Questions to ask about a culture ancient egypt
description
Transcript of Questions to ask about a culture ancient egypt

Questions to Ask About a Culture
1. Geography
2. Economics
3. Religion and Philosophy
4. Knowledge, Education, and the Arts
5. Political Science
6. Sociology
7. History
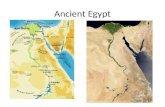
Protection from attacks and enemy
North border is Mediterranean Sea
South border- series of cataracts (large, steep
waterfall)
Divided into Lower and Upper Egypt
Pharaohs were considered gods
Four main gods and a goddess (Ra, Osiris, Isis, Anubis) Believed in the afterlife
Only a few Egyptians could read or write hieroglyphs
Scribes were valued in society and they were the only ones who could
read or write hieroglyphs
Children games; throwing/ playing ball, board game, bows and arrows,
etc.
Pharaoh was supreme ruler
Vizier helped manage country and in charge of almost all areas
of government
Egyptian laws considered more humane than earlier societies
Had approx. 31 ruling dynasties
Girls married at 13 Men made decisions for family Pharaohs; religious leader and head of government Wealthy men; worked outside home Vizier; official chosen by pharaoh
Egyptians believed in life after death Time periods; the old kingdom, Middle kingdom, New kingdom Pharaohs married their sisters, mothers, cousins Egyptians were religious invented written and spoken language
East– traded for wood
Traded by using boats and ships through the Nile River
South– traded for jewelry, plants for perfume, cloth from wild ani-
mals (leopard skin, giraffe, etc.)