Plants Chapter 11 Section 2. Make this circle map (NEATLY) Seedless Nonvascular Plants.
-
Upload
samson-pitts -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Plants Chapter 11 Section 2. Make this circle map (NEATLY) Seedless Nonvascular Plants.
- Slide 1
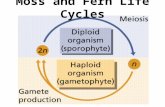
Plants Chapter 11 Section 2 Slide 2 Make this circle map (NEATLY) Seedless Nonvascular Plants Slide 3 Seedless Nonvascular Plants rhizoids- threadlike structures that anchor nonvascular plants to the ground MossesLiverwortsHornworts Slide 4 Mosses Grow on tree trunks, rocks, or ground Commonly in damp areas Multi-celled rhizoids Slide 5 Lab- Measuring Water Absorption by a Moss 1.Place a few teaspoons of Spagnum moss on a piece of cheesecloth. 2.Gather the corners of the cloth and twist, then tie them securely to form a ball. 3.Weigh the ball. 4.Put 200 mL of water in a container and add the ball. 5.Wait 15 minutes. Slide 6 Liverwort Flattened, leaflike bodies One-celled rhizoids Slide 7 Hornworts Flattened body (like liverwort) Spore-producing structure (look like horns) Slide 8 Summarizing Seedless Nonvascular Plants Include mosses, liverworts, hornworts Only a few cells thick (each cell absorbs water directly from its environment) No more than a few centimeters tall Produce spores rather than seeds Are considered pioneer species- 1 st to grow in new area Slide 9 Finished Bubble Map Have ________ threadlike structures that anchor them Are considered ________ species Examples: Mosses __________ Hornworts Produce _______ rather than seeds Only a few centimeters ________ Seedless Nonvascular Plants Only a few Cells ________ Slide 10 Finish Lab 1.Remove the ball and drain the excess water into the container. 2.Weigh the ball and measure the amount of water left in the container. (Remember you started with 200 mL.) 3.Record your results. 4.Clean up your lab area. 5.Wash your hand. Slide 11 Seedless Vascular Plants Also produce spores instead of seeds Have tubelike structures (bigger and thicker than nonvascular) Can live further away from water FernsHorsetails Club Mosses Slide 12 Make this tree map (NEATLY) Seedless Vascular Plants CharacteristicsTypes Slide 13 Ferns Largest group Fern leaves are called fronds Slide 14 Club Mosses A.K.A. ground pines spike mosses Needle like leaves Spores look like tiny pine cones Slide 15 Horsetails Stem is jointed with hollow center Pops apart in sections Conelike at tips Used for: polishing objects sharpening tools scouring utensils polishing objects sharpening tools scouring utensils Slide 16 Importance of Seedless Plants Nonvascular help build new soil Houseplants and landscaping Peat-forms from remains of sphagnum moss Mined from bogs Used as a low-cost fuel Slide 17 What is the largest group of seedless vascular plants? Ferns Slide 18 Seedless plants produce these instead of seeds Spores Slide 19 These two vascular seedless plants produce spores in conelike structure Club Mosses Horsetails Slide 20 What are fronds? Leaves on a fern Slide 21 ________ is to moss as anchor is to ship rhizoids