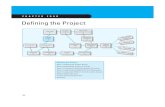
Project management: defining the project
-
Upload
oscar-vadillo -
Category
Business
-
view
9.370 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Project management: defining the project

Project Management:Defining the project
GGSB- Project Management 1
ByO. Vadillo
D. DimitrovC. Klein
F. Bourret

Table of Contents
• Introduction to Work Breakdown Structure
• 5 steps to define a project
• Process breakdown structure and Communication plan
• Key factors to remember
GGSB- Project Management 2

Work breakdown structure
• Importance of a clear structure
– Cope with details
– Stay focused
– Satisfy stakeholders
• 5 steps guide provides a well structured guide
GGSB- Project Management 3

Step 1: Define the scope
• Brief but specific definition of result or mission
• Focuses on the project purpose throughout its life
• Agreement between costumer and project manager
• To plan and control performance
The key stone of a project
GGSB- Project Management 4

Project Scope Checklist
GGSB- Project Management 5
1/ Project objectives Overall goalwhat, when, how much
2/ Deliverables Major expected outputs
3/ MilestonesNatural and significant events time, cost, resources
4/ Technical requirements To assure performance
5/ Limits and exclusion Avoid false expectations
6/ Reviews with costumersUnderstanding and agreement of expectations
Avoid scope creep : added costs or delays

GGSB- Project Management 6
Step 2: Establishing priorities
• Primary job of the Project Manager

GGSB- Project Management 7
• Need to define priorities priority matrix
• Which criterions have to be:
– Constrained
– Enhanced
– Accepted
Creates shared expectationsAvoids misunderstanding

• Variation of priorities
Microsoft / Event
• Which criteria can be compromised?
• Priorities may change
GGSB- Project Management 8
Need for vigilance and anticipation

• Outline of the project with different levels of detail
• Evaluation of
– Cost
– Time
– Technical performance
GGSB- Project Management 9
Step 3: Create the WBS

• Work package
– The basic unit of planning, scheduling and
controlling
– Maximum 10 days
– Independent from other work packages
– No more than 1 sub-deliverable
• Components
What/ How long/ Cost/ How much/ Who / How well
GGSB- Project Management 10

WBS Example
GGSB- Project Management 11Reference: Gray and Larson, Project Management, Irwin/McGraw-Hill, 2000

Step 4: WBS in Organisations
• Result of linking the WBS with the organisational units (hereafter OU):
OBS (Organizational Breakdown Structure)
GGSB- Project Management 12
Purposes
Framework to summarize OU work performance
Identify OU responsible for Work Packages
Tie the OUs to control cost accounts

Example: Integration of WBS and OBS
GGSB- Project Management 13
Cost accountnumber
Personal computerprototype
Vendor,software,
applications
Mouse,keyboard,
voice
Diskstorage
units
Microprocessorunit
Moreitems
Floppy HardOptical Internalmemory
unit
BIOS (basicinput/output
system)
ROM RAM I/O File Utilities
Motor Circuitboard
Chassisframe
Read/writehead
~ ~ ~ ~ ~
~ ~
~ ~
Lowest manageablesubdeliverables
Level1
2
3
4
5
1.0
1.2 1.3 1.1 1.4
1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.31.4.1 1.4.2
1.4.1.1 1.4.1.2 1.4.2.1 1.4.2.2 1.4.2.3
1.1.3.1 1.1.3.2 1.1.3.3 1.1.3.4
Cost 1.1.3.4.1account
Cost Costaccount account
Cost Costaccount account
Costaccount
Costaccount
Work packagesWP1.1.3.4.2.1WP1.1.3.4.2.2WP1.1.3.4.2.3
Budget byperiod
Production
Design
Test
Purchasing
Software
Manufacturing
Organization
Reference: Gray and Larson, Project Management, Irwin/McGraw-Hill, 2000

Step 5: Coding WBS for IS
• Codes define levels and elements in
– WBS
– Work Packages
– Budget/cost information
• Allows reports to be consolidated at any level in the organization structure
GGSB- Project Management 14

GGSB- Project Management 15
Facility Area Pipe 2” WP#
3R-237A-P2-33.61
Example: Integration of WBS and OBS

GGSB- Project Management 16
Process Breakdown Structure
Intangible projects: phases
USE
Process-oriented projects
• Project organized around phases
• PBS vs. WBS

• Project Communication Plan– WWWH the information will be transmeted
• 5 Steps– Stakhoder analysis– Information needs– Sources of Information– Disseminiation modes– Responsibility and timing
GGSB- Project Management 17
Communication Plan

Key factors to remember
• Scope definition focuses on end items
• Priorities (PM) trade-off decisions
• BS project control
Key stones
• Use of WBS, PBS or RM depends on size and nature
• First step of planning / Major reason for failure
GGSB- Project Management 18

Thank you
We would be delighted to answer any question.
GGSB- Project Management 19