1 The Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell.
Plasma Membrane
description
Transcript of Plasma Membrane

Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane
Movement in and out of a cellMovement in and out of a cell

Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane
A flexible boundary between the cell and A flexible boundary between the cell and it’s environmentit’s environment
JOB: allow steady supply of nutrients to JOB: allow steady supply of nutrients to come into the cell no matter what the come into the cell no matter what the external conditions areexternal conditions are Too much of any nutrient or other substance Too much of any nutrient or other substance
can be harmfulcan be harmful

Plasma Membrane (PM)Plasma Membrane (PM)
Process of maintaining balance in a cell’s Process of maintaining balance in a cell’s environment is environment is homeostasishomeostasis Selective permeability Selective permeability allows some allows some
molecules to pass through while keeping molecules to pass through while keeping other outother out
Ex: screen on a windowEx: screen on a window

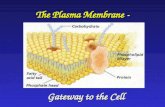
PM: StructurePM: StructureLipidsLipids are large are large biomolecules biomolecules composed of glycerol composed of glycerol and 3 fatty acidsand 3 fatty acids If a phosphate If a phosphate
replaces one of the replaces one of the fatty acids, a fatty acids, a phospholipidphospholipid is is formedformed
PM is made up of a PM is made up of a phospholipid bilayerphospholipid bilayer (2 layers of (2 layers of phospholipids back-to-phospholipids back-to-backback

PM: StructurePM: Structure
2 2 fatty acidfatty acid chains are chains are non-polarnon-polar and and form the form the tailtail of the phospholipid of the phospholipid
The The headhead contains the contains the phosphatephosphate group group and is and is polarpolar

ContinuedContinued
Water is a key component of lifeWater is a key component of life
Polar head allows PM to interact with Polar head allows PM to interact with watery environment (H2O is a polar watery environment (H2O is a polar molecule) (molecule) (Hydrophyllic) Hydrophyllic) water lovingwater loving
Non-polar tails avoid water (Non-polar tails avoid water (HydrophobicHydrophobic) ) water fearingwater fearing
Phospholipid molecules make a sandwich Phospholipid molecules make a sandwich with tails in, heads out.with tails in, heads out.

PM: Fluid Mosaic ModelPM: Fluid Mosaic ModelPM is not static (it PM is not static (it doesn’t stay still)doesn’t stay still)Phospholipids move Phospholipids move within the membrane within the membrane like water molecules like water molecules move with currents in a move with currents in a lakelakeProteins also move Proteins also move through phospholipids through phospholipids like boatslike boats Proteins create “mosaic” Proteins create “mosaic”
or pattern on membrane or pattern on membrane surfacesurface

PM: Other ComponentsPM: Other Components
CholesterolCholesterol: helps stabilize phospholipids : helps stabilize phospholipids by preventing tails from sticking togetherby preventing tails from sticking together
Transport proteins:Transport proteins: Span entire Span entire membranemembrane Regulate which molecules enter and leave Regulate which molecules enter and leave
cellcellProteins on OUTER surface help cells identify Proteins on OUTER surface help cells identify chemical signals and each otherchemical signals and each other
Proteins on INNER surface help attach PM to cells Proteins on INNER surface help attach PM to cells internal support structure internal support structure flexibility flexibility

PM: Other ComponentsPM: Other Components

Show me What You KnowShow me What You Know
The structure most responsible for The structure most responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis is the ___.maintaining cell homeostasis is the ___.
A.A. CytoplasmCytoplasm
B.B. MitochondrionMitochondrion
C.C. Cell WallCell Wall
D.D. Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane

Show me What You KnowShow me What You Know
The structure most responsible for The structure most responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis is the ___.maintaining cell homeostasis is the ___.
A.A. CytoplasmCytoplasm
B.B. MitochondrionMitochondrion
C.C. Cell WallCell Wall
D.D. Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane

Show Me What You KnowShow Me What You Know
Movement of particles from an area of Movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to one of lower higher concentration to one of lower concentration is ______________?concentration is ______________?

Show Me What You KnowShow Me What You Know
Movement of particles from an area of Movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to one of lower higher concentration to one of lower concentration is ______________?concentration is ______________?
DiffusionDiffusion

Show Me What You KnowShow Me What You Know
Which of the following structures is the most Which of the following structures is the most complex?complex?
A.A. CellCell
B.B. Organ SystemOrgan System
C.C. OrganOrgan
D.D. TissueTissue

Show Me What You KnowShow Me What You Know
Which of the following structures is the most Which of the following structures is the most complex?complex?
A.A. CellCell
B.B. Organ SystemOrgan System
C.C. OrganOrgan
D.D. TissueTissue

ActivityActivity
Write your summary of notesWrite your summary of notes
On the left hand side of your notebook, On the left hand side of your notebook, draw and label a phospholipid bilayer. draw and label a phospholipid bilayer. Use p. 177-178 of your text. Don’t forget Use p. 177-178 of your text. Don’t forget to add color.to add color.

Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane
Day TwoDay Two

Cell TransportCell Transport
2 types of cell transport:2 types of cell transport: Passive TransportPassive Transport: Movement of particles : Movement of particles
across a membrane requiring across a membrane requiring NONO energy energyHigh concentration High concentration Low concentration Low concentration
Active Transport:Active Transport:

Passive Transport: OsmosisPassive Transport: OsmosisOsmosis:Osmosis: diffusion of H2O across a diffusion of H2O across a selectively permeable membrane.selectively permeable membrane. Ex. If membrane that only allows water to Ex. If membrane that only allows water to
pass through, water will diffuse to side where pass through, water will diffuse to side where H2O concentration is lower and will continue H2O concentration is lower and will continue until equal concentration is reached on both until equal concentration is reached on both sidessides

Passive Transport: OsmosisPassive Transport: Osmosis
Isotonic SolutionIsotonic Solution: Concentration is the : Concentration is the samesame both both insideinside andand outsideoutside the cell the cell
Hypotonic Solution:Hypotonic Solution: concentration is concentration is lower lower outsideoutside than inside the cell than inside the cell
Hypertonic Solution: Hypertonic Solution: concentration is concentration is higherhigher outside outside than inside the cellthan inside the cell

Passive Transport: OsmosisPassive Transport: Osmosis

Passive Transport: DiffusionPassive Transport: Diffusion
Diffusion:Diffusion: net movement of particles from net movement of particles from higher concentration to lower.higher concentration to lower. Results from random movement of particles Results from random movement of particles
running into one anotherrunning into one another Very slow process because it relies on Very slow process because it relies on
random motionrandom motion

ContinuedContinued
3 key factors:3 key factors:Concentration: Increase in concentration will Concentration: Increase in concentration will increase the rate of diffusionincrease the rate of diffusion
Temperature: Increase in temperature will increase Temperature: Increase in temperature will increase rate of diffusionrate of diffusion
Pressure: Increase in pressure will increase rate of Pressure: Increase in pressure will increase rate of diffusiondiffusion
Dynamic EquilibriumDynamic Equilibrium: continuous : continuous movement with no overall concentration movement with no overall concentration changechange

Passive Transport: DiffusionPassive Transport: Diffusion

Active TransportActive Transport
Active Transport:Active Transport: Movement of materials Movement of materials through a membrane against a through a membrane against a concentration gradient (concentration gradient (requires energyrequires energy))

Active Transport: Carrier Transport Active Transport: Carrier Transport ProteinsProteins
Carrier Proteins:Carrier Proteins: Bind with particle of the Bind with particle of the
substance to be substance to be transportedtransported
Lock and Key!!Lock and Key!! With the right fit, chemical With the right fit, chemical
energy allows shape of energy allows shape of carrier protein to change carrier protein to change releasing particle on other releasing particle on other sideside
Much like the action of a Much like the action of a doordoor

Active Transport: Carrier Active Transport: Carrier ProteinsProteins

Active Transport: EndocytosisActive Transport: Endocytosis
EndocytosisEndocytosis occurs when the cell occurs when the cell surrounds and takes in large material from surrounds and takes in large material from it’s environmentit’s environment
Does not pass through membraneDoes not pass through membrane
Engulfed and enclosed by part of the PMEngulfed and enclosed by part of the PM
Membrane breaks away creating a vacuole with Membrane breaks away creating a vacuole with the material insidethe material inside
Phagocytosis: Phagocytosis: cell brings in a solidcell brings in a solid Pinocytosis:Pinocytosis: cell brings in liquid cell brings in liquid

Active Transport: ExocytosisActive Transport: Exocytosis
Exocytosis occurs when the cell expels or Exocytosis occurs when the cell expels or secretes large particles from the cellsecretes large particles from the cell Ex. wastes, hormonesEx. wastes, hormones

Show Me What You KnowShow Me What You Know
Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) __________ solution.__________ solution.
A.A. OsmoticOsmotic
B.B. HypertonicHypertonic
C.C. HypotonicHypotonic
D.D. IsotonicIsotonic

Show Me What You KnowShow Me What You Know
Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) Water moves into a cell placed in a(n) __________ solution.__________ solution.
A.A. OsmoticOsmotic
B.B. HypertonicHypertonic
C.C. HypotonicHypotonic
D.D. IsotonicIsotonic

Show Me What You KnowShow Me What You Know
Water moves out of a cell if the cell is placed Water moves out of a cell if the cell is placed in a(n) ___________ solution.in a(n) ___________ solution.
A.A. HypertonicHypertonic
B.B. IsotonicIsotonic
C.C. HyptonicHyptonic
D.D. passivepassive

Show Me What You KnowShow Me What You Know
Water moves out of a cell if the cell is placed Water moves out of a cell if the cell is placed in a(n) ___________ solution.in a(n) ___________ solution.
A.A. HypertonicHypertonic
B.B. IsotonicIsotonic
C.C. HyptonicHyptonic
D.D. passivepassive

Show Me What You KnowShow Me What You Know
A cell moves particles from a region of A cell moves particles from a region of lesser concentration to a region of lesser concentration to a region of greater concentration by ____________.greater concentration by ____________.
A.A. Facilitated diffusionFacilitated diffusion
B.B. Passive transportPassive transport
C.C. OsmosisOsmosis
D.D. Active TransportActive Transport

Show Me What You KnowShow Me What You Know
A cell moves particles from a region of A cell moves particles from a region of lesser concentration to a region of lesser concentration to a region of greater concentration by ____________.greater concentration by ____________.
A.A. Facilitated diffusionFacilitated diffusion
B.B. Passive transportPassive transport
C.C. OsmosisOsmosis
D.D. Active TransportActive Transport

ActivityActivity
Write a summary for your notesWrite a summary for your notes
Create a foldable to be glued into the Create a foldable to be glued into the activity page of your notebook. Use p. 195 activity page of your notebook. Use p. 195 of your text to create the foldable. Don’t of your text to create the foldable. Don’t forget to use at least 4 colorsforget to use at least 4 colors

![Plasma Membrane [7.2] Goals: Understand the concept of homeostasis in relation to the plasma membrane Demonstrate and understand how the plasma membrane.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5697c01d1a28abf838cd0a9a/plasma-membrane-72-goals-understand-the-concept-of-homeostasis-in-relation.jpg)