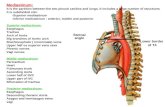
Nostrils Esophagus Cartilage Ring Lobes of lung Pleural Cavity Heart/Mediastinum Diaphragm.
-
Upload
dulcie-hicks -
Category
Documents
-
view
246 -
download
0
Transcript of Nostrils Esophagus Cartilage Ring Lobes of lung Pleural Cavity Heart/Mediastinum Diaphragm.


Nostrils
Esophagus
Cartilage Ring
Lobes of lung
Pleural Cavity
Heart/Mediastinum
Diaphragm


Name Description and/or Function
Nasal Cavity Moisten, warm, clean air
Nostrils Entry for air
Epiglottis Flap covering glottis that closes glottis during swallowing
Larynx Voice box/Adam’s apple – holds vocal chords
Trachea Cartilaginous tube/air pipe
Lung Contains air sacs that are the site of gas exchange
Pleural Cavity Space between inner and outer pleura (membrane covering lung)

Heart (Mediastinum)Pumps blood (with O2 and CO2) throughout body (where heart is
located)
DiaphragmMuscle wall between thoracic and
abdominal cavities – changes chest pressure for breathing
Bronchioles Small branches of bronchi – delivers O2 to alveoli
Bronchus (Bronchi pl) Lower branch of trachea – delivers O2 to bronchioles
Cartilage Ring (in Trachea) Holds trachea in place – prevents collapsing of tube/airway
Esophagus Passageway for food from mouth to stomach
Pharynx Passageway for food and air
Alveolus (Alveoli pl) Actual site of gas exchange
Capillary Network Cover alveoli – blood supply for gas exchange

Happen when a spasm contracts the diaphragm› This separates the
chest (thoracic) cavity with abdominal cavity
This causes an intake of breath, suddenly stopped by the closure of the glottis› Causes the hiccup
sound

A very full stomach can cause bouts of hiccups that go away on their own
A full stomach can be caused by:› Eating too much food too quickly› Drinking too much alcohol› Swallowing too much air› Smoking› A sudden change in stomach temperature› Emotional stress or excitement

INHALATION EXHALATIONIntercostal muscles
between ribs contractIntercostal muscles between ribs relax
Rib cage moves up and out
Rib cage moves in and down
Diaphragm contracts and moves down
Diaphragm relaxes and moves up
Chest volume increases Chest volume decreasesPressure decreases Pressure increases
Air moves in Air moves out