MGT2306-Marketing-Management-Lesson3
-
Upload
jacqueline-quek -
Category
Education
-
view
72 -
download
0
description
Transcript of MGT2306-Marketing-Management-Lesson3

Marketing ManagementMGT 2306Lesson 3

Lesson 3 Objectives
• Explain what is consumer behavior and consumer markets
• Describe all the factors that influences what a consumer will buy
• List and explain the steps to a consumer buying decision.

Consumer Markets
and
Consumer Buyer Behavior

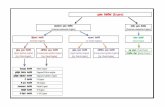
Model of Consumer BehaviorConsumer buyer behavior refers to the buying behavior of final consumers—individuals and households who buy goods and services for personal consumption.
Consumer market refers to all of the personal consumption of final consumers.

Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior

Culture (Budaya)
Culture is the learned values, perceptions, wants, and behavior from family and other important institutions.
A subculture explains a culture within a culture. Example: Malaysian Culture Malay, Chinese, Indian culture Kelantanese Malay, Mongolian Chinese and Northern Indian culture

Discussion..
• What differences do you see in Malay and Chinese culture when it comes to their buying behavior?
- food
- clothing
- electronic items
- household items

Cultural diversity

Social Class (Lapisan Masyarakat)
• Social classes are society’s relatively permanent (tetap) and ordered (teratur) divisions whose members share similar values, interests, and behaviors.
• Measured by a combination of occupation, income, education, wealth, and other variables.
(pekerjaan, pendapatan, pendidikan, kekayaan)


• Reference Groups: Groups that form a comparison or reference in forming attitudes or behavior
• Family is the most important consumer-buying organization in society.
• The groups, family, clubs, and organizations that a person belongs to define his/her social role and status.

Which group(s) would you join?

Personal Factors
• Occupation affects the goods and services bought by consumers.
• Age and Life-cycle stage• Economic situation includes trends in:
Personal income Savings Interest
rates

• Lifestyle is a person’s pattern of living as expressed in his or her psychographics.
• Self-Concept looks at how people look at themselves, how they perceive other people are looking at them.

The 4 perceptions of self
• How you see yourself
• How you would like to see yourself
• How you would like others to see you
• How you see others see you

Discussion
• How different are people’s purchasing needs and behaviors through each stage of life?

Physiological
• Motivation : what drives a person• Perception : how a person thinks of
himself and how he thinks other people sees him
• Learning : Knowledge & Experiences gained in life
• Beliefs & Attitudes: Faith and behavior towards a product or service

Perception commercial

Stages in the consumer decision making process
• Problem recognition• Information Search• Evaluation of
alternatives• Purchase decision• Post-purchase behavior

Problem Recognition
• Current Product finished? Spoilt? • Need to reorder• Same item or try new item?

Information Search
• Personal sources—family and friends
• Commercial sources—advertising, Internet
• Public sources—mass media, consumer organizations
• Experiential sources—handling, examining, using the product
Sources of Information

Evaluation of alternatives
• How many types of product are there?• Compare the features, price and advantages
of each product• Which offers more benefit (value) to the
consumer?

Purchase decision
• Decision to purchase
- which product?
- from where?
- when to buy it?
- how to pay for it?
- who to buy it for you?

Post-purchase decision
• Happy with decision?• Happy with product?• Will you repeat buy?