Muscular System Animal movement is based on contraction of muscles working against part of the...
Transcript of Muscular System Animal movement is based on contraction of muscles working against part of the...

Muscular System• Animal movement is based on contraction
of muscles working against part of the skeleton

Muscle Tissue
• Cells that contract
• Three types of muscle tissue:
1. Skeletal
2. Cardiac
3. Smooth

Types of Muscle Tissue
• Skeletal: voluntary
attached to bones
striated: repeating units of contractile proteins, actin and myosin
long, cylinders
multinucleated
many
mitochondria

Types of Muscle Tissue
• Cardiac: involuntary
only in the heart
unit contractions
due to gap junctions
branched
striated

Types of Muscle Tissue
• Smooth: involuntary
walls of organs
tapered cells
unstriated

Classification of muscle
Voluntary Involuntary
Limbs Heart Viscera
Striated Non-striated
Skeletal Cardiac Smooth
Note: Control, Location and Structure

Muscle Control
Type of muscle
Nervouscontrol
Type of control
Example
SkeletalSkeletal Controlled by CNS
Voluntary Lifting a glass
Cardiac Regulated by ANS
Involuntary Heart beating
Smooth Controlled by ANS
Involuntary Peristalsis

REMEMBER!
• Tendon connects muscle to bone
• Ligament connects bone to bone

Tendons
• Muscles are attached to TWO different bones by tendons.
• When the muscle contracts only ONE bone moves.
• The place where the muscle is attached to the stationary bone is called the Origin.
• The place where the muscle is attached to the moving bone is called the Insertion.

Muscles Pull NEVER Push!!
• Muscles only contract and relax
• Contraction (=shortening) of a muscle pulls a bone

Antagonist Muscle Pairs• To make a joint move
in two directions, you need two muscles that can pull in opposite directions.
• Antagonistic muscles are pairs of muscles that work against each other.
• One muscle contracts while the other one relaxes

Muscles work in Antagonistic Pairs Flexor and Extensor
Flexor
Extensor
Flexor = decreases the angle between two bones
Extensor = increases the angle between two bones

True or False
Muscles cause movement by pushing and pulling on the bones of the skeleton.

True or False
Muscles cause movement by pushing and pulling on the bones of the skeleton.
FALSE!
Muscles NEVER push. They can only pull.

Short Answer
List the three types of muscle tissue.

Short Answer
List the three types of muscle tissue.
Skeletal Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Cardiac Muscle

Multiple Choice
Voluntary muscle tissue is also called
A. skeletal muscle.
B. smooth muscle.
C. cardiac muscle.
D. All of the above.

Multiple Choice
Voluntary muscle tissue is also called
A. skeletal muscle.
B. smooth muscle.
C. cardiac muscle.
D. All of the above.

Multiple Choice
A muscle that decreases the angle between two bones is called
A. an extensor.
B. a flexor.
C. a tendon.
D. an antagonistic pair.

Multiple Choice
A muscle that decreases the angle between two bones is called
A. an extensor.
B. a flexor.
C. a tendon.
D. an antagonistic pair.

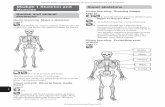
Biceps brachii
Deltoid
Frontalis
Gastrocnemius
Pectoralis major
Rectus abdominis
Rectus femoris
Sartorius
SternocleidomastoidTrapezius

Biceps femoris
Deltoid
Gastrocnemius
Gluteus maximus
Latissimus dorsi
Sartorius
Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius
Tricepsbrachii

Skeletal Muscle Organization
• Skeletal muscle fibers (= cells) are bundled into packages called fascicle


Skeletal Muscle Organization
• Fibers (=cells) are made up of myofibrils that consist of actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament)

Sarcomere repeating unitsof actin and myosin within a myofibril

Myosin (Thick Filament)
Actin (Thin Filament)


• When the muscle is at rest, a long, rod-like tropomyosin molecule blocks the myosin-binding sites that are instrumental in forming cross bridges.
•When another protein complex, troponin, binds calcium ions, the actin binding sites are exposed, cross-bridges with myosin can form, and contraction begins.
Sliding Filament Model Mechanism for Muscle Contraction

Sliding Filament Model (continued)
• Ca+ comes from the sacroplasmic reticulum in the plasma membrane around each myofibril

Cross Bridging b/t Actin and Myosin

Sliding Filament Theory Animations
• http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/matthews/myosin.html
• http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter42/animations.html#