Intel® HPC Orchestrator · Intel® HPC Orchestrator •Open Source Community under Linux...
Transcript of Intel® HPC Orchestrator · Intel® HPC Orchestrator •Open Source Community under Linux...

Intel® HPC OrchestratorSystem Software Stack Providing Key Building Blocks for Intel® Scalable System Framework
Nivi Muthu SrinivasanTechnical Support Manager, Intel Corporation
1

Legal Notices and DisclaimersIntel technologies’ features and benefits depend on system configuration and may require enabled hardware, software or service
activation. Learn more at intel.com, or from the OEM or retailer.
No computer system can be absolutely secure.
Software and workloads used in performance tests may have been optimized for performance only on Intel microprocessors.
Performance tests, such as SYSmark and MobileMark, are measured using specific computer systems, components, software,
operations and functions. Any change to any of those factors may cause the results to vary. You should consult other information and
performance tests to assist you in fully evaluating your contemplated purchases, including the performance of that product when
combined with other products. For more complete information visit http://www.intel.com/performance.
Cost reduction scenarios described are intended as examples of how a given Intel- based product, in the specified circumstances and
configurations, may affect future costs and provide cost savings. Circumstances will vary. Intel does not guarantee any costs or cost
reduction.
No license (express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise) to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document.
Intel, the Intel logo and others are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
© 2016 Intel Corporation.
2

3
Agenda
• Background Why a community solution is needed OpenHPC*
• Intel® HPC Orchestrator Overview
• Architecture
• Value Add
• Installation
• Summary

THE REALITY: We will not be able to get where we want to go without a major change in system software development
Fragmented efforts across the ecosystem –“Everyone building their own solution.”
A desire to get exascaleperformance & speed up software adoption of hardware innovation
New complex workloads (ML1, Big Data, etc.) drive more complexity into the software stack
1Machine Learning (ML)
Current State of System Software Efforts in HPC Ecosystem
4

Stable HPC Platform Software that:
Fuels a vibrant and efficient HPC software ecosystem
Takes advantage of hardware innovation & drives revolutionary technologies
Eases traditional HPC application development and testing at scale
Extends to new workloads (ML, analytics, big data)
Accommodates new environments (i.e., cloud)
A Shared Repository
Community Effort to Realize Desired Future State
5

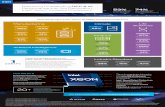
Intel® HPC Orchestrator
• Open Source Community under Linux Foundation
• Ecosystem innovation building a consistent HPC SW Platform
• Platform agnostic
• Multiple distributions
Intel Scalable System Framework
• Intel’s distribution of OpenHPC
• Expose best performance for Intel HW
• Advanced testing & premium features
• Product technical support & validated updates
OpenHPC* to Intel® HPC Orchestrator to
Intel® Scalable System Framework
6
OpenHPC

Small Clusters Through Supercomputers
Compute and Data-Centric Computing
Standards-Based Programmability
On-Premise and Cloud-Based
Intel® Xeon® Processors
Intel® Xeon Phi™ Processors
Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessors
Intel® Server Boards & Platforms
Intel® Solutions for Lustre*
Intel® Optane™ Technology
3D XPoint™ Technology
Intel® SSDs
Intel® Omni-Path Architecture
Intel® True Scale Fabric
Intel® Ethernet
Intel® Silicon Photonics
Intel® HPC Orchestrator
Intel® Software Development Tools
Intel Supported SDVis
Intel® Scalable System FrameworkA Holistic Design Solution for all HPC needs
7

8
Intel® HPC Orchestrator Overview

9
High Performance Computing Terminology
Term Definition
Head Node Main Admin interface to the system, orchestrates the rest of the system
Compute Node Nodes dedicated to the batch processing of user applications
Login Nodes Main User interface to the system, for job submission, compiles, etc.
Router Nodes Centralized connectivity to filesystems and networks external to the system
Management Control Nodes
Nodes that take some of the responsibilities of the Head Node and distribute and parallelize them across the system allowing for additional scaling
FabricHigh performance/Low latency network utilized primarily by user apps, and for access to parallel filesystems (Lustre*)
Management Network
Network over which the Head Node controls the rest of the system. Used for Provisioning,Resource Management, Time Synchronization, etc.
Power Control / Console Network
An optional additional network for security to isolate power and console functions from the user accessible parts of the system

Operator Interface Applications (not part of the stack initially)
Fa
bri
c M
gt
Sy
ste
m D
iag
no
stic
s
Pro
vis
ion
ing
Sy
ste
m M
an
ag
em
en
t(C
on
fig
, In
ve
nto
ry)
Data Collection
AndSystem
Monitors
DB Schema
WorkloadManager
OptimizedI/O
Libraries Scalable Debugging
& PerfAnalysis
Tools
High Performance
Parallel Libraries
SoftwareDevelopment
Toolchain
User SpaceUtilities
Scalable DB
ResourceMgmnt
Runtimes
I/O Services
Compiler and Programming-
Model Runtimes
Overlay & Pub-Sub Networks, Identity
Linux Distro Runtime Libraries
Node-specific OS Kernel(s)
ISV Applications
Hardware
10
Intel® HPC Orchestrator Overview• Intra-stack APIs for customization/differentiation (OEMs)• Defined external APIs for consistency across versions (ISVs)

11
Perimeter
PrivilegedAccess
UserAccess
Eth
Fabric
Planned
DB
Router Nodes
NFS / LAN / Internet
Head Node •Provisioning•Resource Management•Fabric Manager•Power Control•Console Access•Monitoring
Login Nodes
Lustre Parallel File System
Intel® HPC Orchestrator System Architecture

12
Intel® HPC Orchestrator Highlights
What How
Provisioning Method Image based (vs Package based)
Provisioning Time (128 nodes) ~4-5 Minutes
Configuration Site-specific inputs (IP addresses, MAC addresses, BMC addresses, Provisioning interface, etc.)
Supported Distros Red Hat Enterprise Linux* - RHEL 7.2SUSE Linux Enterprise Server* - SLES12 SP1
Install Procedure Fully scripted, Intel distributes iso
Component Distribution Standard YUM/Zypper RPM repository
Install Interface Command line

13
Functional Areas Components
Base OS compatibility RHEL 7.2, SLES12 SP1, CentOS 7.2
Administrative Tools Conman, Ganglia, Intel® Cluster Checker, Lmod, Losf, Nagios, pdsh, prun
Provisioning Warewulf
Resource Mgmt Slurm, Munge
I/O Services Lustre* Client (Intel® Enterprise Edition for Lustre* software)
Numerical/Scientific Libraries Boost, GSL, FFTW, Metis, PETSc, Trilinos, Hypre, SuperLU, Mumps, Intel MKL**
I/O Libraries HDF5 (pHDF5), NetCDF (incl C++ & Fortran libraries), Adios
Compiler Families GNU (gcc, g++, gfortran), Intel Parallel Studio XE (icc, icpc, ifort)**
MPI Families OpenMPI, MVAPICH2, Intel MPI**
Development Tools Autotools (autoconf, automake, libtool), Valgrind, R, SciPy, Numpy
Performance Tools PAPI, Intel IMB**, mpiP, pdtoolkit, TAU, Intel Advisor**, Intel Trace Analyzer & Collector**, Intel Vtune Amplifier**
Intel® HPC Orchestrator High-Level Component List
** Additional license required

• Advanced integration testing & extensive validation
• Professional support for- All Intel components
- Components where Intel maintains a support contract
• Best effort support for all other components
• Enhanced documentation- Readme, Release Notes
- Components Guide
- Troubleshooting Guide, including Knowledge Base
- Technical Update
- Security Best Practices
- Architecture
Intel® HPC Orchestrator Enhancements
14

Intel® HPC Orchestrator Enhancements
• Validated patches & updates
• Early new hardware integration with System Software
• Inclusion of proprietary Intel Software- Intel® Parallel Studio XE 2017 Cluster Edition
- Intel® Enterprise Edition for Lustre* software (client)
• SLES 12 SP1 Base OS redistribution
• Integrated Test Suite
• Intel® Cluster Checker Baseline Extensions
• Planned Additional components- Support for high availability
- Visualization tools
15

16
Intel® Cluster Checker Baseline Extensions
• New set of extensions to Intel® Cluster Checker
• Baseline: system data collected when it is in a good, dependable state
• Collects baseline data for:
• RPMs
• Virtual Node File System
• Configuration files (along with whitelist/blacklist capabilities)
• Hardware/Firmware
• Compare current state of system with baseline

17
Intel® Cluster Checker Baseline Extensions
• Collecting RPM baseline data
- Create nodefile
# cat nodefile
- Run rpm-baseline command
# rpm-baseline –f <path-to-nodefile>
- Data captured in
/var/tmp/rpms-baseline.txt
[sms]# cat nodefilesms #role: headc1c2
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/rpms-baseline.txtsms, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c1, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c2, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...
Node name
Architecture
Release
Version
RPM name
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/rpms-baseline.txtsms, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c1, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c2, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/rpms-baseline.txtsms, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c1, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c2, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/rpms-baseline.txtsms, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c1, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c2, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/rpms-baseline.txtsms, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c1, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c2, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/rpms-baseline.txtsms, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c1, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...c2, libpciaccess 0.13.4 2.el7 x86_64...

18
Intel® Cluster Checker Baseline Extensions
• Collecting Files baseline data
# files-baseline –f <path-to-nodefile>
Data captured in /var/tmp/files-baseline.txt
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/files-baseline.txtsms, /etc/sysconfig/httpd, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 65947590cfc1df04aebc4df81983e1f5..c1, /etc/os-release, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 1359aa3db05a408808522a89913371f3...c2, /etc/sysconfig/munge, -rw-r--r--, root, root, e0505efde717144b039329a6d32a798f..
Permissions
Owner Group MD5 SumFile
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/files-baseline.txtsms, /etc/sysconfig/httpd, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 65947590cfc1df04aebc4df81983e1f5..c1, /etc/os-release, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 1359aa3db05a408808522a89913371f3...c2, /etc/sysconfig/munge, -rw-r--r--, root, root, e0505efde717144b039329a6d32a798f..
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/files-baseline.txtsms, /etc/sysconfig/httpd, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 65947590cfc1df04aebc4df81983e1f5..c1, /etc/os-release, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 1359aa3db05a408808522a89913371f3...c2, /etc/sysconfig/munge, -rw-r--r--, root, root, e0505efde717144b039329a6d32a798f..
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/files-baseline.txtsms, /etc/sysconfig/httpd, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 65947590cfc1df04aebc4df81983e1f5..c1, /etc/os-release, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 1359aa3db05a408808522a89913371f3...c2, /etc/sysconfig/munge, -rw-r--r--, root, root, e0505efde717144b039329a6d32a798f..
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/files-baseline.txtsms, /etc/sysconfig/httpd, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 65947590cfc1df04aebc4df81983e1f5..c1, /etc/os-release, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 1359aa3db05a408808522a89913371f3...c2, /etc/sysconfig/munge, -rw-r--r--, root, root, e0505efde717144b039329a6d32a798f..
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/files-baseline.txtsms, /etc/sysconfig/httpd, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 65947590cfc1df04aebc4df81983e1f5..c1, /etc/os-release, -rw-r--r--, root, root, 1359aa3db05a408808522a89913371f3...c2, /etc/sysconfig/munge, -rw-r--r--, root, root, e0505efde717144b039329a6d32a798f..

19
Intel® Cluster Checker Baseline Extensions
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/hw-baseline.txtsms, 00:0d.0, Intel Corporation 82801HM/HEM (ICH8M/ICH8M-E) SATA Controller [AHCI mode]..c1, 00:03.0, Intel Corporation 82540EM Gigabit Ethernet Controllerc1, 00:07.0, Intel Corporation 82371AB/EB/MB PIIX4 ACPI..c2, 00:05.0, Intel Corporation 82801AA AC’97 Audio Controller..
Hardware descriptionBus:Device.Function
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/hw-baseline.txtsms, 00:0d.0, Intel Corporation 82801HM/HEM (ICH8M/ICH8M-E) SATA Controller [AHCI mode]..c1, 00:03.0, Intel Corporation 82540EM Gigabit Ethernet Controllerc1, 00:07.0, Intel Corporation 82371AB/EB/MB PIIX4 ACPI..c2, 00:05.0, Intel Corporation 82801AA AC’97 Audio Controller..
[sms]# cat /var/tmp/hw-baseline.txtsms, 00:0d.0, Intel Corporation 82801HM/HEM (ICH8M/ICH8M-E) SATA Controller [AHCI mode]..c1, 00:03.0, Intel Corporation 82540EM Gigabit Ethernet Controllerc1, 00:07.0, Intel Corporation 82371AB/EB/MB PIIX4 ACPI..c2, 00:05.0, Intel Corporation 82801AA AC’97 Audio Controller..
• Collecting Hardware baseline data
# hw-baseline –f <path-to-nodefile>
Data captured in /var/tmp/hw-baseline.txt

20
Intel® Cluster Checker Baseline Extensions
• Comparing/Analyzing:
- Collect current system state
# clck-collect –f <path-to-nodefile> –m uname –m files_head –m files_comp
- Analyze current system state against baseline
# clck-analyze –f <path-to-nodefile> –I files
1 undiagnosed sign:
1. The file /etc/pam.d/ppp has been added since the baseline was generated.[ Id: files-added ][ Severity: 25%; Confidence: 90% ][ Node: RHEL2 ]
This analysis took 0.388902 seconds.
FAIL: All checks did not pass in health mode.
1 undiagnosed sign:
1. The file /etc/pam.d/ppp has been added since the baseline was generated.[ Id: files-added ][ Severity: 25%; Confidence: 90% ][ Node: RHEL2 ]
This analysis took 0.388902 seconds.
FAIL: All checks did not pass in health mode.

21
Installation

Install Guide - CentOS7.1 Version (v1.0)
eth1eth0
Data
Center
Network
high speed network
tcp networking
to compute eth interface
to compute BMC interface
compute
nodes
Lustre* storage system
Master
(SMS)
Figure 1: Overview of physical cluster architecture.
the local data center network and eth1 used to provision and manage the cluster backend (note that these
interface names are examples and may be di↵erent depending on local set t ings and OS convent ions). Two
logical IP interfaces are expected to each compute node: the first is the standard Ethernet interface that
will be used for provisioning and resource management . The second is used to connect to each host ’s BMC
and is used for power management and remote console access. Physical connect ivity for these two logical
IP networks is often accommodated via separate cabling and switching infrast ructure; however, an alternate
configurat ion can also be accommodated via the use of a shared NIC, which runs a packet filter to divert
management packets between the host and BMC.
In addit ion to the IP networking, there is a high-speed network (InfiniBand in this recipe) that is also
connected to each of thehosts. Thishigh speed network isused for applicat ion messagepassing and opt ionally
for Lustre connect ivity as well.
1.3 Br ing your own license
OpenHPC provides a variety of integrated, pre-packaged elements from the Intel® Parallel Studio XE soft -
ware suite. Port ions of the runt imes provided by the included compilers and MPI components are freely
usable. However, in order to compile new binaries using these tools (or access other analysis tools like
Intel® Trace Analyzer and Collector, Intel® Inspector, etc), you will need to provide your own valid license
and OpenHPC adopts a bring-your-own-license model. Note that licenses are provided free of charge for
many categories of use. In part icular, licenses for compilers and developments tools are provided at no cost
to academic researchers or developers contribut ing to open-source software projects. More informat ion on
this program can be found at :
ht tps:/ / software.intel.com/ en-us/ qualify-for-free-software
1.4 Input s
As this recipe details installing a cluster start ing from bare-metal, there is a requirement to define IP ad-
dresses and gather hardware MAC addresses in order to support a controlled provisioning process. These
values are necessarily unique to the hardware being used, and this document uses variable subst itut ion
(${ var i abl e} ) in the command-line examples that follow to highlight where local site inputs are required.
A summary of the required and opt ional variables used throughout this recipe are presented below. Note
6 Rev: bf8c471
1Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE)
Basic Cluster Install Example
• Starting install guide/recipe targeted for flat hierarchy
• Leverages image-based provisioner(Warewulf)
- PXE1 boot (stateless)
- optionally connect external Lustre*
file system
• Obviously need hardware-specific information to support (remote) bare-metal provisioning
22

23
Installation
• Walks a system administrator through the various steps needed to bootstrap a cluster
• Ease of Use:
• Describes what needs to be accomplished
• Followed by example commands
• Copy & paste the commands with site-specific inputs
• For faster integration:
• Edit site specific inputs file
• Execute install script
Site-Specific Inputs + Install Script = Cluster

24
Minimum Requirements – Hardware & Software
• 1 head node, at least 2 compute nodes: can ping each other
• Head node and compute nodes are clustered using Ethernet (if not fabric)
• Support at least one network file system: NFS (or) Lustre*
• Mechanism to boot the compute nodes: IPMI (or) Physical access to compute nodes
• Pre-defined local site inputs
• Hostnames for head & compute nodes
• IP & MAC addresses for head node & all compute nodes
• Name of interface that will be used for provisioning
• Subnet netmask for internal network

25
Install Script Expectations
• 1 head node that hosts an NFS file system, 4 stateless compute nodes
• IPMI can talk to the compute node BMCs
• Head node has 2 Eth interfaces
• eth0 to ensure external network connectivity• eth1 to provision/manage cluster
• 2 logical IP interfaces to each compute node
• 1st for provisioning & resource management• 2nd to connect to BMCs
Wherever expectations!= system setup, editing the install script will be necessary

26
Installation using the iso file
[root@localhost Desktop]# mkdir /mnt/hpc_orch_iso
[root@localhost Desktop]# mount -o loop hpc-orchestrator-rhel7.2-16.01.003.beta.iso /mnt/hpc_orch_iso/
[root@localhost Desktop]# cd /mnt/hpc_orch_iso/
[root@localhost Desktop]# lsgroup.xml noarch repodata x86_64
[root@localhost Desktop]# rpm -ivh x86_64/Intel_HPC_Orchestrator_release-16.01.003.beta-6.1.x6_64.rpm
[root@localhost Desktop]# yum -y install docs-orch-16.01.003.beta-58.1.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost Desktop]# cp -p /opt/intel/hpc-orchestrator/pub/doc/recipes/vanilla/input.local .[root@localhost Desktop]# cp -p /opt/intel/hpc-orchestrator/pub/doc/recipes/vanilla/recipe.sh .[root@localhost Desktop]# mkdir sections[root@localhost Desktop]# cp -p /opt/intel/hpc-orchestrator/pub/doc/recipes/vanilla/sections/* sections/
[root@localhost Desktop]# export INPUT_LOCAL=./input.local
[root@localhost Desktop]# ./recipe.sh -f

27
Directory Structure
images
lmod
clck
doc
modulefiles
examples
[root@localhost Desktop]# cd /opt/intel/hpc-orchestrator
[root@localhost Desktop]# ls
admin pub
NFS Mountedmodulefiles
advisor
compiler
inspector
mpi

Integration/Test/Validation
OS Distribution
Hardware +
Integrated Cluster Testing
+
Dev Tools
Parallel Libs
Perf. Tools
User Env
MiniApps
Serial Libs
System
Tools
Resource
Manager
Provisioner
I/O Libs
Compilers
Software
OpenHPC
Individual Component Validation
Hardware
Intel® HPC Orchestrator
OS Distribution
OS Distribution
Hardware +
Integrated Cluster Testing
+
Dev Tools
Parallel Libs
Perf. Tools
User Env
MiniApps
Serial Libs
System
Tools
Resource
Manager
Provisioner
I/O Libs
Compilers
Software
OpenHPC
Individual Component Validation
• Cross-package interaction
• Each end-user test need to touch all of the supported compiler & MPI families
• Abstracted to repeat the tests with different compiler/MPI environments:
• gcc/Intel compiler toolchains
• Intel, OpenMPI, MVAPICH2 MPI families
28

Post Install Integration Tests - Overview
• Major components have configuration options to enable/disable
• Suite of integration tests
• Installed by default by the install script
• Root-level tests
• User-level tests: short & long versions
------------------------------------------------------------Type of test | Approximate running time------------------------------------------------------------Root-level | single digit number of minutesUser-level short | less than 30 minutesUser-level long | a few hours ------------------------------------------------------------
29
ProvisioningOOB
MgmtO/S
Config
Mgmt.
Resource
Manager
User
EnvFabric
Node-Level
PerfI/O
3rd Party
LibsApps
Root Level User Space

Post Install Integration Tests – Root level tests
300

Post Install Integration Tests – User level tests
311

OEMs – reduce R&D
ISVs/Developers – reduce time and resources to constantly retest apps
IT Admins - reduce R&D to build and maintain a fully integrated SW stack
End Users - hardware innovation reflected in SW faster on path to exascale
Benefits
• Integrated open source and proprietary components• Modular build; Customizable; Validated updates• Advanced integration testing, testing at scale• Level 3 technical support provided by Intel• Optimization for Intel® Scalable System Framework components• Available through OEM & Channel Partners in Q4’16
Intel® HPC Orchestrator: Summary
322

333