Mechanism of plant nutrient absorption by plant root and plant tissue
-
Upload
sohel-rana -
Category
Environment
-
view
2.193 -
download
2
Transcript of Mechanism of plant nutrient absorption by plant root and plant tissue

Welcome to My Presentation

BY – RAZIA SULTANA JEMIM
Mechanism of plant nutrient absorption by plant root and
plant tissue

Nutrients Absorption

Mechanisms of Nutrient Uptake
Prior to absorption, nutrients reach the root by 3 mechanisms:
Mass flow – movement with the water flow. Most prominent.
Diffusion – movement in response to a concentration gradient. Slow.
Root interception – root extension. Very important to find new nutrient sources.

Absorption through roots
Passive Uptake: Some ions such as nitrate, can move passively through the outer membrane of the root surface along with water in the transpiration stream.
Active Uptake: Not well understood, but many nutrients (e.g., K+ and H2PO4
-) must somehow bond with an ion-specific carrier (see Insight: p.270).
Maintaining an Electrical Balance: As cations are absorbed H+ is excreted or organic anions are produced. As anions are absorbed HCO3
- is excreted or compensating cations are absorbed.


Stomatal Absorption: •Rapid absorption of soluble ions from nutrient enriched water.•Used mostly for the immediate correction of critical nutrient deficiencies. •Most efficient for the micronutrients. Does not build soil fertility. Danger of phytotoxic effects if over applied.
Absorption through leaves

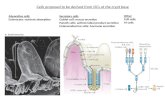
The plasma membranes of root cells control solute uptake A plant can absorb enough water and inorganic ions
through its roots to survive and grow Root hairs greatly expand surface area for absorption

Substances enter roots in solution Water and solutes can move through the root's
epidermis and cortex by two routes Intracellular: via cell interiors, through plasmodesmata Extracellular: via cell walls; stopped by Casparian strip Plants usually use a combination of both

Water and solutes must cross a plasma membrane to enter the xylem for transport upward Controls solutes that enter xylem

LE 32-2b
Dermal tissue systemKey
Ground tissue system
Vascular tissue system
Root hair Epidermis Cortex Phloem
XylemCasparianstrip
Endodermis
Casparian stripExtracellular route,via cell walls;stopped byCasparian strip
Root hair
Xylem
Plasmodesmata
Endodermis
Cortex
Intracellularroute, viacell interiors,throughplasmodesmata Epidermis

Transpiration pulls water up xylem vessels Xylem sap travels from roots to top of plant through
the tracheids and vessel elements in xylem Root pressure can push sap up a few meters Most sap is pulled up by the transpiration-cohesion-
tension mechanism Transpiration
Loss of water from plant's aerial parts Aided by two properties of water: cohesion, adhesion

LE 32-3-3
Water uptake from soil
Root hair
Soil particle
Water
Flow
of
wat
er
Cohesion andadhesion in the xylem
Xylemcells Cohesion,
by hydrogenbonding
Watermolecule
AdhesionCellwall
Transpiration
Xylem sap
Mesophyll cells
Air space within leafStoma
Outside air

Guard cells control transpiration Plants can lose water through transpiration Leaf stomata help plants regulate their water
content Opened and closed by flanking guard cells
Controlled by movement of H2O and K+
Generally stay open during the day, allowing for entry of CO2 for photosynthesis
Stay closed at night, conserving water Respond to cues from sunlight, CO2 level,
biological clock

LE 32-4
Stoma Guard cells
Vacuole
K+
Stoma opening Stoma closing

Root hairs take up certain inorganic particles by cation exchange Hairs are in direct contact with water films on soil
particles Ca2+, Mg2+, K+ adhere tightly to soil particles H+ released into soil solution by root hairs displaces
them Can then be absorbed
Anions less tightly bound to soil particles More readily available, but may leach from soil

LE 32-8bSoil particle surroundedby film of water
Root hair
Water
Air space

LE 32-8c
Clayparticle
Root hair
H+
K+
K+
K+K+
K+
K+
K+
K+

Thank you!