. GABA
4. Glutamate
A. Inhibitory neurotransmitter, natural tranquilizer
B. Regulates movement and emotional responses, involved in the rewards pathway of the brain
C. Mood, emotion, sleep and appetite
D. Excitory neurotransmitter, important for learning and memory
5. Name six ways that drugs and/or toxins can alter the transmission of a nerve impulse at synapse.
Station 9
Station 10