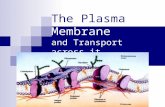
MOVEMENT THROUGH THE MEMBRANE Section 7-3. The cell membrane Function : Regulates what enters and...
-
Upload
clifford-horn -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of MOVEMENT THROUGH THE MEMBRANE Section 7-3. The cell membrane Function : Regulates what enters and...

MOVEMENT THROUGH THE MEMBRANE
Section 7-3

The cell membrane
• Function:
• Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support
• Selective permeability• Some substances can pass across the cell
membrane and others can’t

StructurePhospholipid Bilayer (Fluid Mosaic Model): a
double-layer sheet that makes up nearly all membranes.

Components of the lipid bilayer
• Polar Head– Phosphorous group– Hydrophilic
“Water Loving”
• Lipid Tails– Hydrophobic
“Water Fearing”
- Fatty acid tails

Why is the lipid bilayer important?
• Tough, flexible structure
• Strong barrier between the cell and its environment

What does it do for the cell?
• Allows only certain materials in or out at certain times. –Ions–Glucose–Water–Electrolytes–Oxygen


• Cells live in fluid environments, with water inside and outside the cell.
• Components of plasma membrane:–2 layers of phospholipids
• Polar head and nonpolar tail–Integral proteins–Peripheral proteins–Cholesterol–Carbohydrates

• Proteins:
• Peripheral proteins
• On inside surface
• Held in place by cytoskeletal filaments
• Integral proteins
• Embedded in membrane, can move laterally

Functions of membrane proteins• Some help to transport materials across
the membrane. •Channel Protein – allows certain molecules or ions to cross membrane freely
•Protein pumps – interact with certain molecule or ions to help move it across membrane, requires energy

•Cholesterol - strengthens the plasma membrane.
•Carbohydrates:•Glycoproteins – proteins with carbohydrates attached•Glycolipids – phospholipids with carbohydrates attached

Other Membrane Structures
• Carbohydrate molecules–Act like ID markers for the cell
–Basis for blood typing: the antigens on the blood cells (A, B, AB) are carbohydrate chains

Cell recognition protein
•Foreign carbohydrate chains are why transplanted tissue is often rejected by the body

Diffusion
Definition: The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, until an equilibrium is reached.
Concentration?Mass of Solute/Volume of solution (g/L)
Equilibrium?Animation

What causes diffusion?
• Diffusion is caused by the constant movement and collision of molecules.
More molecules = More collision
• The collisions cause the molecules to spread out.

Examples of Diffusion
Air Fresheners Perfume Farts

Diffusion in CellsMolecules are able to diffuse through the
cell membrane and allow the cell to function.
Facilitated Diffusion – some molecules need help from protein channels to cross the cell membrane.
Animation

Osmosis (A special kind of diffusion)
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane.
Selectively Permeable - Osmosis

OsmosisIsotonic – concentration is the same on both
sides of the membrane (equilibrium)
Hypertonic – the solution with a greater concentration
Hypotonic – the solution with the lesser concentration.

Osmosis PracticeThe cytoplasm of Elodea cells is composed
of about 70% water molecules and 30% other kinds of molecules.
What happens when the Elodea cells are put into a liquid that is a. 50 percent water.
b. 70 percent water.
c. 100 percent water .

Moving down a concentration gradient is like riding a bike down a hill. It doesn’t require energy
Osmosis and diffusion are examples of passive transport!
Moving up a concentration gradient is like riding up a hill. IT REQUIRES ENERGY.

Active Transport• Active Transport: is the movement of
materials through a cell membrane using energy.
• Molecules move from low concentration to high concentration.
• Proteins use ATP to pump ions and small molecules against concentration gradient.

Types of Active Transport
1. Endocytosis – the process of taking material into the cell by means of infoldings of the cell membrane.
– Phagocytosis – extension of the cytoplasm surround and engulf the particle
– Pinocytosis – similar to phagocytosis, but cells take up liquid instead of particles.

Types of Active Transport
2. Exocytosis– Large molecules move from inside the cell to
outside the cell.– Contractile Vacoule – an organelle that
constantly pumps H2O out of the cell.
Animation

Specialized Cells
• Cells with a specific structure and function and are found in multi-celled organisms.
• We have blood cells, brain cells, bone cells, liver cell, skin cells, etc.

We are all made of cells
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ
System

Tissue
• Definition: A group of similar cells working together.
• Examples

Organs
• Definition: A groups of tissues working together to perform a specific job.

Organ Systems• Definition: Many organs working
together to do a specific job.

7.3-7.4 Wrap up Questions
1. Explain Diffusion
2. Explain Osmosis
3. What does selectively permeable mean?
4. What is facilitated diffusion?
5. Are phospholipids the only molecules in a cell membrane?
6. What is active transport?
7. What are tissues, organs, and organ systems? Give Examples

= cell
= cell
10% salt
10% salt
10% salt
20% salt
20% salt
10% salt
10% salt
10% salt
10% salt
20% salt
10% salt
20% salt
Label the environment around the cell in each beaker as hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic. Label the net flow of water and state what will happen to the cell in each beaker?
Label the environment around the cell in each beaker as hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic. Label the net flow of water and state what will happen to the cell in each beaker?

= cell
10% salt
10% salt
10% salt
20% salt
20% salt
10% salt
Label the environment around the cell in each beaker as hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic. Label the net flow of water and state what will happen to the cell in each beaker?