Presipitasi - Bhupalaka's Blog · NEXt generation RADar: is a doppler radar used for obtaining...
Transcript of Presipitasi - Bhupalaka's Blog · NEXt generation RADar: is a doppler radar used for obtaining...

2/12/2010
1
Dalam 103 km3
Curahan atau jatuhnya air dari atmosfer kepermukaan bumi dan laut dalam bentuk yang berbedaHujan di daerah tropisCurah hujan di iklim sedangSalju di kutub
Fungsi : sebagai pelindung permukaan bumiSuhu udara↑kapasitas udara dalam penampunguap air↑
Dib i j di j iDibagi menjadi 2 jenis :Kelembaban spesifik : tidak dipengaruhi tek. udaraKelembaban absolut : dipengaruhi tek. udara
“mesin” yang mempertahankanberlangsungnya daur hidrologiPerubahan iklimSumber energi untuk :▪ Evaporasi : berlangsung pada permukaan badanperairan
▪ Transpirasi : kehilangan air dari dalam vegetasi
Heating of earth surface is uneven
Solar radiation strikes perpendicularly near the equator (270 W/m2)equator (270 W/m )Solar radiation strikes at an oblique angle near the poles (90 W/m2)
Emitted radiation is more uniform than incoming radiation
Amount of energy transferred from equator to the poles is approximately 4 x 109 MW

2/12/2010
2
Gerakanmassa udara : gerakan atmosferatau udara nisbi terhadap permukaan bumiParameter :ArahKecepatan
Berpengaruh dalam proses evapotranspirasidanmempengaruhi kejadian‐kejadian hujanHujan terjadi gerakan udara lembab yang berlangsung terus menerus
Mempengaruhi besarnya curah hujan, lajuevaporasi dan transpirasiDapat dianggap sebagai salah satu faktoryang dapat memprakirakan danmenjelaskankejadian dan penyebaran air di muka bumi
Warm air rises, cool air descends creating two huge convective cells.
1 Tropical Easterlies/Trades
Ferrel Cell
Polar Cell 1. Hadley cell
2. Ferrel Cell
3. Polar cell
Winds
Circulation cells
1. Tropical Easterlies/Trades
2. Westerlies
3. Polar easterlies
1. Intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ)/Doldrums
2. Horse latitudes
3. Subpolar low
4. Polar high
Latitudes
Owing to the tilt of the Earth's axis in orbit, the ITCZ shifts north and south.
Southward shift in January
Northward shift in July
Creates wet Summers (Monsoons) and dry winters, especially in India and SE Asia

2/12/2010
3
Sejumlah uap air di atmosfer bergerak ketempat yang lebih tinggi oleh adanya bedatekanan uap air. Tekanan uap tinggitekanan uap rendah. Uap air bergerakbergerak ke tempat yang lebih tinggi (T udararendah) jenuh kondensasi
Udara di atmosfer mengalami prosespendinginan melalui beberapa cara :Pertemuan antara duamassa udara dengan suhuyang berbedaSentuhan antara massa udara dengan obyek ataubenda dingin
Atmospheric water exists Mostly as gas or water vaporLiquid in rainfall and water droplets in cloudsS lid i f ll d i h il tSolid in snowfall and in hail storms
Accounts for less than 1/100,000 part of total water, but plays a major role in the hydrologic cycle
Suppose we have an elementary volume of atmosphere dV and we want quantify how much water vapor it contains
dVdVmv
v =ρWater vapor density
Atmospheric gases:Nitrogen – 78.1%Oxygen – 20.9%Other gases ~ 1%http://www.bambooweb.com/articles/e/a/Earth's_atmosphere.html
ma = mass of moist airmv = mass of water vapor
dVma
a =ρAir density
Specific humidity measures the mass of water vapor per unit
f i t i
vvq ρ=
mass of moist airIt is dimensionless a
vqρ

2/12/2010
4
Vapor pressure, e, is the pressure that water vapor exerts on a surfaceAir pressure, p, is the total pressure that air makes on pa surfaceIdeal gas law relates pressure to absolute temperature T, Rv is the gas constant for water vapor0.622 is ratio of mol. wt. of water vapor to avg mol. wt. of dry air
TRe vvρ=
peqv 622.0=
John Dalton studied the effect of gases in a mixture. He observed that the Total Pressure of a gas mixture was the sum of the Partial Pressure of each gas.
P total = P1 + P2 + P3 + .......Pn
The Partial Pressure is defined as the pressure of a single gas in the mixture as if that gas alone occupied the container. In other words, Dalton maintained that since there was an enormous amount of space between the gas molecules within the mixture that the gas molecules did not have any influence on the motion of other gas molecules, therefore the pressure of a gas sample would be the same whether it was the only gas in the container or if it were among other gases.
http://members.aol.com/profchm/dalton.html
Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules regardless of their chemical nature and physical properties. This number (Avogadro's number) is 6.023 X 1023
in 22.41 L for all gases.
Dry air
W t
Dry air ( z = x+y molecules) Moist air (x dry and y water vapor)
Water vapor
ρd = (x+y) * Md/Volume ρm = (x* Md + y*Mv)/Volume
ρm < ρd, which means moist air is lighter than dry air!
Saturation vapor pressure occurs when air is holding all the water vaporthat it can at a given air temperature
⎞⎛ T2717⎟⎠⎞
⎜⎝⎛
+=
TTes 3.237
27.17exp611
Vapor pressure is measured in Pascals (Pa), where 1 Pa = 1 N/m2
1 kPa = 1000 Pa
es
e
sh e
eR = Relative humidity measures the percentof the saturation water content of the airthat it currently holds (0 – 100%)
e
Dewpoint temperature is the air temperatureat which the air would be saturated with its current vapor content
TTd

2/12/2010
5
We have three equations describing column:
Hydrostatic air pressure, dp/dz = ‐ρagLapse rate of temperature
Column
Element, dz
2
Lapse rate of temperature, dT/dz = ‐ αIdeal gas law, p = ρaRaT
Combine them and integrate over column to get pressure variation elevation
aRg
TTpp
α/
1
212 ⎟⎟
⎠
⎞⎜⎜⎝
⎛=
1
In an element dz, the mass of water vapor is dmpIntegrate over the
Column
Element, dz
2
Integrate over the whole atmospheric column to get precipitable water,mpmp/A gives precipitable water per unit area in kg/m2
1
Adzqdm avp ρ=
Area = A
Kenaikan massa uap air ke tempat yang lebihtinggi sampai saatnya atmosfer menjadijenuh
d k d k l k lTerjadi kondensasi atas partikel‐partikel uapair di atmosferPartikel‐partikel uap air tersebut bertambahbesar sejalan dengan
Air mass : A large body of air with similar temperature and moisture characteristics over its horizontal extent.Front: Boundary between contrasting air masses.Cold front: Leading edge of the cold air when it is d i t d iadvancing towards warm air.Warm front: leading edge of the warm air when advancing towards cold air.
1. Frontal lifting2. Orographic lifting 3. Convective lifting
Hujan konveksi (Convectional storms) adanya bedapanas yangditerima permukaan tanah dengan panas yang diterima oleh lapisan udara di atas permukaan tanahHujan frontal (frontal/cyclonic storms) bergulungnya duamassa udara yang berbeda suhu dan kelembabanHujan orografik (Orographic storms) jenis hujan yang umum terjadi di daerah pegunungan, yaitu ketika massaudara bergerak ke tempat yang lebih tinggi mengikutibentang lahan pegunungan sampai saatnya terjadi proseskondensasi

2/12/2010
6
Convective precipitation occurs when the air near the ground is heated by the Convective precipitation occurs when the air near the ground is heated by the earth’s warm surface. This warm air rises, cools and creates precipitation. earth’s warm surface. This warm air rises, cools and creates precipitation.
Hot earth surface
Boundary between air masses with different properties is called a frontCold front occurs when cold air advances towards warm airWarm front occurs when warm air overrides cold air
Cold front (produces cumulus cloud) Cold front (produces stratus cloud)
Orographic uplift occurs when air is forced to rise because of the physical presence of elevated land.
Condensation is the change of water vapor into a liquid. For condensation to occur, the air must be at or near saturation in the presence of condensation nuclei. Condensation nuclei are small particles or aerosol Condensation nuclei are small particles or aerosol upon which water vapor attaches to initiate condensation. Dust particulates, sea salt, sulfur and nitrogen oxide aerosols serve as common condensation nuclei. Size of aerosols range from 10‐3 to 10 μm.
Lifting cools air masses so moisture condensesCondensation nuclei
Aerosols water molecules attach
Rising & growing0.5 cm/s sufficient to carry 10 μm dropletCritical size (~0.1 mm)Gravity overcomes and drop falls
FdFd
Fb
Fg
DThree forces acting on rain drop
Gravity force due to weightBuoyancy force due to
g
displacement of airDrag force due to friction with surrounding air
3
6DVolume π
=
2
4DArea π
=
3
6DgF wg
πρ= 3
6DgF ab
πρ=
242
22
2 VDCVACF adaddπρρ ==

2/12/2010
7
Terminal velocity: velocity at which the forces acting on the raindrop are in equilibrium.If released from rest, the raindrop will accelerate until it reaches its terminal velocity
32
236246
0
DgVDCDg
WFFF
wada
DBvert
πρπρπρ −+=
−+==∑
WFF BD −=⎞⎛4gD ρ FF
Fb
D
332
26624
DgDgVDC wat
adπρπρπρ −= ⎟⎟
⎠
⎞⎜⎜⎝
⎛−= 1
34
a
w
dt C
gDVρρ
• Raindrops are spherical up to a diameter of 1 mm• For tiny drops up to 0.1 mm diameter, the drag force is specified by
Stokes law
FdFd
Fg
V
Re24
=dCa
aVDμ
ρ=Re
At standard atmospheric pressure (101.3 kpa) and temperature (20oC), ρw = 998 kg/m3 and ρa = 1.20 kg/m3
Alat penakar hujan otomatisAlat penakar hujan tidak otomatis emberatau kontainer yang telah diketahui
lvolumenya
Influenced by Atmospheric circulation and local factors▪ Higher near coastlines▪ Seasonal variation – annual oscillations in some places▪ Variables in mountainous areas▪ Increases in plains areas▪ More uniform in Eastern US than in West

2/12/2010
8
Isohyet – contour of constant rainfallIsohyetal maps are prepared by interpolating rainfall data at gaged points.
Austin, May 1981 Wellsboro, PA 1889
Rainfall hyetograph – plot of rainfall depth or intensity as a function of timeCumulative rainfall hyetograph or rainfall
l f f f llmass curve – plot of summation of rainfall increments as a function of timeRainfall intensity – depth of rainfall per unit time
Time (min) Rainfall (in) Cumulative 30 min 1 h 2 hRainfall (in)
0 05 0.02 0.0210 0.34 0.3615 0.1 0.4620 0.04 0.525 0.19 0.6930 0.48 1.17 1.1735 0.5 1.67 1.6540 0.5 2.17 1.8145 0.51 2.68 2.2250 0.16 2.84 2.3455 0.31 3.15 2.4660 0.66 3.81 2.64 3.81
Running Totals
65 0.36 4.17 2.5 4.1570 0.39 4.56 2.39 4.275 0.36 4.92 2.24 4.4680 0.54 5.46 2.62 4.9685 0.76 6.22 3.07 5.5390 0.51 6.73 2.92 5.5695 0.44 7.17 3 5.5100 0.25 7.42 2.86 5.25105 0.25 7.67 2.75 4.99110 0.22 7.89 2.43 5.05115 0.15 8.04 1.82 4.89120 0.09 8.13 1.4 4.32 8.13125 0.09 8.22 1.05 4.05 8.2130 0.12 8.34 0.92 3.78 7.98135 0.03 8.37 0.7 3.45 7.91140 0.01 8.38 0.49 2.92 7.88145 0.02 8.4 0.36 2.18 7.71150 0.01 8.41 0.28 1.68 7.24Max. Depth 0.76 3.07 5.56 8.2Max. Intensity 9.12364946 6.14 5.56 4.1
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
Rain
fall
(in p
er 5
min
)
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125 130 135 140 145 150
Time (min)
Incr
emen
tal
Rainfall Hyetograph
6
7
8
9
10
Rai
nfal
l (in
.)
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 30 60 90 120 150
Time (min.)
Cum
ulat
ive
R
30 min
1 hr
2 hr
3.07 in
5.56 in
8.2 in
Rainfall Mass Curve

2/12/2010
9
Data are generally available as points with precipitation stored in attribute table.attribute table.
Nearest Neighbor “Thiessen” Polygon Interpolation
Spline Interpolation
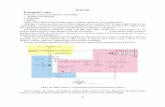
NEXt generation RADar: is a doppler radar used for obtaining weather informationA signal is emitted from the radar which returns after striking a rainfall dropReturned signals from the radar are analyzed to compute the rainfall intensity and integrated over time to get the precipitation
NEXRAD Tower Working of NEXRAD
1. Analisis Curah Hujan2. Melengkapi Data Hujan3 Tes Konsistensi3. Tes Konsistensi4. Uji Homogenitas5. Analisis Curah Hujan Harian Maksimum6. Analisis Intensitas Hujan
1. Metode Aritmatika2 Metode Polygon‐Thiessen2. Metode Polygon Thiessen3. Metode Isohiet

2/12/2010
10
Simplest method for determining areal average
P1
P2
P1 = 10 mm
P2 = 20 mm
P3 = 30 mm
N1
P3
• Gages must be uniformly distributed• Gage measurements should not vary greatly about the
mean
∑=
=N
iiP
NP
1
1
mmP 203
302010=
++=
P1
P2
P
A1
A2
Any point in the watershed receives the same amount of rainfall as that at the nearest gageRainfall recorded at a gage can be applied to any point at a distance halfway to the next station in any directionSteps in Thiessen polygon method1 Draw lines joining adjacent gages P3
A3
1. Draw lines joining adjacent gages 2. Draw perpendicular bisectors to the lines created in
step 13. Extend the lines created in step 2 in both directions
to form representative areas for gages4. Compute representative area for each gage5. Compute the areal average using the following
formula
∑=
=N
iiiPA
AP
1
1
P1 = 10 mm, A1 = 12 Km2
P2 = 20 mm, A2 = 15 Km2
P3 = 30 mm, A3 = 20 km2mmP 7.20
47302020151012
=×+×+×
=
Memadai guna menentukan curah hujansuatu daerahTidak cocok digunakan di daerah bergunung‐
d d h d hgunung dan daerah dengan itensitas curahhujan yang tinggi (Shaw, 1985)
P1
P
10
20
StepsConstruct isohyets (rainfall contours)Compute area between each pair of adjacent isohyets (Ai)Compute average precipitation for each pair of
A1=5 , p1 = 5
A2=18 , p2 = 15
P2
P330
precipitation for each pair of adjacent isohyets (pi)Compute areal average using the following formula
∑=
=M
iii pAP
1
A3=12 , p3 = 25
A4=12 , p3 = 35
mmP 6.2147
35122512151855=
×+×+×+×=
∑=
=N
iiiPA
AP
1
1
Dipandang paling baik, bersifat subjektif dantergantung pada keahlian, pengalaman, danpengetahuan pamakai terhadap sifat curahh d d hhujan di daerah setempatMemerlukan banyak waktu lebih telitiDaerah dengan hujan orografik gariskontur dapat dijadikan isohit
P1=10
P2= 20
P3=30
• Prediction at a point is more influenced by nearby measurements than that by distant measurements
• The prediction at an ungaged point is inversely proportional to the distance to the measurement points
d1=25
d2=153
• Steps– Compute distance (di) from ungaged
point to all measurement points.
– Compute the precipitation at the ungaged point using the following formula
∑
∑
=
=
⎥⎦
⎤⎢⎣
⎡
⎟⎟⎠
⎞⎜⎜⎝
⎛
=N
i i
N
i i
i
d
dP
P
12
12
1ˆ
d3=10
mmP 24.25
101
151
251
1030
1520
2510
ˆ
222
222=
++
++=
p
( ) ( )2212
2112 yyxxd −+−=

2/12/2010
11
Tempat Pengukuran di dalam Daerah
Curah Hujan (mm)
H I F
3575 2929 2371
E D A
2174 1767 867
13683
Rata-rata hitung = 2281 mm
Tempat pengamatan
(1)
Curah Hujan
(2)
Luas Daerah Thiessen
(3)
Persentase Luas
(4)
(2) x (4)
(5) A D E B
867 1767 2174 1781
90 249 186 72
5,4 14,7 11,0 4 2
47 260 240 76B
C F G H J K I
1781 1825 2371 2495 3575 3319 3553 2929
72 33 320 62 115 115 96 349
4,2 2,0 19,0 3,7 6,8 6,8 5,7 20,7
76 36 450 92 243 226 201 606
1687 100,0 2477
Curah hujan rata-rata equivalen = 2477 mm
Isohit Luas Luass Netto
Hujan Rata-rata
(3) x (4) ∑ (5) Hujan Ekuivalen di Atas Luas Netto
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) = (6) : (2) 3000 2500 2000 1500
426 742 1200 1557
426 316 458 357
3250 2700 2250 1800
1384500 853200 1030500 642600
1384500 2237700 3268200 3910800
3250 3016 2724 25121500
1000 1000
15571673 1687
357116 14
18001300 900
642600 150800 12600
3910800 4061600 4074200
25122428 2415
Curah hujan rata-rata ekuivalen = 2415 mm
Tidak lengkap karena:Kerusakan alat penakarKelalaian petugas untuk mencatat
HalHal‐‐hal yang harus diperhatikan:hal yang harus diperhatikan:•• Minimum stasiun pengukuran adalah 3Minimum stasiun pengukuran adalah 3•• Jika mungkin, data statiun pembanding Jika mungkin, data statiun pembanding adalah lengkapadalah lengkap
•• Data yang kurang, maksimum 20% selama Data yang kurang, maksimum 20% selama kurun waktu pendataankurun waktu pendataan
1. Menggunakan rata‐rata hitung data tempat terdekat, jika li ih k d i
∑=
=n
nnx r
nr
1
1
selisih kurang dari 10%
2. Menggunakan cara pembanding normal, jika selisih melebihi 10%
∑=−
=n
n n
n
x
x
Rr
nRr
1)(
11

2/12/2010
12
Data tidak konsisten karena:Perubahan mendadak pada sistem lingkungan hidrologisPemindahan tempat stasiun pengukur hujan atau pemindahan alat pengukurPerubahan cara pengukuran
Teknik Kurva Massa‐Ganda (Double mass curve technique)Akumulasi rata‐rata hujan stasiun dasar dan stasiun utama mulai dengan pengamatan kalender terakhir utama mulai dengan pengamatan kalender terakhir, diplotkan sebagai sumbu x dan y pada suatu grafikJika terjadi perubahan slope, maka data harus dikalibrasi dengan suatu faktor koreksi
Koreksi untuk data yang tidak konsisten:
00
.HtgtgH z αα
=0tgα
HHzz = = curahcurah hujanhujan yang yang diperkirakandiperkirakanHH00 = = curahcurah hujanhujan hasilhasil pengamatanpengamatantgtgαα = slope = slope setelahsetelah perubahanperubahantgtgαα00 = slope = slope sebelumsebelum perubahanperubahantgtgαα/ tg/ tgαα00 = = faktorfaktor koreksikoreksi
α
asiu
n ut
ama
α0
Kum
ulat
if st
a
Kumulatif rata-rata stasiun dasar
Data curah hujan yang telah konsistenkemudian perlu dites kehomogenannyaTidak homogen dikarenakan gangguan‐
fgangguan atmosferTes Homogenitas dilakukan dengan memplotharga (TR,N) padaGrafikTes Homogenitas
Didapat denganmenggunakan PersamaanGumbelModifikasi (PUH 10 tahun):
T SDTTrRRr
T ).45.0))1
ln(ln(78.0( −−
−+=
2/12
)1
)((
−−
= ∑n
RRiSD

2/12/2010
13
rTR
RTR ).( 10=
R10= curah hujan tahunan dengan PUH 10 tahunR = curah hujan tahunan rata‐rata dalam suatu array dataTr = PUH untuk curah hujan tahunan rata‐rata (2,33 tahun)
rR
Sistem hidrologi terkadang dipengaruhi oleh peristiwa‐peristiwa yang luar biasa, seperti hujan lebat, banjir, dan kekeringan. Besaran peristiwa ekstrim berbanding terbalik dengan peristiwa ekstrim berbanding terbalik dengan frekuensi kejadiannya, peristiwa yang sangat ekstrim kejadiannya sangat langka (Suripin. Sistem Drainase Perkotaan yang Berkelanjutan. 2004).
Tujuan analisis frekuensi data hidrologi berkaitan dengan besaran peristiwaperistiwa ekstrim yang berkaitan dengan frekuensi k d l l d bkejadiannya melalui penerapan distribusi kemungkinan. Data hidrologi yang dianalisis diasumsikan tidak bergantung (independent), terdistribusi secara acak, dan bersifat stokastik.
Frekuensi hujan adalah besaran kemungkinan suatu besaran hujan disamai atau dilampaui. Sebaliknya, periode ulang adalah waktu hipotetik dimana hujan dengan suatu besaran tertentu akan disamai atau dilampaui. Analisis frekuensi ini didasarkan pada sifat statistik data kejadian yang telah lalu untuk memperoleh probabilitas besaran hujan di masa yang akan datang dengan anggapan bahwa sifat statistik kejadian hujan di masa akan datang akan masih sama dengan sifat statistik kejadian hujan masa lalu.
1. MetodeGumbel2. Metode Log Pearson Type III3. Metode Distribusi Normal
d4. Metode Iwai

2/12/2010
14
MetodeMetodeGumbelGumbel MetodeMetodeGumbelGumbel
Metode Log Pearson Type IIIMetode Log Pearson Type IIIMetode ini telah mengembangkan serangkaian fungsi probabilitas yang dapat dipakai untuk hampir semua distribusi probabilitas empiris. Tiga parameter penting dalam Metode Log Pearson Ti III iTipe III, yaitu:
1. Harga rata‐rata ( R )2. Simpangan baku (S)3. Koefisien kemencengan (G)
Hal yang menarik adalah jika G = 0 maka distribusi kembali ke distribusi Log Normal.
Langkah‐langkah penggunaan distribusi Log Pearson Tipe III
Metode Log Pearson Type IIIMetode Log Pearson Type III

2/12/2010
15
Metode ini disebut juga distribusi Gauss.
Analisis Intensitas HujanAnalisis Intensitas Hujan
Analisis intensitas hujan digunakan untuk menentukan tinggi atau kedalaman air hujan per satu satuan waktu. Sifat umum hujan adalah makin singkat hujan berlangsung, maka makin besar pula intensitasnya dan semakin besar periode ulangnya, maka makin tinggi pula intensitas hujan yang terjadi
Analisis Intensitas HujanAnalisis Intensitas Hujan
Analisis tahap ini dimulai dari data curah hujan harian maksimum yang kemudian diubah ke dalam bentuk intensitas hujan.Pengolahan data dilakukan dengan metoda statistik yang umum digunakan dalam aplikasi hidrologi. Data yang digunakan b ik d l h d h j j k d k i l i sebaiknya adalah data hujan jangka pendek, misalnya 5 menit, 10
menit, 30 menit, 60 menit, dan jam‐jaman. Bila tidak diketahui data untuk durasi hujan maka diperlukan pendekatan empiris dengan berpedoman pada durasi enam puluh menit dan pada curah hujan harian maksimum yang terjadi setiap tahun. Cara lain yang lazim digunakan adalah mengambil pola intensitas hujan dari kota lain yang mempunyai kondisi yang hampir sama
Metode BellMetode Van Breen dan TalbotMetode Hasper dan Der Weduwen
Evaporasi = proses pertukaran molekul air di permukaan menjadi molekul uap air di atmosfer melalui kekuatan panasFaktor‐faktor yang mempengaruhi:‐ faktor‐faktor meteorologis‐ jenis permukaan tanahjenis permukaan tanahTranspirasi = proses penguapan pada tumbuh‐tumbuhan, lewat sel‐sel stomataFaktor‐faktor yang mempengaruhi:‐ faktor‐faktor meteorologis, terutama sinar matahari‐ jenis tumbuhan‐ jenis tanah

2/12/2010
16
Evapotranspirasi/Evaporasi Total = peristiwa evaporasi dan transpirasi yang terjadi bersama‐samaEvapotranspirasi potensial (potential evaporation, PET) = evaporasi yang terjadi, apabila tersedia cukup air (dari presipitasi atau irigasi) untuk memenuhi pertumbuhan presipitasi atau irigasi) untuk memenuhi pertumbuhan optimumEvapotranspirasi sesungguhnya (Actual evapotranspiration, AET) = evapotranspirasi yang terjadi sesungguhnya, dengan kondisi pemberian air seadanyaConsumptive use = air yang diperlukan tumbuh‐tumbuhan untuk pertumbuhan sel‐selnya
1. Perkiraan evaporasi berdasarkan pan evaporasi
Evaporasiperm. Air bebas = Cpan x Evaporasipan
Penguapan dari evaporasi pan biasanya lebih besar dari evaporasi sebenarnya, karena:luas permukaan sempit gel dan turbulensi udara kecil‐ luas permukaan sempit gel. dan turbulensi udara kecil‐ kemampuan menyimpan panas berbeda antara pan dan danau‐ terjadinya pertukaran panas antara pan dgn tanah, udara, air sekitar‐ pengaruh panas, kelembaban, angin akan berbeda bagi perm. kecil dgn perm. besar
atmometer, lysimeter, phytometer
∅ = 1.21 m = 4”
H = 25.4 cm = 10”
2. Perkiraan evaporasi dengan menggunakan rumus empiris‐ aerodynamic method/Dalton law
Ea = K. Uz (ew – ez)
E b b l tEa = evap perm bebas selama pengamatanK = konstanta empirisUz = fungsi antara evap thd kec angin pada ketinggian zew = tekanan uap jenuh di udara pada temperatur sama dengan airez = tekanan uap sesungguhnya di udara pd ketinggian z
Persamaan Rohwer
E = a (ew – ea) (1 + b V)E = 0.484 (1+0.6 V) (ew – ea)
E = evaporasi (mm/hari)ew = tekanan uap jenuh pada temperatur sama dengan temp air (millibar)ea = tekanan uap di udara sesungguhnya (millibar)V = kecepatan angin rata‐rata dalam sehari (m/detik)

2/12/2010
17
Persamaan Orstom
E = 0.358 (1 + 0.588 V) (ew – ea)
Persamaan Danau Hefner
E = 0.00177 V (ew – ea)E = inch/hariV = meter/jam
3. Pengukuran Evaporasi secara langsung
Water‐balance:EL = P + Isurf + Igw –Osurf –Ogw ‐ ΔS
EL = evaporasi muka air bebas per hariL p pP = presipitasi/hujan harianIsurf = surface inflow/aliran perm masukIgw = ground water inflow/air tanah masukOsurf = surface outflow/aliran perm keluarOgw = ground water outflow/air tanah keluarΔS = perubahan jumlah simpanan air selama pengamatan (1 hari)