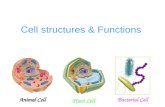
Cell structures & Functions Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell.
Plant cell
Transcript of Plant cell

- Kavaj Burdak
Animal Cell


Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell from outside forces. It consists of the lipid bilayer with embedded proteins.

Fungi, bacteria and plants also have the cell wall which provides a mechanical support for the cell and precludes the passage of larger molecules. The cell membrane also plays a role in anchoring the cytoskeleton to provide shape to the cell, and in attaching to the extracellular matrix and other cells to help group cells together to form tissues.


Cell wall & Plasmodesmata - In addition to cell membranes, plants have cell walls. Cell walls provide protection and support for plants. Unlike cell membranes materials cannot get through cell walls. This would be a problem for plant cells if not for special openings called plasmodesmata. These openings are used to communicate and transport materials between plant cells because the cell membranes are able touch and therefore exchange needed materials.
Cell Wall

Ribosomes Organelles that help in the creation of
proteins. Some ribosome's are found in the cytoplasm, but most are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. While attached to the ER, ribosome's make proteins that the cell needs and also ones to be exported from the cell for work elsewhere in the body.

NucleusIn cell biology, the nucleus is a
membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes.

The main function of the cell nucleus is to control gene expression and mediate the replication of DNA during the cell cycle. The nucleus provides a site for genetic transcription that is segregated from the location of translation in the cytoplasm, allowing levels of gene regulation that are not available to prokaryotes.


VacuoleA vacuole is a membrane-
bound organelle which is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed.

Some Vacuole functions are as follows:
1) Removing unwanted structural debris
2) Isolating materials that might be harmful to the cell
3) Containment of waste products
4) Maintaining internal hydrostatic pressure or turgor within the cell
5) Maintaining an acidic internal pH
6) Containing small molecules
7)Exporting unwanted substances from the cell.
8)Enabling the cell to change shape.

The cell organelle in which photosynthesis takes place. In this organelle the light energy of the sun is converted into chemical energy. Chloroplasts are found only in plant cells not animal cells. The chemical energy that is produced by chloroplasts is finally used to make carbohydrates like starch, that get stored in the plant. Chloroplasts contain tiny pigments called chlorophylls . Chlorophylls are responsible for trapping the light energy from the sun.
Chloroplast


Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures (organelles), except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm. It is within the cytoplasm that most cellular activities occur, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and processes such as cell division.

The main function of the cytoplasm is to hold the cell organelles of the cell. Cell organelles are basically components of the cell which control all the activities of the cell.For example, mitochondria are cell organelles which control almost all of the cell's metabolic activities.

Endoplasmic reticulum
•Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) - when ribosomes are attached it is called rough ER and smooth ER when there are no ribosomes attached. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is where most protein are made in the cell. The function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is to help to get rid of harmful substances in the cell.

•The general structure of an endoplasmic reticulum is a membranous network of cisternae (sac-like structures) held together by the cytoskeleton. The endoplasmic reticulum serves many general functions, including the facilitation of protein folding and the transport of synthesized proteins in sacs called cisternae.


Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures (organelles), except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm. It is within the cytoplasm that most cellular activities occur, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and processes such as cell division.

The main function of the cytoplasm is to hold the cell organelles of the cell. Cell organelles are basically components of the cell which control all the activities of the cell.For example, mitochondria are cell organelles which control almost all of the cell's metabolic activities.

Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was identified in 1898 by the Italian physician Camillo Golgi and named after him. Part of the cellular endomembrane system, the Golgi apparatus packages proteins inside the cell before they are sent to their destination; it is particularly important in the processing of proteins for secretion. It synthesise a large number of different macromolecules.


Mitochondria In cell biology, a mitochondrion is a membrane-
enclosed organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. These organelles range from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometre in diameter. The most prominent roles of mitochondria are to produce the energy currency of the cell ATP , through respiration, and to regulate cellular metabolism. The central set of reactions involved in ATP production are collectively known as the citric acid cycle, or the Krebs Cycle. However, the mitochondrion has many other functions in addition to the production of ATP.


DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN ANIMAL AND PLANT CELL -

Animal Cell Plant Cell
Nucleus: Present Present
Cilia: Present It is very rare
Shape: Round (irregular shape) Rectangular(fixed shape)
Chloroplast: Animal cells don't have chloroplasts
Plant cells have chloroplasts because they make their own food
Cytoplasm: Present Present
Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth and Rough):
Present Present
Ribosomes: Present Present
Mitochondria: Present Present

Animal Cell Plant Cell
Golgi Apparatus: Present PresentCell wall: Absent Present
Plasma Membrane: only cell membrane cell wall and a cell membrane
Microtubules/ Microfilaments:
Present Present
Flagella: May be found in some cells
May be found in some cells
Lysosomes: Lysosomes occur in cytoplasm.
Vacuole: One or more small vacuoles (much smaller than plant cells).
One, large central vacuole taking up 90% of cell volume.
Centrioles: Present in all animal cells
Only present in lower plant forms.
Plastids: Absent Present

THANK YOU