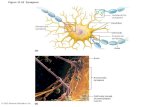
Nervous System **Axon terminals **Nodes of Ranvier **Schwann cells **axon **Dendrites **Cell...
-
Upload
susanna-hodge -
Category
Documents
-
view
240 -
download
0
Transcript of Nervous System **Axon terminals **Nodes of Ranvier **Schwann cells **axon **Dendrites **Cell...

The Neuron is the basic unit of the nervous system. Commonly referred to as a “nerve.”
Nervous System
**Axon terminals
**Nodes of Ranvier
**Schwann cells
**axon
**Dendrites
**Cell body
**Nucleus

The neurons connect the brain to the entire body and its parts. But the neurons do not touch each other!
**Synaptic cleft or gap is the gap between neurons

• Substance• P
Pain• Substance• P
Receptor• Substance• P
Receptor
Messages are sent from one neuron to the next via chemicals called Neurotransmitters. In this case, the message of pain is being transmitted by a neurotransmitter called “Substance P” **A Neurotransmitter is a chemical released by 1 neuron that has an effect on another neuron

Each Neuron has specific receptors for each neurotransmitter, which then relay the message through the axon of the neuron toward the axon terminal.

*During a nerve impulse, there is a reversal of polarity in the axon

Hmwk: p 1009 #1, 4

The Dendrites are the receiving end of the neuron and the axon terminal is the sending end
Dendrite(s)Receives information, carries to cell body
Cell body contains nucleus
***Axon is cell extension (conducts action potential)Transmits information away from cell body to the axon terminal
Cell has only 1 axon

If the message is being sent to a muscle to contract, the last axon terminal will end at a motor end plate of the target muscle/muscles. That message will stimulate the muscle to contract… This happens in a millisecond. That’s fast!

*Axons are covered with a lipid layer called the myelin sheath
***Myelin sheath increases the speed of nerve impulses or action potential

◦ Resting cell membrane is more permeable to potassium ions than sodium ions
◦ More positive charges leave the cell than enter it
◦ ***Sodium ions are more concentrated outside the cell
◦ *Potassium ions are more concentrated inside the cell
◦ *The inside of the cell is negatively charged◦ The outside of the cell is positively charged
**Resting Potential

*Visual information is processed by the occipital lobe in the brain
**Cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the cerebrum
*Cerebellum smoothes and coordinates movements like walking and running
*The brain stem connects the cerebral hemisphere with the cerebellum
***Brain

**Diencephalon*Contain important relay centersMade up of the thalamus and hypothalamus

Like an interstate, it carries information back and forth
The outer ◦ Composed of a white matter (insulates)
The inner◦ Composed of **gray matter made up of
Dendrites, axons, cell bodies but **does not include motor neurons
**Spinal Cord

1. The Central Nervous System (CNS) a) Brain (includes cranial neurons-so that lobes of
the brain can talk to each other)
b) Spinal Cord (includes spinal neurons, which relay
messages from the body’s extremities and internal organs to the spinal cord)
There are three parts to the nervous system:

*The Central Nervous System (CNS) *Is made up of the Brain and the spinal
cord
There are three parts to the nervous system

*This connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body
**Sensory receptor is a neuron that detects stimuli
* Two principal components of the peripheral nervous system are :1. *Sensory2. *Motor **Includes Spinal Nerves (spinal cord =
CNS)
2. ***The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)

*Somatic Nervous system ◦part of the PNS◦*Contains neurons that control skeletal
muscle **Afferent Neurons
◦ Collect information from the body and transmit it toward the CNS
◦ Includes neurons in the ear, **eyes (optic nerve) Efferent Neurons
◦ Transmit information away from the CNS. **Included in the PNS:
◦ Somatic system◦ Autonomic system◦ Sensory system

Involuntary muscle contractions in digestive and cardiovascular systems.
This happens ”automatically!” You do not have to think about it. **A spinal reflex is an example of an
involuntary movement
3. **Autonomic Nervous System

Autonomic nervous system has two parts:1. *Sympathetic division
*In times of stress it is the sympathetic nervous system is activated
2. Parasympathetic division

Hmwk Pg 1015 #1,3, 4, 5

SENSORY SYSTEM Sense organs
Eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and skin

**HEARING AND BALANCEAuditory canal
Connect to external ear with tympanic membrane (eardrum)
**Tympanic membrane**Vibrates in response to sound
waves Eustachian tube
Opening to throatEqualizes pressure on both sides of
the tympanic membrane

*CochleaInner ear
*Coiled tube essential to hearing
**Contain hair cells are important for hearing and balance
*Semicircular canals*Essential for balance

**AUDITORY INFORMATION
**Travels to the brain stem thalamus cerebral cortex

VISION Retina
Light sensitive inner layer of eye Receives image formed by lens Transmits them through optic nerve to the brain
Pupil Opening at center of iris Controls amount of light that enters the eye
Iris Colored circular part of eye
Lens Convex transparent structure in the eye that focuses light
on retina Rods
Detects dim light Plays major role in non-color and night vision
Cones Distinguishes color Sensitive to bright light

*Photoreceptors in the retina convert light energy to electrical signals

TASTE AND SMELL Pressure and Temperature