P ROTISTS Eukaryotic Evolution Structure Metabolism Reproduction.
-
Upload
edwina-boone -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
Transcript of P ROTISTS Eukaryotic Evolution Structure Metabolism Reproduction.

PROTISTSEukaryotic Evolution
Structure
Metabolism
Reproduction

EUKARYOTIC EVOLUTION
evidence suggests that eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells mitochondria and chloroplasts have two membranes inner membrane is similar in composition to
prokaryotic cells outer membrane is similar in composition to
eukaryotic cells mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own genetic
information genetic information is in the form of a chromosomes
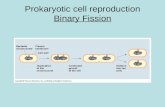
similar to prokaryotic chromosomes mitochondria and chloroplasts reproduce within the
cell using binary fission

EUKARYOTIC EVOLUTION evidence suggests that eukaryotic cells evolved when
ancestral eukaryotic cells (with a membrane bound nucleus) engulfed prokaryotic cells and established an endosymbiotic relationship with them endosymbiosis – relationship in which a singled-celled organisms
lives within another organism

EUKARYOTIC EVOLUTION
benefits of eukaryotic cells increased surface area where reactions can take
place increase efficiency in exchanging material with
environment allows cell to grow to a larger size

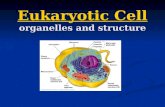
PROTISTS – STRUCTURE made up of eukaryotic cells dramatic range in size from unicellular to
multicellular include all eukaryotic organisms that do not fit
into the fungi, plant and animal kingdoms

PROTISTS – METABOLISM
autotrophic produce their own food using sunlight major producer in aquatic ecosystems
Euglena, kelp
heterotrophic main food source in many aquatic ecosystems
Paramecium, Amoeba
parasitic live in or on a host organism
Plasmodium (causes malaria), Giardia lamblia (causes Beaver fever)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W6rnhiMxtKU&feature=related
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a4aZE5FQ284
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C3KLhRdMGaA&feature=related
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o-IQiQXH9Ew&feature=related

PROTISTS – REPRODUCTION TERMS:sex cell
cell used in sexual reproduction, contains half the amount of genetic information needed by an organism (a.k.a. haploid)
body cell cell used in the body, contains a full set of genetic information needed by the organism (a.k.a.
diploid)zygote
cell formed by two sex cells, contains a full set of genetic information

PROTISTS – REPRODUCTION unicellular protists
asexual reproduction – binary fission offspring carry identical genetic information to one parent
sexual reproduction – conjugation offspring contain genetic information that is a combination of genetic
information from two parents
multicellular protists asexual/sexual reproduction – alternation of
generations cycle between asexual and sexual reproduction alternations between multicellular haploid and multicellular
diploid forms multicellular haploid form – gametophyte
contains half the amount of genetic information multicellular diploid form – sporophyte
contains a full set of genetic information

PROTISTS - REPRODUCTION
1. Mature sporophyte produces spores (haploid).
2. Some spores develop into a female gametophyte.
3. Other spores develop into a male gametophyte.
4. Female gametophyte produces and matures egg cell.
5. Male gametophyte produces sperm cells.
6. Sperm cells fertilize egg cells to produce a zygote.
7. Zygote develops into a mature sporophyte.

PROTISTS – EXAMPLES Type Characteristics Picture
euglenoids• Euglena
• photosynthetic autotrophs• unicellular• two flagella for moving
ciliates• Parameciu
m• Didinium
• heterotrophs• unicellular• many cilia
apicomplexa• Plasmodiu
m
• heterotrophs• unicellular• parasitic to animals

PROTISTS - PHYLAType Characteristics Picture
slime moulds • heterotrophs• life cycles include both unicellular and multicellular stages• flagella for moving
green, red and brown algae
• seaweed
• kelps
• photosynthetic autotrophs• multicellular• no cilia or flagella• cell walls made of cellulose