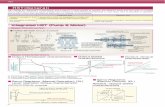
Lab #7 Integumentary System. Overview of the Integumentary System.
Integumentary System Exam HST III 2009-2010. Matching Match the following pictures with the correct...
-
Upload
reynold-carpenter -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
2
Transcript of Integumentary System Exam HST III 2009-2010. Matching Match the following pictures with the correct...

Integumentary System Exam
HST III 2009-2010

Matching
• Match the following pictures with the correct key term.

Key Terms
• Erythema
• Chronic Poisoning
• Cyanosis
• Jaundice
• Albino

1. reddish color that can be caused by burns or a congestion of blood in the vessels

2. Absence of melanin or pigments in the skin
•Skin has pinkish tint
•Hair is pale yellow or white
•Eyes lack pigment; are red; very sensitive to light

3. bluish discoloration caused by insufficient oxygen; associated with heart, lung, and circulatory diseases or disorders

4. may cause gray or brown skin discoloration

5. yellow discoloration; indicates bile in the blood resulting from liver and gallbladder disease; also seen in diseases that involve destruction of RBC

Fill in the Blank
• Complete the following passages using the following key terms.
• Membrane
• Organ
• Hypodermis
• Dermis
• Epidermis

Considered to be both:
• ___6______ – covers the body
• ____7_____contains several types of tissue– Largest organ in body -
covering (c) 3,000 square inches
– About (d) 15% total body weight

Tissue:
_____8______the innermost layer
• Made of:
• Elastic and fibrous connective tissue
• Adipose (fatty) tissue
• Connects the skin to underlying muscles

Tissue:• 3 layers of tissue
1. _____9______outermost layer of skin• (f) NO blood vessels or nerve cells
(avascular)2. _____10_____ corium or “true skin”• Includes:–Elastic connective tissue–Blood vessels–Lymph vessels–Nerves– Involuntary muscle–Sweat and oil glands–Hair follicles

True/False
• On your answer sheet, mark whether the following statements are true or false.

11. Sweat is odorless until it interacts with bacteria on the skin
12. Perspiration (sweating) removes excess water from the body and cools the body
13. Another name for the sweat glands is the sebaceous glands
14. The sebaceous glands produce sebum which keep the hair from becoming brittle and dry
15. The hair shaft covers the entire body except the palms of the hands, and the soles of the feet

Completion
• Use your knowledge of the integumentary system to answer the following questions.

16. What is the definition of a follicle?
17. What is the name of the skin condition, that is genetically inherited,
permanent hair loss?

18. What part of the integumentary system is made up of dead, keratinized epithelial cells?
19. Name the 7 functions of the skin.

20. What happens when blood vessels in the skin dilate? Constrict? Explain

21. The definition of primary skin lesions is:
A. Result from changes in the original lesion, usually related to the disease process.
B. Appear on previously healthy skin in response to disease or external irritation.
C. Is the first skin lesion a person ever develops.
D. None of the above.

22. Flat spots on the skin, such as freckles are:
A. Macules
B. Papules
C. Pustules
D. Vesicles

23. Firm, raised areas such as pimples are:
A. Macules
B. Papules
C. Pustules
D. Vesicles

24. Blisters, or fluid-filled sacs, such as those seen in chickenpox are called:
A. Vesicles
B. Comedo
C. Bulla
D. Pustules

25. Plugged pilosebaceous duct, formed from sebum and keratin is called:
A. Vesicles
B. Comedo
C. Bulla
D. Pustules

26. Pus-filled sacs such as those seen in acne are known as:
A. Vesicles
B. Comedo
C. Bulla
D. Pustules

27. Fluid filled lesion greater than 2cm in diameter; caused by severe poison oak or ivy dermatitis
A. Vesicles
B. Comedo
C. Bulla
D. Pustules

28. Semi-solid or fluid-filled encapsulated mass extending deep into the dermis is known as:
A. Cyst
B. Nodule
C. Patch
D. Plaque

29. Firm, raised lesion; extending into dermal layer is known as:
A. Cyst
B. Nodule
C. Patch
D. Plaque

30. A ______is described as a flat, pigmented, circumscribed area
greater than 1cm in diameter
A. Patch
B. Plaque
C. Wheal
D. Tumor

31. Itchy, elevated areas with an irregular shape are known as:
A. Patch
B. Plaque
C. Wheal
D. Tumor

32. _______ are described as Elevated, solid lesion larger than 2cm in diameter, extending into dermal and subcutaneous layers.
A. Patch
B. Plaque
C. Wheal
D. Tumor

33. A _______ is described as a circumscribed, solid, elevated lesion greater than 1cm in diameter
A. Patch
B. Plaque
C. Wheal
D. Tumor

34. _______ is defined as a deep loss of skin surface that may extend
into the dermis
A. Ulcer
B. Crusts
C. Atrophy
D. Erosion

35. _______ are areas of dried pus and blood, commonly called scabs
A. Ulcer
B. Crusts
C. Atrophy
D. Erosion

36. __________ is a circumscribed lesion involving loss of superficial epidermis
A. Ulcer
B. Crusts
C. Atrophy
D. Erosion

37. __________ is defined as Thinning of skin surface at site of disorder. An example is aging skin.
A. Ulcer
B. Crusts
C. Atrophy
D. Erosion

38. Thick, red, or dark firm scar formed by hyperplasia of fibrous
tissue is known as:
A. Excoriation
B. Fissure
C. Keloid
D. Lichenification

39. __________ are linear scratched
or abraded areas, often self-induced.
A. Excoriation
B. Fissure
C. Keloid
D. Lichenification

40. Linear cracking of the skin, extending into the dermal layer is
known as:
A. Excoriation
B. Fissure
C. Keloid
D. Lichenification

41. __________ is defined as Thickened, prominent skin markings caused by constant rubbing.
A. Excoriation
B. Fissure
C. Keloid
D. Lichenification

42. Thin, dry flakes of shedding skin; for example psoriasis are known as:
A. Scar
B. Fissure
C. Scale
D. Lichenification

43. Fibrous tissue caused by trauma, deep inflammation, or surgical incision is known as:
A. Scar
B. Fissure
C. Scale
D. Lichenification

44. The most common type of cancer is:
A. Melanoma
B. Skin cancer
C. Basal cell carcinoma
D. Squamous cell carcinoma

45. Melanoma:
A. Affects the thin cells of the epithelium, and spreads quickly
B. Is cancer of the basal cells in the epidermis
C. Is not a form of cancer at all
D. Develops in the melanocytes and is the most dangerous type of skin cancer.

Matching
• Match the following pictures with the correct key term.

Key Terms
• Eczema
• Psoriasis
• Impetigo
• Ringworm
• Tinea
• Scabies
• Warts
• Athlete’s Foot
• Acne
• Scleroderma

46. inflammation of the sebaceous glands

47. noncontagious, inflammatory skin disorder caused by allergens or irritants

48. contagious fungal infection that usually affects the feet

49. highly contagious fungal infection of the skin or scalp

50. Highly contagious condition resulting from staphylococcus or streptococcal infection

51. general name for many different types of mycoses

52. chronic, noncontagious skin disease with periods of exacerbations (symptoms present) and remission (decrease or disappearance of symptoms)

53. caused by papilloma virus; type of benign neoplasm of the skin;

54. contagious skin condition caused by the itch mite

55. an autoimmune disease that affects the blood vessels and connective tissue of the skin;

Bonus Points
• Using the following scenario, write a SOAP note.

Scenario
• Mr. Roberto Cavaelli, age 52, is a single Caucasian male fashion designer. He has noted changes in his skin over the past 3 months. He states that he has been under a lot of stress with fashion week coming up, and has noticed some blackheads forming on his face and upper chest.
• He also states that he visited a new country club last week, and since then his feet have had a burning sensation, and are very itchy.
• He states that he sunbathes regularly.

• Patient is found to have a few blackheads and whiteheads on this cheeks and forehead with a discrete amount being present on his chest and upper back.
• His skin is noted to have poor skin turgor, and is dry and leathery to touch. His mucous membranes are pink and moist, and his nails are clean and well kempt.
• His feet are reddened around the soles and in between the toes, with scaling and hard thickened skin in some area from rubbing, along with linear abraded areas from scratching.