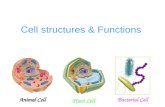
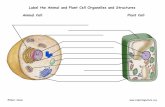
Plant vs. Animal Cell. Plant Cell Cell wall Large central vacuole Plastids Animal Cells Centrioles...
-
Upload
todd-booth -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
4
Transcript of Plant vs. Animal Cell. Plant Cell Cell wall Large central vacuole Plastids Animal Cells Centrioles...

Plant vs. Animal Cell

Plant Cell Cell wall
Large central vacuolePlastids
Animal CellsCentrioles
Both: Nucleus, Mitochondria, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi
apparatus, vesicles, cytoskeleton


Cell Wall• Structure: rigid layer of carbohydrates (cellulose) outside cell
membrane
• Function: support and protection

Central Vacuole• Structure: Large, fluid-filled organelle
• Function: • Stores water, enzymes, metabolic wastes, and other materials• Allows plant to stand upright
• Can make up 90% of the plant cell’s volume

Plastids• Structure• Double membrane• Contain DNA
• Types of plastids:1. Chloroplast2. Chromoplast3. Amyloplasts
What does this sound like?

Chloroplast• Structure:• Contains thylakoids (flattened, membranous sacs)• Thylakoids contain chlorophyll (molecule that absorbs light
energy for the cell)
• Function: Use light energy to make carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water = photosynthesis

Evolution of Plastids and Mitochondria = Endosymbiosis