Lecture 2 cell components
description
Transcript of Lecture 2 cell components

DEN 1114 Lecture 2Professor Maria-Elena Bilello
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1B4F2V0_yYg

Cell Smallest living unit of organization: Epithelial cell, neuron, myofiber,
chondrocyte, fibroblast, erythrocyte, macrophage. sperm
Tissue Collection of similarly specialized cells: Epithelium, nervous tissue, muscle,
cartilage, bone, blood
Organ Independent body part formed from tissues: Skin, brain, heart, liver
System
Organs functioning together: Central nerous system, respiratory system,
immune system, cardiovascular system

:
Criteria for LifeReproduction Ability to replicate ones self (going from one to two)
Growth Ability to increase in size
Metabolism The process by which substances are produced, maintained and destroyed and energy is produced Anabolism - put particles together (synthesis) from smaller ones (constructive metabolism)Catabolism – Complex molecules are broken down into simpler one and release energy(Destructive metabolism).
Assimilation The conversion of absorbed food into the substance of the body
Excretion Ability to eliminate
respiration Total process of conveying O2 to tissues & cells and the oxidation process whereby CO2 & H2O are given off.
Irritability Ability to respond to a stimulus
Conductivity Ability to transmit that stimulus
Homeostasis Ability to work together to maintain equilibrium (harmony)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NiiLS_ovLwM&feature=related

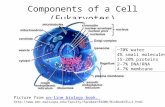
Cell contains:Cell membraneCytoplasmOrganelles Cellular inclusions
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NiiLS_ovLwM&feature=related


Lipids diffusion regulator (barrier)
Only allows substancessoluble in lipid to pass
through the membrane.
Proteins Structural
reinforcement - stabilize cell membrane
Receptor – hormones
neurotransmitters immunoglobulins (antibodies)
Types of proteins: Transmembrane proteins
(transport materials through bi-layer) Surface membrane proteins
(receptors AB & hormones)http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GW0lqf4Fqpg&feature=related


Semi-fluid portion Between liquid & gel (75-90%)
Contains - IonsMolecules - Amino Acids
Sugars - glucose & fructose
Cytoskeleton System of support
Contains – microfilaments intermediate filaments microtubulesThese create stability and compartmentalize the cytoplasm.
Chemical messages from the cytoplasm & membrane (the cellular environmental) influence gene activity.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kud4qUhsCxg&feature=related


Major Organelles:Nucleus
MitochondriaRibosomes
Endoplasmic ReticulumGolgi Complex
LysosomesCytoskeleton
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1IqsE8CVTms&feature=related

Nucleus‘Command Central’
Contains: DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid RNA - ribonucleic acid Nucleolus
DNA & RNA – Memory Bank (genetic coding)control all functions of the cell

COMPONENTS:NUCLEOPLASM: in the form of chromatin contains DNA - Chief nucleic acid– linked into chromosomes
NUCLEOLUS:PRODUCES - rRNA (ribosomal RNA) - nucleotides of the 2 other types of RNA*IMPORTANT for PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (No Nucleolus – No Protein Synthesis)
NUCLEAR ENVELOP - double-layered Membrane which may be pierced by nuclear pores.
NUCLEAR PORES – communicates between the nucleoplasm and the outer cytoplasm
•http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lTHY430ohJI

DNA GENETIC INFORMATION
RNA TRANSLATES DNA-
CARRIES THE TRANSLATION TO THE SITE OF PROTEIN
SYNTHESISDeoxyribonucleic acid
Adenine cytosine Guanine thymine Chromatin – ‘loose’ DNA
when no division is occurring (just strands)http://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=qy8dk5iS1f0&feature=related
Besides hereditary activity,DNA directs synthesis of
manyenzymes, proteins and
secretory products
TYPES OF RNA:mRNA – Messenger RNAcomplementary copies of segments of DNA
tRNA – Transfer RNA molecules that bind to & transport amino acids units for protein systhesisrRNA – Ribosomal RNA
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fiJupfbSpg&feature=related

Energy Production (Conversion) – ATP Cristae – folds inside mitochondria
Cristae – contain enzymes on surface to aid in cell metabolism
cell function depends on the amount (increase # mitochondria = increased cellular
activity)Increase # cristae = more active cell
* Cardiac muscle and the liver contain the most mitochondria.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TgJt4KgKQJI&feature=related

Made in the Nucleolus from rRNA & protein molecules and assembled in the cytoplasm
Found: free in cytoplasm (bound to membranes)
within mitochondria attached to mRNA molecule bound to rough endoplasmic reticulum outer nuclear membrane
Sequences protein chains Within ribosomes – free amino acids are being joined together
in accordance with the order specified by the mRNA transcript


Network of parallel membrane-bound channels
and folds which is continuous (connects) with
nuclear envelope.Functions: modifies, stores, segregates
and transports proteinsSmooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Free of Ribosomes
Smooth – lipid/fat synthesis
Ribosomes on outer surface
Rough – protein synthesis


Composed of stacks of 3 to 20 flattened, smooth-membraned vesicular sacs – parallel to each other
Fuses with vesicles of protein molecules (hormones, enzymes, secretory products) from RER
Protein molecules are further modified concentrated and packaged.
Packaging – wraps larger #’s of molecules into a single membranous vesicle (using merocrine secretion)
Prepares proteins for export by EXOCYTOSIS Produces lysosomes – a separate organellehttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bD4z27ASN1M&feature=related


Function –Digestion Intracellular & Extracellular
Vesicle – develops and pinches off Golgi complex
Enzymes of the lysosomes are produced on RER, transported for
packaging to Golgi complex
lyses – to digest - breaks down particles (good & bad – foreign particles)during phagocytosisAutolysis – self destructionCaused by:Powerful hydrolytic enzymes and digestive enzymes
•Main hydrolytic enzyme - hyaluronidase
* All cells – except red blood cells (RBC) have digestive activityhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E3Zfgtkv-ik

Function: Significant role in reproduction - cell division (mitosis)
Aids in spindle formation Oval-shaped organelle Always located near nucleus Contains: Centrioles - pair of cylindrical
structures*Without self-replicating centriole-
centrosome unit , animal cells cannot reproduce
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N0JCD3ofyIM

Function: Support - a 3-dimensional
System that gives stabilityCompartmentalizes thecytoplasm for movement
of moleculesComponents:
Microfilaments, Intermediate filamentsMicrotubules
(these consists of specialized proteins)
Microfilaments: Delicate, thread-like, not
hollow Maintain cell shape Transport intracellular
materials
Microtubules: Slender, hollow, tubular Assist microfilaments Framework for cilia,
flagella, centrioles
Intermediate filaments: Thicker, thread-likeExamples: Tonofilaments – role in
intercellular junctions Keratin –found in calloused
epithelial tissueshttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5rqbmLiSkpk&feature=related

Inert (not active) substances that are produced in the cell to be used later -
transient.Vacuoles – spaces/cavities in the cytoplasm Are released from storage by the cell as needed water Lipids and glycogen can be decomposed for
energy from inclusions. Melanin (a pigment) stored as inclusion in skin
cells and oral mucosa. Residual bodies such as old lysosomes & their
digested material.


Fills the spaces between cells in a tissue
Serves as barrier Serves as a medium for the exchange
of gases & metabolic substances. Produced by the cells. Colorless, shapeless and transparent.

• Tissue Fluid (interstitial fluid)– Dissolves, mixes, transports substance and
carries out chemical reactions. (contains small amount of plasma proteins)– Diffuses through capillary walls from plasma of
blood.– Returns into blood as lymph by osmosis via the
lymphatic system
The amount of tissue fluid varies.Excess tissue fluid = EDEMA

DESMOSOME CELL TO CELL - IS DISC-SHAPED
HEMIDESMOSOMECELL TO NON-CELLULAR
SUBSTANCE
as in upper layers of skin as in gingival epithelium & tooth surface
Attachment device - attachment plaque in the cell & tonofiliments
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XdaUthOUvIo&feature=related

Hemidesmosomes as mechanism for attaching the epithelium to
connective tissue such as in the oral mucosa by way of the basement membrane
Desmosomes as mechanism for attaching upper
layers of the skin

http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W0HQt1MTrAc&feature=related