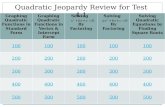
Holt Algebra 2 5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form 2.1 a and b Finding the vertex...
-
Upload
susana-lestrange -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
2
Transcript of Holt Algebra 2 5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form 2.1 a and b Finding the vertex...

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
2.1 a and b
Finding the vertex and y-intercept from standard form
Graphing in standard form

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
These properties can be generalized to help you graph quadratic functions.

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
When a is positive, the parabola is happy (U). When the a negative, the parabola is sad ( ).
Helpful Hint
U
The Axis of Symmetry is the same as the x-coordinate of the vertex.

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Consider the function f(x) = 2x2 – 4x + 5.
Example 2A: Graphing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
a. Determine whether the graph opens upward or downward.
b. Find the axis of symmetry.
Because a is positive, the parabola opens upward.
The axis of symmetry is the line x = 1.
Substitute –4 for b and 2 for a.
The axis of symmetry is given by .

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Consider the function f(x) = 2x2 – 4x + 5.
Example 2A: Graphing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
c. Find the vertex.
The vertex lies on the axis of symmetry, so the x-coordinate is 1. The y-coordinate is the value of the function at this x-value, or f(1).
f(1) = 2(1)2 – 4(1) + 5 = 3
The vertex is (1, 3).
d. Find the y-intercept.
Because c = 5, the intercept is 5.

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Consider the function f(x) = 2x2 – 4x + 5.
Example 2A: Graphing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
e. Graph the function.Graph by making a table of values with the x-coordinate of the vertex in the center.
x f(x) y
-1 11
0 5
1 (vert) 3
2 5
3 11

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Consider the function f(x) = –x2 – 2x + 3.
Example 2B: Graphing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
a. Determine whether the graph opens upward or downward.
b. Find the axis of symmetry.
Because a is negative, the parabola opens downward.
The axis of symmetry is the line x = –1.
Substitute –2 for b and –1 for a.
The axis of symmetry is given by .

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Example 2B: Graphing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
c. Find the vertex.
The vertex lies on the axis of symmetry, so the x-coordinate is –1. The y-coordinate is the value of the function at this x-value, or f(–1).
f(–1) = –(–1)2 – 2(–1) + 3 = 4
The vertex is (–1, 4).
d. Find the y-intercept.
Because c = 3, the y-intercept is 3.
Consider the function f(x) = –x2 – 2x + 3.

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Example 2B: Graphing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
e. Graph the function.Graph by making a table of values with the x-coordinate of the vertex in the center.
Consider the function f(x) = –x2 – 2x + 3.
x f(x) y
-3 0
-2 3
-1 (vert) 4
0 3
1 0

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
For the function, (a) determine whether the graph opens upward or downward, (b) find the axis of symmetry, (c) find the vertex, (d) find the y-intercept, and (e) graph the function.
a. Because a is negative, the parabola opens downward.
The axis of symmetry is the line x = –1.
Substitute –4 for b and –2 for a.
Check It Out! Example 2a
f(x)= –2x2 – 4x
b. The axis of symmetry is given by .

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
c. The vertex lies on the axis of symmetry, so the x-coordinate is –1. The y-coordinate is the value of the function at this x-value, or f(–1).
f(–1) = –2(–1)2 – 4(–1) = 2
The vertex is (–1, 2).
d. Because c is 0, the y-intercept is 0.
Check It Out! Example 2a
f(x)= –2x2 – 4x

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
e. Graph the function.Graph by making a table of values with the x-coordinate of the vertex in the center.
Check It Out! Example 2a
f(x)= –2x2 – 4x
x f(x) y
-3 -6
-2 0
-1 (vert) 2
0 0
1 -6

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
g(x)= x2 + 3x – 1.
a. Because a is positive, the parabola opens upward.
Substitute 3 for b and 1 for a.
b. The axis of symmetry is given by .
Check It Out! Example 2b
The axis of symmetry is the line .
For the function, (a) determine whether the graph opens upward or downward, (b) find the axis of symmetry, (c) find the vertex, (d) find the y-intercept, and (e) graph the function.

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
d. Because c = –1, the intercept is –1.
Check It Out! Example 2b
c. The vertex lies on the axis of symmetry, so the x-coordinate is . The y-coordinate is the value of the function at this x-value, or f( ).
f( ) = ( )2 + 3( ) – 1 =
The vertex is ( , ).
g(x)= x2 + 3x – 1

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
e. Graph the function.Graph by making a table of values with the x-coordinate of the vertex in the center.
Check It Out! Example2
x f(x) y
-3 -1
-2 -3
(vert)
-1 -3
0 -1
g(x)= x2 + 3x – 1

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Lesson Quiz: Part I
1. Determine whether the graph opens upward or downward.
2. Find the axis of symmetry.
3. Find the vertex.
4. Identify the maximum or minimum value of the
function.
5. Find the y-intercept.
x = –1.5
upward
(–1.5, –11.5)
Consider the function f(x)= 2x2 + 6x – 7.
min.: –11.5
–7

Holt Algebra 2
5-2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
Lesson Quiz: Part II
Consider the function f(x)= 2x2 + 6x – 7.
6. Graph the function.
By making a table