Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
-
Upload
angie-kong-su-mei -
Category
Documents
-
view
229 -
download
1
Transcript of Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
1/46
CLASSES OF FOODS
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
2/46
1. Food can be classified into seven main classes.
a. Carbohydrate
b. Protienc. Fat
d. Vitamin
e. Mineral salts
f. Fibre
g. Water
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
3/46
a. Contain carbon,
hydrogen, and
oxygen.
b.Supply most of
the energy our
body needs.
c. Examples:sugar, starch,
cellulose,
glycogen.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
4/46
a.Contain carbon,hydrogen, oxygen,
and nitrogen.
b. Needed for growthand repair of body
tissues.
c. Examples: fish,
meat, egg
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
5/46
a.Contain
carbon,hydrogen, and
oxygen.
b.Help to keepus warm and
protect internal
organs.
c.Examples:
animal fats,
vegetable oils
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
6/46
a. Organic compounds
needed in small
amounts by our
body.
b. Needed for health
and growth.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
7/46
Vitamin Source Function Deficiency
disease
A Carrot, liver,fish liver oil,
and green
vegetables
For night vision Healthy skin
Night blindness Skin infections
B Eggs, milk,
meat, yeast,and cereals
Releases energy
fromcarbohydrates
Healthy nervous
system
Healthy skin
Formation of redblood cells
Beriberi
Anaemia
C Fresh fruits and
vegetables
Healing of
wounds
Resistance to
diseases
Scurvy (bleeding
gums)
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
8/46
Vitamin Source Function Deficiency
disease
D Made by our
body in
sunlight, also
found in milk,
eggs, fish liver
oil
Strong bones
and teeth
Rickets (soft
bones and dental
decay)
E Vegetable oil,
whole grains,
nuts,
wheatgerm
May be needed
for reproduction
Helps to fight
against diseases
Sterility
K Made in thehuman
intestines, also
found in egg
yolk, green
vegetables
Clotting of blood Prolongedbleeding
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
9/46
a.Inorganic
compounds
needed by ourbody,
b.Needed for
healthy growth
and development.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
10/46
Mineral Source Function Deficiency
disease
Calcium Cheese,
milk, eggs,
green
vegetables
Strong bones and
teeth
Blood clotting
Muscle and nerve
activities
Rickets
Osteoporosis Prolonged
bleeding
Muscular cramps
Sodium Table salt,cheese,
meat
Maintains bodyfluid
Proper
functioning of
nerves
Muscular cramps
Iron Meat, eggs,green
vegetables
Needed to formhaemoglobin in red
blood cells
Anaemia
Iodine Seafood,
iodised salt
Needed to make
harmones of the
thyroid gland
Goitre (swelling of
the thyroid gland in
the neck)
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
11/46
Mineral Source Function Deficiency disease
Phosphorus Eggs, meat,
milk, cheese,
vegetables
Strong
bones and
teeth Muscle
contraction
Stores
energy
Rickets
Weakness
Potassium Meat, nuts,
bananas
Maintains
body fluid
Proper
functioning of
nerves
Regulation
of heartbeat
Weak muscles
Paralysis
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
12/46
a.Made up of cellulose
b.Prevent constipation
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
13/46
a. Solvent for many
substances in the
body
b.Regulate body
temperature
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
14/46
Date :
Day :
Tittle : Food test
Aim : To test for starch, glucose, protien and fatMaterials :
Apparatus :
A. Iodine test for starch1. 2 cm3 of starch solution is poured into a test tube.
2. 2 drops of iodine solution are added . The colour
changes is observed.
B. Benedicts test for glucose
1. 2cm3 of glucose is poured into a test tube.
2. 2cm3 of Benedicts solution is added.
3. The mixture in a water bath as shown in figure 2.2 is
heated. Any changes in mixture is observed.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
15/46
C.Millons test for protien
1. 2 cm3 of albumen solution is poured into a test tube
2. 2 drops ofMillons reagent are added to the
albumen solution.
3. The mixture is heated in a water bath. Any changes
in the mixture is observed.
D. Emulsion test for fat
1. 5 drops of ethanol are added into a test tube.
2. 2 drops of cooking oil is added into the same test tube.
the mixture is shaked in the test tube.3. The distilled water is added into the same test tube
until it half full and shake.
4. The mixture is allowed to stand for about 2 minutes.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
16/46
Observation:
Test Observation Inference
Iodine test for
starch
The solution
becomes blue-
dark
Food contain
starch
Benedicts test
for glucose The red-orangeprecipitated is
formed
Food containglucose
Millons test for
protien
The redorange
precipitated is
formed
Food contain
protien
Emulsion test
for fat
The emulsion layer
occurs on the
solution
Food contain fat
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
17/46
Discussion:
1. Water cannot mix with cooking oil
Conclusion :
1. Iodine solution turns the starch solution dark-blue2. Glucose solution forms a red-orange precipitate when heated
with Benedicts solution
3. Protien solution forms a red-orange when heated with
millons reagent
4. The mixture of fat, ethanol and water becomes cloudy becausean emulsion has been formed
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
18/46
1. A balanced diet contains the right amount of the
seven classes of food to meet the dailyrequirements of the body.
2. A balanced diet is necessary for:a. supplying the required energy
b. balanced body growthc. maintaining the health of the body
d. preventing deficiency diseases such as scurvyand rickets
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
19/46
FACTOR THE GROUP
REQUIRING MORE
ENERGY
REASON
A. Sex Men requiringmore energy of
the same age
and body size
Men are moreactive
B. Age Babies, children
and teenagers
require more
energy
This group is
more active and
the life process
are faster
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
20/46
FACTOR THE GROUP
REQUIRING MORE
ENERGY
REASON
c. Body size Big sized
individualsrequire more
energy size
compared to
small sizedindividuals.
Big sized
individualsrequire more
energy for their
life process.
d. Physical
activity
An individual
who does heavy
work uses moreenergy
compared to
another who
does light work
Heavy work
require more
energy toperform.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
21/46
FACTOR THE GROUP
REQUIRING MORE
ENERGY
REASON
e. Weather Individuals living
in places with
cold weather
require moreenergy
compared to
individuals living
in places withwarm weather
More energy is
required to
maintain the
bodytemperature in a
cold place.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
22/46
1. The calorific value of food is the total energy
produced when one gram of food is completely
burnt.
2. The quantity of energy in a food is measured in
calorie (cal) or joule (j)
3. 1 calorie (cal) = 4.2 joule (j)
1 kilocalorie (kcal) = 4.2 kilojoules (kJ)
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
23/46
Digestion
1. Digestion is the process of breaking down
complex food to simple molecules for absorption
the blood circulatory system.
2. Digestion take place in two stages:
a. physical digestion big pieces of food are
broken down into smaller pieces by teeth
b. chemical digestion enzymes break up
complex food molecules into smaller molecules
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
24/46
3. Enzymes are proteins that speed up the process
of digestion. Enzymes break up complex food molecules
to smaller and simpler molecules.
4. Characteristic of enzymes
a. enzymes are small quantities only
b. enzymes are not destroyed at the end of digestion
c. specific enzymes act only in specific acidic or alkaline
conditions
d. specific enzymes act only on specific foods
e. enzymes function best at normal body temperature (370 C)
Enzymes are destroyed at high temperature.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
25/46
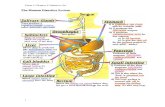
1. The digestive system consists of all the organ in
the body that help in the digestion of food.
2. The alimentary canal is made up of the mouth,
oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, big
intestine and anus (starts from the mouth and
ends at the anus).
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
26/46
3. Summary of the digestive system
mouth oesophagus stomach small
intestine big intestine anus
4. Food is pushed along the alimentary canal by the
muscular walls that contract and expand alternately
through theprocess of peristalsis.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
27/46
Duodenum
Oesophagus
Mouth
Stomach
Lower part of
small intestine
Appendix
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
28/46
1. Food is chewed and broken up into small pieces bythe teeth.
2. Small pieces of food have a wide surface area for
the saliva to act upon.3. The salivary gland secretes saliva that is alkalineand contains salivary amylase enzymes.
4. Salivary amylase digests starch into maltose(sugar)
amylase
starch maltose
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
29/46
1. Food is pushed through the oesophagus into the
stomach by the alternating r contraction and
relaxation of the oesophagus.
2. This process of alternating muscular contraction
and relaxation is known asperistalsis.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
30/46
1. Food is mixed with gastric juice in the stomach.
2. Gastric juice is secreted from the cells of the stomachwall. Gastric juice contains:
a. hydrochloric acidb. enzymes (rennin and pepsin)
3. The function of hydrochloric acid include
a. providing an acidic medium for enzymic action.
b. killing bacteria found in foodc. neutralising the alkaline property of saliva
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
31/46
Protien pepsin peptones/ polypeptides
4. Pepsin digest protien to peptones / polypeptides
5. Rennin coagulates milk in the stomach to help in the enzymic
enzymes.
rennin
Liquid milk protiens solid milk protiens
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
32/46
1. The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine.
2. The duodenum received bile and pancreatic juice.
3. The function of bile are:
a. emulsification of fat
b. preparation of an alkaline medium for enzymic action
4. Pancreatic juice contains three types of enzymes:
a. maltaseb. protease
c. lipase
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
33/46
5. The maltase digests maltose into glucose
maltase
maltose glucose
6. The protease digests peptones into amino acids
proteasepeptones amino acids
7. The lipase digests fat into fatty acid and glycerol
lipase
fat fatty acids + glycerol
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
34/46
8. Digestion is completed in small intestine.
9. The digest food is then ready to be absorbed through
the thin walls of the small intestine into the bloodstream.
10. Food digestion is completed in the small intestine.
11. The end products of digestion are
a. Carbohydrate - glucose
b. Protien - amino acids
c. Fats - fatty acids and glycerol .
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
35/46
E. BIG INTESTINE
1. Water is reabsorbed in the big intestine
2. Undigested food is expelled from the body
through the anus asfaeces.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
36/46
1. The inner surface of the small intestine has many
villi.
2. The villi increase the surface area for theabsorption of digested food.
3. Absorption is the movement of digested food intothe bloodstream
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
37/46
Villus
Blood capillary
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
38/46
Reabsorption of Water and Defecation
Residue from thesmall intestine
Solid waste called faeces
Stored in the last part of
the large intestine
Defecation through the anus
Reabsorption of water
+ minerals + vitamins
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
39/46
Difficulty in defecation is called
constipation.
Prolonged and serious
constipation can lead to ..
Hemorrhoids (piles)
Cancer of the large intestine
Defecation is removal of faeces
from the body through the anus
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
40/46
Why causes constipation?
Not eating enough roughage Not drinking enough water
Cause
Constipation
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
41/46
1. Therefore, constipation can be cured
by taking laxatives
eating high fibre foods such as wholemeal cereals and
grains, fruits and vegetables taking more fluid
Remember, prevention is always better than curing
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
42/46
Unhealthy eating habits is the main cause of many diseases
Too much sugar diabetes
Too much salt high blood pressure
Too much fat obesity, high blood cholesterol level, cancers
Too much food obesity
Too little food anorexia nervosa, bulimia
Too little roughage constipation, haemorroids
HEALTY EATING HABITS.
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
43/46
So, cultivate healthy eating habits to stay healthy
Eat a variety food according to the recommended amount
shown in a food guide pyramid.
Eat least
Eat most
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
44/46
Eat in moderation. Balance food intake with exercise
Choose nutritious food
Nutritious food
Fresh fruits
Fresh vegetables
Wholemeal
cereal, grains or
bread
Unpolished rice
Less nutritious food
Junk food
Highly processed
food
Fast foods
Fizzy drinks
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
45/46
Read food labels
Do not be misled by food advertisements
Eat at regular time
-
7/29/2019 Nutrition form 2 chapter 2 science
46/46
Nutrition
Healthy eating habits
Balanced diet
Absorption of
water and
dissolved minerals
Food
Classes,sources and
functions
Food tests Calorific value
Digestion
Absorption of
digested food Defecation
Summary Chart