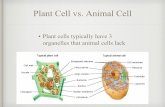
Plant Cell Wall
-
Upload
teoyuxun07 -
Category
Documents
-
view
229 -
download
0
Transcript of Plant Cell Wall
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
1/14
Plant Cell WallPlant Cell Wall
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
2/14
Introduction of Cell Wall:Introduction of Cell Wall:
thickness ranging from 0.1 micrometre tothickness ranging from 0.1 micrometre toseveral micrometres.several micrometres.
a nona non--living component located outsideliving component located outside
the cell membrane and is generally notthe cell membrane and is generally notconsider to be part of protoplasm, thoughconsider to be part of protoplasm, though
it is a secretory product of the cell.it is a secretory product of the cell.
determines the cell shape and providesdetermines the cell shape and providesprotection and support to the plant cell.protection and support to the plant cell.
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
3/14
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
4/14
Structures of the cell wallStructures of the cell wall
The main structural components of cell walls areT
he main structural components of cell walls arebundles of cellulose molecules known asbundles of cellulose molecules known as
microfibrilsmicrofibrils..
EachEach microfibrilmicrofibril bundle consists ofbundle consists of aproximatelyaproximately
2000 extremely long cellulose molecules.2000 extremely long cellulose molecules.
Each individual cellulose molecule is composed ofEach individual cellulose molecule is composed of
about 3000 glucose residues condensed together.about 3000 glucose residues condensed together.
The celluloseThe cellulose microfibrilsmicrofibrils are cemented and heldare cemented and heldtogether by a matrix oftogether by a matrix ofpectinpectin andand hemicellulosehemicellulose..
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
5/14
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
6/14
The spaces between the fibrils are not entirelyThe spaces between the fibrils are not entirely
filled with matrix which making the cell wallfilled with matrix which making the cell wall
permeable.permeable.
The wall does not determine which materialsThe wall does not determine which materials
can enter the cell and which cannot. Thecan enter the cell and which cannot. The
function is reserved for the plasma membranefunction is reserved for the plasma membrane
located below the cell wall.located below the cell wall.
The mature plant cell wall has made up ofThe mature plant cell wall has made up of
many layers. The first portion of the cell wall ismany layers. The first portion of the cell wall isthe primary wall(formed as long as the cellthe primary wall(formed as long as the cell
continues to grow).continues to grow).
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
7/14
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
8/14
The fibrils that form the primary wall run in allThe fibrils that form the primary wall run in alldirections and form a rather loose network whichdirections and form a rather loose network which
makes the primary wall elastic and allowsmakes the primary wall elastic and allowsstretching during cell grow.stretching during cell grow.
The middle lamella that binds the walls of twoThe middle lamella that binds the walls of twocells together is a sticky, jellylike layer of pectin,cells together is a sticky, jellylike layer of pectin,
generally present in the form of calcium andgenerally present in the form of calcium andmagnesium pectates.magnesium pectates.
When a fruit ripens, pectin deserves and the cellWhen a fruit ripens, pectin deserves and the cellbecome less tightly bound to one another. It isbecome less tightly bound to one another. It is
this loosely arranged cells that make a ripeningthis loosely arranged cells that make a ripeningfruit become softer.fruit become softer.
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
9/14
The cell of soft tissues of plants have onlyThe cell of soft tissues of plants have onlyprimary walls and intercellular middle lamellae.primary walls and intercellular middle lamellae.
After growth stops, cells eventually form harder,After growth stops, cells eventually form harder,more woody portions of the plant by depositingmore woody portions of the plant by depositingfurther layers of cellulose fibrils on the primaryfurther layers of cellulose fibrils on the primary
cell wall forming the secondary wall.cell wall forming the secondary wall. Secondary wall is deposited by the protoplasm,Secondary wall is deposited by the protoplasm,
located outside the plasma membrane but on thelocated outside the plasma membrane but on theoutside of the primary wall formed earlier.outside of the primary wall formed earlier.E
ssentially, the secondary cell wall is insertedE
ssentially, the secondary cell wall is insertedbetween the plasma membrane and primarybetween the plasma membrane and primarywall.wall.
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
10/14
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
11/14
The secondary cell wall is much thicker thanThe secondary cell wall is much thicker thanthe primary cell wall and is composed bythe primary cell wall and is composed bylamellae.lamellae.
The cellulose microfibrils in each lamella lieThe cellulose microfibrils in each lamella lieparallel to each other, tightly packed and areparallel to each other, tightly packed and are
generally oriented at angles of 60generally oriented at angles of 60--90 degrees90 degreesto the fibrils of the adjacent of lamellae. Thisto the fibrils of the adjacent of lamellae. Thisarrangement gives added strength to the cellarrangement gives added strength to the cellwall.wall.
Secondary cell walls contain lignin, whichSecondary cell walls contain lignin, whichmake them even stiffer and impermeable tomake them even stiffer and impermeable towater.water.
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
12/14
When the secondary wall is completed, manyWhen the secondary wall is completed, manycells die leaving the hard tube formed by thecells die leaving the hard tube formed by the
walls to function as a mechanical and internalwalls to function as a mechanical and internalsupports.supports.
Plant cell walls do not form completely andPlant cell walls do not form completely anduninterrupted boundaries around the cells. Thereuninterrupted boundaries around the cells. Thereare often tiny holes in the wall through whichare often tiny holes in the wall through whichcytoplasmiccytoplasmic connections between adjacent cellsconnections between adjacent cellsmay run. These connections are calledmay run. These connections are calledplasmodesmataplasmodesmata..
PlasmodesmataPlasmodesmata is a narrow channels asis a narrow channels as
intercellularintercellular cytoplasmiccytoplasmic bridge to facilitatebridge to facilitatecommunication and transport of materialscommunication and transport of materialsbetween plant cells.between plant cells.
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
13/14
The wall is not thickened further, and
depressions or thin areas known as pits are
formed in the walls. Pits normally pair up
between adjacent cells
Plasmodesmata permit direct cell-cell
communication through the cell wall.
-
8/9/2019 Plant Cell Wall
14/14