PAROTID REGION
description
Transcript of PAROTID REGION

PAROTID REGION
BY
STEVEN J. ZEHREN, PH.D.

GENERAL REMARKS

Cervical branch of VII
Facial vein
GENERAL REMARKS AND RELATIONSHIPS
Parotid gland
Sublingual gland
Mylohyoid m. (cut)Digastric m. (anterior belly)
Digastric m.(posterior belly)
Submandibular gland
Sublingual fold

PAROTID GLAND: Totally serous
SUBMANDIBULAR GLAND:Mostly serous; partly mucous
SUBLINGUAL GLAND:Almost completely mucous
SALIVARY GLANDS (HISTOLOGY)

Palatine glands
Molar minorsalivary glands

RELATIONSHIPS OF THE PAROTID GLAND (PAROTID BED)

PAROTID BED (RELATIONSHIPS OF PAROTID GLAND)Ext. auditory meatus
Ramus of mandible
Stylohyoid m.
Mastoid processStyloid process
Sternocleidomastoid m.Post. belly of digastric m.
Carotid sheath (& contents)

PAROTID BED (HORIZONTAL SECTION)
Masseter m.
Ramus of mandible
Medial pterygoid m.
Facial n. (VII)Retromandibular v.
Ext. carotid a.Parotid gland
Stylohyoid m.Sternocleidomastoid m.
Post. belly of digastric m.
Carotid sheath & contents

LATERAL PHARYNGEAL SPACE
Parotid gland
Medial pterygoid
Superior constrictor of pharynx
Oropharynx
Lateral pharyngeal space

STRUCTURES WITHINTHE PAROTID GLAND

Facial n.Retromandibular v.External carotid a.

Temporal branchesZygomatic branches
Buccal branches
Marginal mandibular branchCervical branch
Main trunk of VII
TO ZANZIBAR BY MOTOR CAR
FACIAL NERVE (VII) WITHIN PAROTID GLAND

Medial pterygoid m.
Ramus of mandible
Masseter m.
Parotid gland
Main trunk of facial n.
Mastoid process
Temporal br.
Zygomatic brs.
Marginal mandibular br.
Cervical br.
Buccal brs.
Main trunk of facial n.
Temporofacial division
Cervicofacial division

Retromandibular v.
Superficial temporal v.Maxillary v.
Facial v.
Common facial v.(to IJV)
Posterior auricular v.
External jugular v.

External carotid a.
Superficial temporal a.
Maxillary a.

PAROTID FASCIA

Parotid fascia
Investing layer ofdeep cervical fascia
PAROTID FASCIA

Stylomandibular lig.
Stylomandibular lig.
Submandibular fossa

PAROTID DUCT(STENSON’S DUCT)

RELATIONSHIPS OF PAROTID DUCT
Parotid gland
Transverse facial a.Accessory parotid gland
Parotid ductBuccinator m.
Masseter m.
Zygomatic arch

Parotid papilla(opposite maxillary 2nd molar)
TERMINATION OF PAROTID DUCT

NERVE SUPPLY TO THE PAROTID GLAND

AUTONOMIC INNERVATION OF PAROTID GLAND
Medulla
Inf. salivatory nucleusIX (Glossopharyngeal n.)
Tympanic n.
Tympanic plexus
Lesser petrosal n.V3Otic ganglion
Auriculotemporal n.
Parotid gland
Presynaptic parasympatheticPostsynaptic parasympathetic

AUTONOMIC INNERVATION OF PAROTID GLAND (DISSECTION, MEDIAL VIEW)
Tympanic cavity
V3 (Mandibular n.)
Otic ganglion
Lesser petrosal n.
Auriculotemporal n.

SENSORY INNERVATION TO THE PAROTID GLAND
Auriculotemporal n. (V3)

FREY’S SYNDROME(GUSTATORY SWEATING)

FREY’S SYNDROME
Auriculotemporal n. (V3)
Great auricular n.(C2,3)

TREATMENT & PREVENTION OF FREY’S SYNDROME
MEDICAL
1. Topical anticholinergic creams/lotions.2. Intracutaneous injection of Botulinum toxin A.
SURGICAL
1. Transmeatal tympanic neurectomy.2. Procedures which involve the interposition of a tissue barier (eg., fascia lata or fat grafts).3. Sternocleidomastoid muscle flap.

Promontory of middle ear cavity withtympanic nerve (branch of IX) and plexusunder mucosa
Mastoid process
TYMPANIC NEURECTOMY

STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID MUSCLE FLAP ROTATED ONTO THE DEEP LOBE OF THE PAROTID GLAND

BLOOD SUPPLY & LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE OF THE PAROTID GLAND

External carotid a.
Superficial temporal a.
Maxillary a.

Retromandibular v.
Superficial temporal v. Maxillary v.
Facial v.
Common facial v.(to IJV)
Posterior auricular v.
External jugular v.

Parotid nodes
Deep cervical nodes


POP TEST

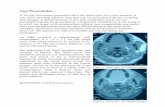
IDENTIFY THESE STRUCTURES
A
BC
D
E

A. RAMUS OF MANDIBLEB. MEDIAL PTERYGOID M.C. POSTERIOR BELLY OF DIGASTRIC M.D. VAGUS N. E. EXTERNAL CAROTID A.
ANSWERS

Extra Slides

POSITIVE MINOR’S TEST SHOWING IODINE REACTION WITH STARCH FOLLOWING GUSTATORY SWEATING (FREY’S SYNDROME)



PAROTID BED & STRUCTURES PIERCING GLAND

Secretion of the parotid gland would be affected by a lesion in the
Grea
ter petr
osal n
erve.
Auriculot
empo
ral nerv
e.
Facial
nerve.
Pteryg
opalatin
e gan
g...
None of th
e abo
ve.
20%
40%
0%
40%
0%
1. Greater petrosal nerve.2. Auriculotemporal nerve.3. Facial nerve.4. Pterygopalatine ganglion.5. None of the above.