Lower Limb 2
-
Upload
azwarmuslimhasballahamin -
Category
Documents
-
view
252 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Lower Limb 2
-
Lower LimbSkeleton (homologous with upper limb)Muscles--anterior, posterior compartmentsNerves--sciatic, femoralSurface anatomyWhat is a limb?SkeletonJointsPelvis or limb girdleHip/Hip MusclesLumber and sacral plexusgetting spinal nerves out onto limbMusclesanterior and posterior compartmentsSurface anatomy
-
What is a limb?Ventral somatic outgrowth of outer tubeBones (made of bony tissue, cartilage, and other tissues)JointsMusclesNerves (with motor neurons to muscles, sensory neurons to skin, proprioceptors)No viscera--all innervation is somatic (motor or sensory) from ventral ramus of spinal nerve (except autonomics to blood vessels)
-
Upper LimbScapulaHumerusRadius, ulnaCarpalsDigitsMetacarpalsPhalangesLower LimbPelvisFemurTibia, fibulaTarsalsDigitsMetatarsalsPhalanges
-
ScapulaHumerusRadius, ulnaCarpalsDigitsMetacarpalsPhalangesUpper Limb
-
Tibia/fibulaTibia--big toe sideFibula--little toe side(no pronation/supination)
-
AnkleTalus--forms ankle jointCalcaneus--forms heel
-
FootFunction:Support weightAct as lever when walkingTarsalsTalus = ankleBetween tibia + fibulaArticulates w/bothCalcaneus = heelAttachment for Calcaneal tendonCarries talusMetatarsalsHomologous to metacarpalsPhalangesSmaller, less nimble
-
Joints of Lower LimbHip (femur + acetabulum)Ball + socketMultiaxialSynovialKnee (femur + patella)Plane Gliding of patellaSynovialKnee (femur + tibia)HingeBiaxialSynovial
-
Joints of Lower LimbProximal Tibia + FibulaPlaneGlidingSynovialDistal Tibia + FibulaSlight giveFibrousAnkle (Tibia/Fibula + Talus)HingeUniaxialSynovial
pg 218
-
Lower Limb MovementsBending on posterior side is flexion (except hip)Bending on anterior sided is extension (except hip)HipFlexion/extensionAbduction/adductionLateral/medial rotationKneeFlexion/extensionAnkleDorsiflexion/plantarflexionInversion/eversionToesFlexion/extension
-
Pelvic tilt and a reverse lumbar curve (or how we got to be upright)
Bowl conceptpelvis spills forwardHerniabeer bellyIn human minor pelvis is behind (posterior) to guts and abdominal cavityCompare human pelvic position with quadruped (cat for instance)
-
Human pelvis still has quadruped orientation
-
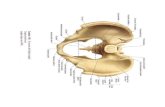
Bony structure of the pelvisMAIN STRUCTURESHip bone (innominate, os coxae)--fusion ofIlium (hips)Ischium (rear)Pubis (anterior midline)Sacrum and coccyxAcetabulumFemur--head, neck, greater trochanterHOLESFalse and true pelvis (major, minor pelvis)Pelvic inlet, pelvic outletSacrotuberous ligamentSacrospinous ligamentGreater, lesser sciatic foramenObturator foramen
-
Female MaleCavity is broad, shallowPelvic inlet oval + outlet roundBones are lighter, thinnerPubic angle largerCoccyx more flexible, straighterIschial tuberosities shorter, more evertedCavity is narrow, deepSmaller inlet + outletBones heavier, thickerPubic angle more acuteCoccyx less flexible, more curvedIschial tuberosities longer, face more medially
-
Posterior and lateral hipGluts (gluteal nn.)Maximusextensor of thighMedius--pelvic tilt (relative to insertion with foot planted)Lateral rotators (spinal nn.)Piriformis syndrome
-
Anterior HipIliopsoasiliacuspsoasQuadratus lumborum
-
Lumbar and sacral plexus Mr. Bill is happyso easyLumbar plexus forms femoral n.anteriorSacral plexus forms sciatic n.--posterior
Femoral n.Sciatic n.
-
Lumbar plexus (femoral nerve)Sacral plexus (sciatic nerve)With leg out to side like quadruped, lumbar-anterior, sacral-posterior makes sense
-
Dermatomes show twisting of leg during developmentDorsal becomes anterior: thus dorsiflexion and extension in anterior compartment (unlike upper limb)
Ventral becomes posterior: thus flexion is in posterior compartment (unlike upper limb)
-
Anterior/Posterior compartments
-
Thigh movements by compartment
-
Anterior thigh (femoral n.)Sartorius (Tailors muscle)Quads (four)Rectus femoris (crosses hip)3 vastus mm. (vast--big)
-
Posterior thigh (sciatic n.)HamstringsBiceps femorisSemimembranousSemitendinous
-
Medial thigh (obturator n.)Adductor musclesGracilisAdductorMagnusLongusbrevis
-
Leg movements by compartment (in leg all nn are branches of sciatic)
-
Anterior Leg (deep fibular n.)Extensors (dorsiflexors)Fibularis (peroneus) longusExtensor digitorum longusExtensor hallicus longusTibialis anteriorus
-
Lateral Leg (superficial fibular n.)Fibularis brevis/longus
-
Posterior Leg (tibial n.)Flexors (plantarflexors)Gastrocs and soleusFlexor digitorum longusFlexor hallucus longus
-
Human gaitHumans only large mammal marathoners, ultra-runnersPrehistoric cultures hunted by exhausting large preyBipedalism very efficient energeticallyGastroc-Achilles springOne other large mammal more efficientalso bipedal
-
Intrinsics of foot
-
Surface Anatomy: Anterior Thigh + LegPalpatePatellaCondyles of femurFemoral TriangleSartorius (lateral)Adductor longus (medial)Inguinal ligament (superior)Femoral a + v, lymph nodespg 785pg 792
-
Surface Anatomy: Posterior LegPopliteal fossaDiamond-shape fossa behind kneeBoundariesBiceps femoris (sup-lat)Semitendinosis + semimembranosis (sup-med)Gastrocnemius heads (inf)ContentsPopliteal a + v
Calcaneal (Achilles) tendonpg 793
-
Blood supply to lower limbInternal IliacCranial + Caudal Gluteals= glutealsInternal Pudendal = perineum, external genitaliaObturator = adductor muscles
External IliacFemoral = lower limbDeep femoral = adductors, hamstrings, quadricepsPopliteal (continuation of femoral) Geniculars = kneeAnterior Tibial = ant. leg muscles, further branches to feetPosterior Tibial = flexor muscles, plantar arch, branches to toes