Mulut, Faring, Laring
-
Upload
niddy-rohim-febriadi -
Category
Documents
-
view
258 -
download
0
Transcript of Mulut, Faring, Laring
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
1/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
2/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
3/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
4/76
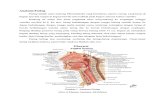
The tongue is a muscularstructure that forms partof the floor of the oral
cavity and part of theanterior wall of theoropharynx.
Apex of tongue inanterior part, with a blunttriangluar shape
The apex is directedanteriorly and sitsimmediately behind the
incisor teeth. The root of tongue is
attached to themandible and the hyoidbone.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
5/76
The oral and pharyngealsurfaces are separated by a V-shapedterminal sulcus oftongue.
fungiform papillae rounder inshapee, larger than the filiformpapillae, concentrated alongthe margins of the tongue
filiform papillae
small cone-shaped
vallate papillae the largest,blunt-ended cylindricalpapillae about 8 to 12 vallatepapillae in a single V-shapedline
foliate papillae linear folds ofmucosa,the sides of thetongue near the terminal sulcusof tongue.
All except the filiform
papillae have taste budson their surfaces
Pharyngeal surface Body
The mucosa covering thepharyngeal surface of the
tongue is irregularin contour
because of the many smallnodules of lymphoid tissue inthe submucosa. These nodules
are collectively the lingualtonsil
There are no papillae on thepharyngeal surface.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
6/76
The sensory structures that detectgustatory, or taste, stimuli are the tastebuds. Most taste buds are associatedwith specialized portions of the tonguecalled papillae.
Taste buds, however, are also located
on other areas of the tongue, the palate,and even the lips and throat, especiallyin children.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
7/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
8/76
Vallate papillae are the largest but least numerous of the
papillae.
8 to 12 of these papillae form a V-shaped row
the border between the anterior and posterior parts of the
tongue
Fungiform papillae are scattered irregularly over the
entire superior surface of the tongue and appear as smallred dots interspersed among the far more numerous filiformpapillae
Foliate papillae are distributed in folds on the sides of the
tongue and contain the most sensitive of the taste buds.
Most numerous in young children and decrease with age.
They are located mostly posteriorly in adults.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
9/76
One type forms the exterior supportingcapsule of the taste bud, whereas theinterior of each bud consists of about 50
taste or gustatory cells.
Like olfactory cells, cells of the tastebuds are replaced continuously, eachhaving a normal life span of about 10
days. Each taste cell has several microvilli,
called gustatory hairs from taste orgustatory pore.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
10/76
Substances called tastants, dissolved insaliva, enter the taste pore and, byvarious mechanisms, cause the taste
cells to depolarize. These cells have no axons and dont
generate their own action potentials.
Neurotransmitters are released from thetaste cells and stimulate actionpotentials in the axons of sensory neuronassociated with them.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
11/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
12/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
13/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
14/76
Taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, exceptfrom the circumvallate papillae, is carried by means of abranch of the facial nerve (VII) called the chorda tympani(because it crosses over the surface of the tympanic mem-brane of the middle ear).
Taste from the posterior one-third of the tongue, the
circumvallate papillae, and the superior pharynx is carriedby means of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX). In addition to these two major nerves, the vagus nerve (X)
carries a few fibers for taste sensation from the epiglottis.
These nerves extend from the taste buds to the tractus
solitarius of the medulla oblongata. Fibers from this nucleus decussate and extend to the
thalamus. Neurons from the thalamus project to the taste area of the
cortex, which is at the extreme inferior end of thepostcentral gyrus.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
15/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
16/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
17/76
The major artery ofthe tongue is thelingual artery
The tongue isdrained by dorsallingual and deeplingual veins
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
18/76
Salivary glands are glands
that open or secrete intothe oral cavity.
Most are small glands in thesubmucosa or mucosa ofthe oral epithelium liningthe tongue, palate,cheeks, and lips, and openinto the oral cavity directlyor via small ducts.
In addition to these smallglands are much largerglands, which include thepaired parotid,submandibular, andsublingual glands.
The parotid duct passes
anteriorly across the externalsurface of the masseter muscleturns medially to penetratethe buccinator muscle of thecheekopen into the oral
cavity adjacent to the crown ofthe second upper molar tooth.
The parotid gland encloses theexternal carotid artery, the
retromandibular vein, and theorigin of the extracranial part of
the facial nerve [VII].
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
19/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
20/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
21/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
22/76
Hard palate separates the oral
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
23/76
Hard palate separates the oralcavity from the nasal cavities.
Consists of a bony platecovered above and below bymucosa:
Abovecovered byrespiratory mucosa and formsthe floor of the nasal cavities;
Belowcovered by oralmucosaand forms the roof ofthe oral cavity
The soft palate continuesposteriorly from the hardpalate and acts as a valve thatcan be:
depressed to help close theoropharyngeal isthmus;
elevated to separate thenasopharynx from theoropharynx
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
24/76
Collections of lymphoid tissue in the mucosa of thepharynx surrounding the openings of the nasal and oralcavities are part of the body's defense system.
The largest of these collections form distinct masses(tonsils).
Tonsils occur mainly in three areas: the pharyngeal tonsil (adenoidswhen enlarged)the
midline on the roof of the nasopharynx; (adenoid-Luschka)
the palatine tonsils are on each side of the oropharynxbetween the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal
arches just posterior to the oropharyngeal isthmus. the lingual tonsil refers collectively to numerous
lymphoid nodules on the posterior one-third of thetongue.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
25/76
The two palatopharyngeusmuscles, one on each side,underlie the palatopharyngealarcheson the oropharyngeal wall.
The palatopharyngeal arches lie
posterior and medial to thepalatoglossal archeswhen viewedanteriorly through the oral cavity
On each side, the palatine tonsil isbetween the palatopharyngealand palatoglossal arches on thelateral oropharyngeal wall.
The palatopharyngeus muscles: depress the palate and move the
palatopharyngeal arches towardsthe midline like curtains-both theseactions help close theoropharyngeal isthmus;
elevate the pharynx duringswallowing.
The palatine tonsil isbetween the palatoglossal
and palatopharyngeal folds
on the lateral oropharyngealwall.
close the oropharyngeal
isthmus.
The palatoglossus musclesdepress the palate, move
the palatoglossal archestoward the midline like
curtains, and elevate theback of the tongue.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
26/76
Tonsil mendapat darah daria.palatina mayor, a.palatina
asendens, cabang tonsil a.maksilaeksterna, a.faring asendens dana.lingualis dorsal.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
27/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
28/76
- Batas superior :
basis cranii- Batas anterior:
koanae
- Batas inferior:palatum mole
- Batas lateral:muara tubaauditoria (torustubarius, fosaRosenmulleri)
-Jenis epitel:kolumner bersilia
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
29/76
-superior : palatum
mole-posterior : vertebra
cervicalis
-anterior: rongga
mulut-inferior: tepi atas
epiglottis
-lateral: plika anterior
(m. palatoglossus),plika posterior (m.palatofaringeus)
-jenis epitel:
skuamus kompleks
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
30/76
- Batas superior :
tepi atas epiglotis
- Batas anterior: larings
- Batas posterior : vertebras
cervicalis
- Batas inferior:
tepi bawah kartilago
krikoid/esofagus
- Jenis epitel orofaringsantara oro-nasofarings:transisional
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
31/76
OTOT2 FARING
(sirkuler&longitudinal)
Eksternal(sirkuler):
- m. konstriktor faringeus superior- m. konstriktor faringeus media
- m. konstriktor faringeus inferior
Kerja otot konstriktor utk mengecilkanlumen faring.
Dipersarafi oleh n.Vagus
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
32/76
Internal (longitudinal)
- m. stilofaringeus, m salfingofaringeus(n.IX)
Utk melebarkan dan menarik laring
- m. palatofaringeus (n.X)
Mempertemukan ismus orofaring danmenaikkan bagian bawah faring danlaring
mengangkat larings saat prosesmenelan
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
33/76
upper parts of the pharynx : the ascending pharyngeal
artery; the ascending palatine and
tonsillar branches of thefacial artery;
numerous branches of themaxillary and the lingualarteries
the external carotid artery
Lower parts of the pharynx: pharyngeal branches from
the inferior thyroid artery,which originates from thethyrocervical trunk of thesubclavian artery.
The major blood supply to thepalatine tonsil is from the tonsillarbranch of the facial artery.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
34/76
Veins of the pharynxform a plexus, whichdrains superiorly intothe pterygoid plexus inthe infratemporal fossa,and inferiorly into thefacial and internal
jugular veins
Lymphatic vessels fromthe pharynx drain intothe deep cervicalnodes and includeretropharyngeal,paratracheal, and
infrahyoid nodes The palatine tonsils
drain into thejugulodigastric nodes inthe region where thefacial vein drains into
the internal jugular vein
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
35/76
1. PROTEKSI oleh cincin Waldeyer
- formasi limfosit
- formasi antibodi- reaksi imunitas
- lokalisasi infeksi rongga mulut & hidung,sebagai filter saluran nafas atas
2. SEKRESI KELENJAR
- oleh kelenjar salivarius (3 pasang) & kelenjarmukosa bukal
- saliva: air (99,42%), garam (0,22%), senyawaorganik
(0,22%), enzim (0,14%)
- sekresi dapat berkurang/berlebih
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
36/76
3. MENELAN
- ada 3 tahap:
a. Stadium rongga mulut
kontraksi m. milohioideus menekan lidah ke
palatum & mendorong ke belakang
gerakan tersebut mendorong makanan ke
orofarings
m. palatoglosus kontraksi, menutup ismus fausium,
mencegah makanan kembali ke rongga mulut
sementara itu respirasi terhenti & laring terangkat
ke atas, sehingga tertutup epiglotis
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
37/76
b. Stadium faring
- gerakan reflektoris
- kontraksi m. konstriktor faringeus mendorongmakanan ke m. krikofaringeus sfingter yangdalam keadaan relaksasi
c. Stadium oesofageal- gerakan reflektoris
- makanan yang telah masuk esofagusdidorong ke kaudal dengan gerakan
peristaltik- gaya berat/gravitasi hanya membantu saja
pada posisi tegak
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
38/76
4. RESPIRASI
- meneruskan udara inspirasi & ekspirasi
5. BICARA
- resonator (bersama kavum nasi & SPN)
- sistem artikulasi (bersama gigi danpalatum, lidah, bibir, pita suara)
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
39/76
3 tahap proses menelan :1. Gerakan makanan dari mulut ke faringvolunter2. Transport makanan melalui faringinvolunter3. Bolus makanan masuk ke esofagusinvolunter
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
40/76
Laring adalah bagian dari saluran
pernafasan bagian atas yangmerupakan suatu rangkaian tulang
rawan yang berbentuk corong dan
terletak setinggi vertebra cervicalis IV
VI,
pada anak-anak dan wanita letaknya
relatif lebih tinggi.
Laring pada umumnya selalu terbuka,hanya kadang-kadang saja tertutup bila
sedang menelan makanan
Batas superior : aditus laring
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
41/76
Batas superior : aditus laring
Batas caudal : kartilago krikoidea
Bangunan kerangka laring tersusun
dari 1 tulang yaitu os hyoid dan
beberapa cartilago
Os hyoid berbentuk huruf U yang
permukaan atasnya dihubungkandengan lidah, mandibula dan
tengkorak oleh tendo dan otot2nya.
Sewaktu menelan, kontraksi otot2 ini
akan menyebabkan laring tertarik ke
atas, sedangkan bila diam, otot2
akan bekerja untuk membuka mulut
dan membantu menggerakkan lidah.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
42/76
KARTILAGO.
Kartilago laring
terbagi atas 2(dua) kelompok,yaitu :
1. Kelompokkartilago mayor,terdiri dari:
Kartilago Tiroidea, 1buah
Kartilago Krikoidea,
1 buah Kartilago
Aritenoidea, 2buah
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
43/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
44/76
2. Kartilago minor,
terdiri dari : Kartilago
Kornikulata, 2 buah
KartilagoKuneiforme, 2buah
Kartilago Epiglotis,
1 buah
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
45/76
Hyaline cartilage
Kartilago terbesar
Ossifies at 20-30
years of age,begins in theinferior margin
and progresscranially
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
46/76
Hyaline
Terletak dibawahkartilago tiroid
Bentuk : Signet ring
Berartikulasi dengan
kornu inferiorkartilago tiroid
Fibroelastik
Berbentuk seperti
daun
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
47/76
Paling banyakterdiri darihyaline
kecil
Bertanggungjawab dalamprosesmembuka danmenutupnya
laring Bentuk:
pyramidal
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
48/76
Fibroelastik Cartilages of Santorini
Kartilago kecil diatas arytenoid
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
49/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
50/76
Ligamentum danmembran laring
terbagi atas 2 grup,yaitu
1. Ligamentum ekstrinsik , terdiri
dari :
Membran tirohioid
Ligamentum tirohioid
Ligamentum tiroepiglotis
Ligamentum hioepiglotis
Ligamentum krikotrakeal
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
51/76
2. Intrinsik
Quadrangular
membrane Conus elasticus
(cricovocalmembrane)
Mediancricothyroidligament
Vocal Ligament
Thyroepiglotticligament
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
52/76
OTOT- OTOT
Otototot laring terbagi dalam 2 (dua)kelompok besar yaitu otot-otot ekstrinsikdan otot-otot intrinsik yang masing-masing mempunyai fungsi yang
berbeda.
Otot-otot ekstrinsik.
Otot-otot ini menghubungkan laring
dengan struktur disekitarnya. Kelompokotot ini menggerakkan laring secarakeseluruhan
Terbagi atas :
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
53/76
Terbagi atas :
1. Otot-otot suprahioid /otot-otot elevator laring,yaitu :
- M. Stilohioideus - M. Milohioideus
- M. Geniohioideus
- M. Digastrikus
- M. Genioglosus - M. Hioglosus
2. Otot-otot infrahioid / otot-otot depresor laring, yaitu
: - M. Omohioideus
- M.Sternokleidomastoideus
- M. Tirohioideus
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
54/76
Menghubungkan kartilago satu denganyang lainnya.
Berfungsi menggerakkan struktur yang adadi dalam laring terutama untukmembentuk suara dan bernafas.
Fungsi otot interaritenoideus dalam prosespembentukkan suara, proses menelan dan
berbafas. Bila m. interaritenoideus berkontraksi, maka
otot ini akan bersatu di garis tengahsehingga menyebabkan adduksi pita
suara.
Y t k
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
55/76
Yang termasuk
dalam kelompok otot
intrinsik adalah :
:
Mm. Interaritenoideus
transversal dan oblik M. Krikotiroideus
M. Krikoaritenoideus
lateral
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
56/76
:
M.Krikoaritenoideusposterior
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
57/76
M. Tiroaritenoideus dan M.Vokalis
: M. Krikotiroideus
.Pada orang tua, m. tensor
internus kehilangansebagian tonusnyasehingga pita suaramelengkung ke lateralmengakibatkan suara
menjadi lemah dan serak
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
58/76
Laring dipersarafi oleh cabang N. Vagus yaitu Nn. Laringeus
Superior dan Nn. Laringeus Inferior (Nn. Laringeus Rekuren) kiri
dan kanan.
1. Nn. Laringeus Superior.
Meninggalkan N. vagus tepat di bawah ganglion nodosum,
melengkung ke depan dan medial di bawah A. karotis internadan eksterna yang kemudian akan bercabang dua, yaitu :
Cabang Interna ; bersifat sensoris, mempersarafi vallecula,
epiglotis, sinus pyriformis dan mukosa bagian dalam laring di
atas pita suara sejati.
Cabang Eksterna ; bersifat motoris, mempersarafi m. Krikotiroid
dan m. Konstriktor inferior.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
59/76
2. N. Laringeus Inferior (N. Laringeus Rekuren).
Berjalan dalam lekukan diantara trakea dan esofagus, mencapai
laring tepat di belakang artikulasio krikotiroidea. N. laringeus
yang kiri mempunyai perjalanan yang panjang dan dekat
dengan Aorta sehingga mudah terganggu.
Merupakan cabang N. vagus setinggi bagian proksimal A.subklavia dan berjalan membelok ke atas sepanjang lekukan
antara trakea dan esofagus, selanjutnya akan mencapai laring
tepat di belakang artikulasio krikotiroidea dan memberikan
persarafan :
Sensoris, mempersarafi daerah sub glotis dan bagian atas trakea
Motoris, mempersarafi semua otot laring kecuali M. Krikotiroidea
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
60/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
61/76
superior laryngeal
veinsdrain intosuperior thyroidveins, which in turn
drain into the internaljugular veins
inferior laryngealveinsdrain intoinferior thyroid veins,which drain into theleft brachiocephalic
veins.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
62/76
1.Proteksi saluran nafas bawah
Benda asing tidak dapat masuk ke dalam laring dengan adanya
reflek otot-otot yang bersifat adduksi, sehingga rima glotis tertutup.
Pada waktu menelan, pernafasan berhenti sejenak akibat adanya
rangsangan terhadap reseptor yang ada pada epiglotis, plika
ariepiglotika, plika ventrikularis dan daerah interaritenoid melalui
serabut afferen N. Laringeus Superior. Sebagai jawabannya, sfingter
dan epiglotis menutup. Gerakan laring ke atas dan ke depan
menyebabkan celah proksimal laring tertutup oleh dasar lidah.
Struktur ini mengalihkan makanan ke lateral menjauhi aditus dan
masuk ke sinus piriformis lalu ke introitus esofagus
2 PHONASI
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
63/76
2. PHONASI
Pembentukan suara merupakan fungsi laring
yang paling kompleks. Suara dibentuk karenaadanya aliran udara respirasi yang konstan dan
adanya interaksi antara udara dan pita suara.
Nada suara dari laring diperkuat oleh adanya
tekanan udara pernafasan subglotik dan vibrasi
laringserta adanya ruangan resonansi seperti
rongga mulut, udara dalam paru-paru, trakea,
faring, dan hidung. Nada dasar yang dihasilkan
dapat dimodifikasi dengan berbagai cara
3 RESPIRASI
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
64/76
3. RESPIRASI Pada waktu inspirasi diafragma bergerak ke bawah untuk
memperbesar rongga dada dan M. Krikoaritenoideus
Posterior terangsang sehingga kontraksinya menyebabkan
rima glotis terbuka. Proses ini dipengaruhi oleh tekanan
parsial CO2 dan O2 arteri serta pH darah. Bila pO2 tinggi
akan menghambat pembukaan rima glotis, sedangkanbila pCO2 tinggi akan merangsang pembukaan rima
glotis. Hiperkapnia dan obstruksi laring mengakibatkan
pembukaan laring secara reflektoris, sedangkan
peningkatan pO2 arterial dan hiperventilasi akan
menghambat pembukaan laring. Tekanan parsial CO2
darah dan pH darah berperan dalam mengontrol posisi
pita suara
4 Fungsi Fiksasi
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
65/76
4. Fungsi Fiksasi.
Berhubungan dengan mempertahankantekanan intratorakal agar tetap tinggi,
misalnya batuk, bersin dan mengedan.
5. Fungsi Batuk.
Bentuk plika vokalis palsu memungkinkanlaring berfungsi sebagai katup, sehinggatekanan intratorakal meningkat. Pelepasantekanan secara mendadak menimbulkan
batuk yang berguna untuk mempertahankanlaring dari ekspansi benda asing ataumembersihkan sekret yang merangsangreseptor atau iritasi pada mukosa laring.
6 Fungsi Menelan
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
66/76
6. Fungsi Menelan. Terdapat 3 (tiga) kejadian yang berhubungan dengan laring
pada saat berlangsungnya proses menelan, yaitu :
Pada waktu menelan faring bagian bawah (M. Konstriktor
Faringeus Superior, M. Palatofaringeus dan M. Stilofaringeus)
mengalami kontraksi sepanjang kartilago krikoidea dan kartilago
tiroidea, serta menarik laring ke atas menuju basis lidah, kemudian
makanan terdorong ke bawah dan terjadi pembukaan
faringoesofageal.
Laring menutup untuk mencegah makanan atau minuman masuk
ke saluran pernafasan dengan jalan menkontraksikan orifisium dan
penutupan laring oleh epiglotis. Epiglotis menjadi lebih datar
membentuk semacam papan penutup aditus laringeus, sehingga
makanan atau minuman terdorong ke lateral menjauhi aditus
laring dan maduk ke sinus piriformis lalu ke hiatus esofagus.
7 Fungsi Ekspektorasi
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
67/76
7. Fungsi Ekspektorasi.
Dengan adanya benda asing pada
laring, maka sekresi kelenjar berusahamengeluarkan benda asing tersebut.
8. Fungsi Emosi.
Perubahan emosi dapat menyebabkanperubahan fungsi laring, misalnya padawaktu menangis, kesakitan, menggigit
dan ketakutan.
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
68/76
IntrinsicMuscles
Origin Insertion Action
Cricothyroid(ELN)
arch of the
cricoid cartilage
inferior border of
the thyroid
cartilage
draws the thyroid
cartilage forward,
lengthening the
vocal ligaments,
tenses vocal cords
Thyroarytenoid(vocalis, ILN)
inner surface of
the thyroid
cartilage
lateral border of
the arytenoid
cartilage
relaxes and
adducts the vocal
folds
Lateralcricoarytenoid(ILN)
arch of the
cricoid cartilage
muscular process
of the arytenoid
cartilage
Adducts the vocal
cords by rotating
the arytenoid
cartilage
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
69/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
70/76
Intrinsic Muscles Origin Insertion Action
Posteriorcricoarytenoid(ILN)
posterior surfaceof the lamina of
the cricoid
cartilage
muscular process ofthe arytenoid
cartilage
Adducts the vocalcords by rotating
the arytenoid
cartilage
Interarytenoidm., transverse(ILN)
posterior surfaceof the arytenoid
cartilage
posterior surface ofthe contralateral
arytenoid cartilage
Closes posteriorpart of rima glottidis
by approximating
arytenoid
cartilages
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
71/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
72/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
73/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
74/76
Supplied by Vagus nerve: Superior laryngeal n.
Cabang internal (sensory)area di atas glottis
Cabang external (motorik dan sensory)MotorikCricothyroid muscle
Sensorym.krikotiroid dan m.konstriktorinferior
Inferior (recurrent) laryngeal n. Motoriksemua otot laring kec. M.
krikotiroidea
Sensoryarea di bawah glottis
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
75/76
-
8/13/2019 Mulut, Faring, Laring
76/76
TERIMAKASIH