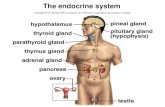
Glands of the Endocrine System
-
Upload
ephraim-jamin -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
0
Transcript of Glands of the Endocrine System
-
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
1/15
Hypothalamus
Secreted hormone Abbreviation Produced by Effect
Thyrotropin-
releasing hormone
(Prolactin-releasing
hormone)
TRH,, orParvocellular
neurosecretory neurons
Stimulatethyroid-stimulating
hormone (TSH) released
fromanterior pituitary (primarily)
Stimulateprolactinrelease
from anterior pituitary
Dopamine
(Prolactin-inhibiting
hormone)
DA or PIHDopamine neurons of
the arcuate nucleus
Inhibitprolactinreleased
from anterior pituitary
Growth hormone-
releasing hormoneGHRH
Neuroendocrineneurons
of theArcuate nucleus
StimulateGrowth hormone
(GH)release from anterior pituitary
Somatostatin
(growth hormone-
inhibiting hormone)
SS, GHIH, or
SRIF
Neuroendocrine cells of
thePeriventricular
nucleus
InhibitGrowth hormone
(GH)release from anterior pituitary
Inhibitthyroid-stimulating hormone
(TSH)release from anterior
pituitary
Gonadotropin-
releasing hormone
GnRH or
LHRH
Neuroendocrine cells of
thePreoptic area
Stimulatefollicle-stimulating
hormone () release from anterior
pituitary
Stimulateluteinizing hormone
(LH)release fromanterior pituitary
Corticotropin-
releasing hormone CRH or CRF
Parvocellular
neurosecretory neurons
or the Paraventricular
Nucleus
Stimulateadrenocorticotropic
hormone (ACTH) releasefromanterior pituitary
Oxytocin OT or OXT Magnocellular
neurosecretory neurons
of the Supraoptic
Uterine contraction
Lactation (letdown reflex)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyrotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyrotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dopaminehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcuate_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcuate_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormone-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormone-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroendocrinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcuate_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcuate_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somatostatinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroendocrinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Periventricular_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Periventricular_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Periventricular_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonadotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonadotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroendocrinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Preoptic_areahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Preoptic_areahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luteinizing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luteinizing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luteinizing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luteinizing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenocorticotropic_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenocorticotropic_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenocorticotropic_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxytocinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Supraoptic_Nucleus_and_Paraventricular_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Supraoptic_Nucleus_and_Paraventricular_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Supraoptic_Nucleus_and_Paraventricular_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterine_contractionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Letdown_reflexhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyrotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyrotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dopaminehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcuate_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcuate_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormone-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormone-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroendocrinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcuate_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somatostatinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroendocrinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Periventricular_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Periventricular_nucleushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonadotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonadotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroendocrinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Preoptic_areahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luteinizing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luteinizing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticotropin-releasing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenocorticotropic_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenocorticotropic_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxytocinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Supraoptic_Nucleus_and_Paraventricular_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Supraoptic_Nucleus_and_Paraventricular_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterine_contractionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Letdown_reflex -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
2/15
Nucleus and
Paraventricular Nucleus
Vasopressin
(antidiuretic
hormone)
ADH or AVP
or VP
Parvocellularneurosecretory neurons,
Magnocellular
neurosecretory neurons
of the Paraventricular
Nucleus and Supraoptic
Nucleus
Increases water permeability in the
distal convoluted tubule and
collecting duct ofnephrons, thus
promoting water reabsorption and
increasing blood volume
Melanocyte Releasing Hormone (MRH) Stimulates the secretion of Melanocyte-stimulating
hormone from intermediate pituitary lobe.
[edit]Pineal body (epiphysis)
Secreted hormone From cells Effect
Melatonin Pinealocytes
Antioxidant
Monitors the circadian rhythm including
inducement ofdrowsinessand lowering of
the middle body temperaturesleep cycle
[edit]Pituitary Gland(hypophysis)[edit]Anterior pituitary lobe (adenohypophysis)
Secreted hormone Abbreviation From cells Effect
Growth hormone
(somatotropin)GH Somatotrophs
Stimulatesgrowthand cell reproduction
StimulatesInsulin-like growth factor 1 release from live
Thyroid-stimulatinghormone
(thyrotropin)
TSH ThyrotrophsStimulatesthyroxine (T4) andtriiodothyronine (T3) syntand release from thyroid gland
Stimulates iodine absorption by thyroid gland
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Supraoptic_Nucleus_and_Paraventricular_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Supraoptic_Nucleus_and_Paraventricular_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasopressinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Parvocellular_neurosecretory_neurons,_Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Paraventricular_Nucleus_and_Supraoptic_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Parvocellular_neurosecretory_neurons,_Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Paraventricular_Nucleus_and_Supraoptic_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Parvocellular_neurosecretory_neurons,_Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Paraventricular_Nucleus_and_Supraoptic_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Parvocellular_neurosecretory_neurons,_Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Paraventricular_Nucleus_and_Supraoptic_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Parvocellular_neurosecretory_neurons,_Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Paraventricular_Nucleus_and_Supraoptic_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Parvocellular_neurosecretory_neurons,_Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Paraventricular_Nucleus_and_Supraoptic_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Parvocellular_neurosecretory_neurons,_Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Paraventricular_Nucleus_and_Supraoptic_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephronshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=4http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=4http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pineal_bodyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melatoninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pinealocyteshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antioxidanthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circadian_rhythmhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drowsinesshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Middle_body_temperature&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sleep_cyclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sleep_cyclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=5http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=5http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pituitary_Glandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pituitary_Glandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=6http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=6http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somatotrophhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_development_(biology)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_development_(biology)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_development_(biology)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_(biology)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin-like_growth_factor_1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin-like_growth_factor_1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liverhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Thyrotroph&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroxinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroxinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triiodothyroninehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triiodothyroninehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_glandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Supraoptic_Nucleus_and_Paraventricular_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Supraoptic_Nucleus_and_Paraventricular_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasopressinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Parvocellular_neurosecretory_neurons,_Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Paraventricular_Nucleus_and_Supraoptic_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Parvocellular_neurosecretory_neurons,_Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Paraventricular_Nucleus_and_Supraoptic_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Parvocellular_neurosecretory_neurons,_Magnocellular_neurosecretory_neurons_of_the_Paraventricular_Nucleus_and_Supraoptic_Nucleus&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephronshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=4http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pineal_bodyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melatoninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pinealocyteshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antioxidanthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circadian_rhythmhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drowsinesshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Middle_body_temperature&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sleep_cyclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=5http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pituitary_Glandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=6http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somatotrophhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_development_(biology)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_(biology)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin-like_growth_factor_1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liverhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Thyrotroph&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroxinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triiodothyroninehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_gland -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
3/15
Adrenocorticotropic
hormone
(corticotropin)
ACTH CorticotrophsStimulatescorticosteroid (glucocorticoid andmineralco
andandrogen synthesis and release from adrenocortica
Beta-endorphin - Corticotrophs Inhibits perception of pain
Follicle-stimulating
hormoneFSH Gonadotrophs
In females: Stimulates maturation ofovarian folliclesin
In males: Stimulates maturation ofseminiferous tubules
In males: Stimulates spermatogenesis
In males: Stimulates production ofandrogen-binding
proteinfromSertoli cellsof the testes
Luteinizing
hormoneLH Gonadotrophs
In females: Stimulates ovulation
In females: Stimulates formation ofcorpus luteum
In males: Stimulates testosterone synthesis from Leydi
(interstitial cells)
Prolactin PRL LactotrophsStimulates milk synthesis and release from mammary g
Mediates sexual gratification
Melanocyte-
stimulating
hormone
MSH
MelanotropesinthePars
intermedia of
the Anterior
Pituitary
Stimulatesmelaninsynthesis and release from
skin/hairmelanocytes
[edit]Posterior pituitary lobe (neurohypophysis)
Secreted hormone Abbreviation From cells Effect
Oxytocin
Magnocellular
neurosecretory
cells
Uterine contraction
Lactation (letdown reflex)
Vasopressin
(antidiuretic
ADH or AVP Parvocellular
neurosecretory
Increases water permeability in the distal
convoluted tubule and collecting duct
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenocorticotropic_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenocorticotropic_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Corticotroph&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticosteroidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticosteroidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucocorticoidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mineralcorticoidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mineralcorticoidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_cortexhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta-endorphinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticotrophshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonadotrophhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovarian_folliclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovarian_folliclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seminiferous_tubulehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spermatogenesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgen-binding_proteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgen-binding_proteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgen-binding_proteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sertoli_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sertoli_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testeshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luteinizing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luteinizing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonadotrophhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovulationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corpus_luteumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corpus_luteumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leydig_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leydig_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactotrophhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mammary_glandshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orgasmhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanocyte-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanocyte-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanocyte-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanotropehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanotropehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pars_intermediahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pars_intermediahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melaninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melaninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melaninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanocyteshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=7http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=7http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Posterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxytocinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnocellular_neurosecretory_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnocellular_neurosecretory_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnocellular_neurosecretory_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterine_contractionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Letdown_reflexhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasopressinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenocorticotropic_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenocorticotropic_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Corticotroph&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticosteroidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucocorticoidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mineralcorticoidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_cortexhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta-endorphinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corticotrophshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonadotrophhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovarian_folliclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seminiferous_tubulehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spermatogenesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgen-binding_proteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgen-binding_proteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sertoli_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testeshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luteinizing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luteinizing_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonadotrophhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovulationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corpus_luteumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leydig_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leydig_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactotrophhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mammary_glandshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orgasmhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanocyte-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanocyte-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanocyte-stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanotropehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pars_intermediahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pars_intermediahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melaninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melanocyteshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=7http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Posterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxytocinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnocellular_neurosecretory_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnocellular_neurosecretory_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnocellular_neurosecretory_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterine_contractionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Letdown_reflexhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasopressinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamus -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
4/15
hormone) neuronsofnephrons, thus promoting water
reabsorption and increasing blood volume
Oxytocin and anti-diuretic hormone are not secreted in the posterior lobe, merely stored.
[edit]Thyroid
Secreted hormone Abbreviation From cells Effect
Triiodothyronine T3Thyroid
epithelial cell
(More potent form ofthyroid hormone)
Stimulates body oxygen and energy
consumption, thereby increasing thebasal
metabolic rate
Stimulates RNA polymeraseI and II, thereby
promotingprotein synthesis
Thyroxine
(tetraiodothyronine)T4
Thyroid
epithelial cells
(Less active form ofthyroid hormone)
(Acts as aprohormoneto triiodothyronine)
Stimulates body oxygen and energy
consumption, thereby increasing thebasal
metabolic rate
Stimulates RNA polymeraseI and II, thereby
promotingprotein synthesis
CalcitoninParafollicular
cells
Stimulates osteoblastsand thus bone
construction
Inhibits Ca2+ release from bone, thereby
reducing blood Ca2+
[edit]Alimentary system
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephronshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephronshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephronshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=8http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=8http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triiodothyroninehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_epithelial_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_epithelial_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_metabolic_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_metabolic_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_metabolic_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_polymerasehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_polymerasehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_synthesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_synthesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroxinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_epithelial_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_epithelial_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prohormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prohormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prohormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triiodothyroninehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_metabolic_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_metabolic_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_metabolic_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_polymerasehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_polymerasehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_synthesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_synthesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcitoninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parafollicular_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parafollicular_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calciumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calciumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=9http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=9http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paraventricular_nucleus_of_hypothalamushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephronshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=8http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triiodothyroninehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_epithelial_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_epithelial_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_metabolic_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_metabolic_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_polymerasehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_synthesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroxinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_epithelial_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_epithelial_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroid_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prohormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triiodothyroninehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_metabolic_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basal_metabolic_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_polymerasehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_synthesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcitoninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parafollicular_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parafollicular_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calciumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=9 -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
5/15
[edit]Stomach
Secreted
hormoneAbbreviation
From
cellsEffect
Gastrin (Primarily)G
cellsSecretion ofgastric acid by parietal cells
GhrelinP/D1
cells
Stimulateappetite,
secretion ofgrowth hormone from anterior pituitary gland
Neuropeptide Y NPYincreased food intake and decreased physical activity. It can
be associated with obesity.
SomatostatinD
cells
Suppress release
ofgastrin,cholecystokinin(CCK),secretin,motilin,vasoactive
intestinal peptide (VIP), gastric inhibitory
polypeptide (GIP), enteroglucagon
Lowers rate of gastric emptying Reduces smooth
musclecontractions and blood flow within the intestine.[1]
HistamineECL
cellsstimulate gastric acidsecretion
EndothelinX
cellsSmooth muscle contraction of stomach[2]
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=10http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=10http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomachhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastrinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastric_acidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parietal_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ghrelinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P/D1_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P/D1_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Appetitehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Appetitehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitary_glandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuropeptide_Yhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obesityhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somatostatinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Delta_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Delta_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastrinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystokininhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystokininhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystokininhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secretinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secretinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motilinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motilinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motilinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasoactive_intestinal_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasoactive_intestinal_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastric_inhibitory_polypeptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastric_inhibitory_polypeptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enteroglucagonhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-Colorado-0http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-Colorado-0http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histaminehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ECL_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ECL_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastric_acidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastric_acidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endothelinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=X_cell&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=X_cell&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Endocrine_Alimentary_system_en.svghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Endocrine_Alimentary_system_en.svghttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=10http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stomachhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastrinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastric_acidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parietal_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ghrelinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P/D1_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/P/D1_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Appetitehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitary_glandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuropeptide_Yhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obesityhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somatostatinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Delta_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Delta_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastrinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystokininhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secretinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motilinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasoactive_intestinal_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasoactive_intestinal_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastric_inhibitory_polypeptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastric_inhibitory_polypeptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enteroglucagonhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-Colorado-0http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histaminehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ECL_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ECL_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastric_acidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endothelinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=X_cell&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=X_cell&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-1 -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
6/15
[edit]Duodenum
Secreted hormone From cells Effect
Secretin S cells
Secretion
ofbicarbonate fromliver,pancreasand
duodenalBrunner's glands
Enhances effects ofcholecystokinin Stops
production of gastric juice
Cholecystokinin I cells
Release of digestive enzymesfrom pancreas
Release
ofbile from gallbladderhungersuppressant
[edit]Liver
Secreted hormone Abbreviation From cells Effect
Insulin-like growth factor(or
somatomedin) (Primarily)IGF Hepatocytes
insulin-like effects
regulate cell growth and
development
Angiotensinogenandangiotensi
nHepatocytes
vasoconstriction
release
ofaldosterone from adrenal
cortexdipsogen.
Thrombopoietin Hepatocytesstimulates megakaryocytes to
produce platelets[3]
[edit]Pancreas
Secreted
hormoneFrom cells Effect
Insulin (Primarily) Islet cells Intake
ofglucose,glycogenesisand glycolysisin liverandmusclefrom
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=11http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=11http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duodenumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secretinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/S_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bicarbonatehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bicarbonatehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liverhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liverhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreashttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreashttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreashttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brunner's_glandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brunner's_glandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystokininhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystokininhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystokininhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzymehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzymehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreashttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gallbladderhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hungerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hungerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=12http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=12http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liverhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin-like_growth_factorhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin-like_growth_factorhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_growthhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensinogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensinogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasoconstrictionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aldosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aldosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_cortexhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_cortexhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_cortexhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dipsogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thrombopoietinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Megakaryocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plateletshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plateletshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-Kaushansky2006-2http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=13http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=13http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreashttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucosehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucosehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogenesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogenesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogenesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycolysishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycolysishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liverhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liverhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=11http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duodenumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secretinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/S_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bicarbonatehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liverhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreashttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brunner's_glandhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystokininhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystokininhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholecystokininhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzymehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreashttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gallbladderhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hungerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=12http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liverhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin-like_growth_factorhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_growthhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensinogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasoconstrictionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aldosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_cortexhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_cortexhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dipsogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thrombopoietinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hepatocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Megakaryocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plateletshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-Kaushansky2006-2http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=13http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreashttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucosehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogenesishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycolysishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liverhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscle -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
7/15
-
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
8/15
fasciculataand zona
reticularis cells
Stimulates fat breakdown in adipose
tissue
Inhibits protein synthesis
Inhibits glucose uptake in muscle
and adipose tissueInhibits immunological responses
(immunosuppressive)
Inhibits inflammatory responses (anti-
inflammatory)
Mineralocorticoids(chieflyaldosterone)
Zona
glomerulosa cells
Stimulates activesodium reabsorption
in kidneys
Stimulates passive water reabsorption
in kidneys, thus increasingblood
volumeand blood pressure
Stimulates potassiumandH+secretio
into nephron of kidney and subsequen
excretion
Androgens (includingDHEAandtestosterone
)
Zona
fasciculataand Zona
reticularis cells
In males: Relatively small effect
compared to androgens from testes
In females: masculinizing effects
[edit]Adrenal medulla
Secreted hormone From cells Effect
Adrenaline (epinephrine)
(Primarily)
Chromaffin cells Fight-or-flight response:
Boost the supply
ofoxygen and glucose to
the brainand muscles(by
increasing heart rate and stroke
volume,vasodilation,
increasing catalysisofglycogenin liver,
breakdown oflipidsinfat cells)
Dilate thepupils
Suppress non-emergency bodily
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_fasciculatahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_fasciculatahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_reticularishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_reticularishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fat_breakdownhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adiposehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunosuppressivehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunosuppressivehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anti-inflammatoryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anti-inflammatoryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mineralocorticoidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mineralocorticoidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aldosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_glomerulosahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_glomerulosahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kidneyshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potassiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potassiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_ionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_ionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_ionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_ionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephronhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dehydroepiandrosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dehydroepiandrosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_fasciculatahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_fasciculatahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_fasciculatahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_reticularishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_reticularishttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=17http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=17http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_medullahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenalinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromaffin_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fight-or-flight_responsehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fight-or-flight_responsehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxygenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucosehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_brainhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_brainhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stroke_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stroke_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasodilationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasodilationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasodilationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalysishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalysishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pupilhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pupilhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_fasciculatahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_fasciculatahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_reticularishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_reticularishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fat_breakdownhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adiposehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunosuppressivehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anti-inflammatoryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anti-inflammatoryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mineralocorticoidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aldosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_glomerulosahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_glomerulosahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kidneyshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potassiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_ionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nephronhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dehydroepiandrosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_fasciculatahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_fasciculatahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_reticularishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zona_reticularishttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=17http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_medullahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenalinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromaffin_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fight-or-flight_responsehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxygenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucosehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_brainhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stroke_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stroke_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasodilationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalysishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pupil -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
9/15
processes (e.g.,digestion)
Suppressimmune system
Noradrenaline(norepinephrine) Chromaffin cells
Fight-or-flight response:
Boost the supply
ofoxygen and glucose to
the brainand muscles(by
increasing heart rate and stroke
volume,vasoconstriction and
increased blood pressure, breakdown
oflipidsin fat cells)
Increase skeletal muscle readiness.
Dopamine Chromaffin cells Increase heartrate and blood pressure
Enkephalin Chromaffin cells Regulate pain
[edit]Reproductive
[edit]Testes
Secreted hormone From cells Effect
Androgens(chieflytestosterone) Leydig cells Anabolic: growth ofmuscle massand
strength, increased bone density, growth
and strength,
Virilizing:maturationofsex organs,
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digestionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digestionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immune_systemhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immune_systemhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noradrenalinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromaffin_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fight-or-flight_responsehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fight-or-flight_responsehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxygenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucosehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_brainhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_brainhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stroke_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stroke_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasoconstrictionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasoconstrictionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skeletal_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dopaminehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromaffin_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hearthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hearthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enkephalinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromaffin_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=18http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=18http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=19http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=19http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testeshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leydig_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anabolichttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anabolichttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscle_masshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscle_masshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bone_densityhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virilizinghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virilizinghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maturationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maturationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sex_organshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Endocrine_reproductive_system_en.svghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Endocrine_reproductive_system_en.svghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digestionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immune_systemhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noradrenalinehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromaffin_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fight-or-flight_responsehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxygenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucosehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_brainhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart_ratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stroke_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stroke_volumehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vasoconstrictionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skeletal_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dopaminehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromaffin_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hearthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enkephalinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromaffin_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=18http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=19http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testeshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Testosteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leydig_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anabolichttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscle_masshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bone_densityhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virilizinghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maturationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sex_organs -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
10/15
formation ofscrotum, deepening of voice,
growth ofbeard and axillary hair.
Estradiol Sertoli cells Preventapoptosisof germ cells[5]
Inhibin Sertoli cells Inhibit production ofFSH
[edit]Ovarian follicle / Corpus luteum
Secreted hormone From cells Effect
Progesterone Granulosa
cells,theca
cells
Support pregnancy[6]:
Convert endometriumto secretory stage
Makecervical mucus thick and impenetrable to sperm.
Inhibit immuneresponse, e.g., towards thehuman embryo
Decrease uterine smooth musclecontractility[6]
Inhibit lactation
Inhibit onset oflabor.
Other:
Raiseepidermal growth factor-1 levels
Increase core temperature during ovulation[7]
Reducespasm and relaxsmooth muscle (widen bronchi a
regulate mucus)
Anti-inflammatory
Reducegall-bladderactivity[8]
Normalize bloodclotting and vascular
tone, zinc and copperlevels,celloxygen levels, and use of fat
for energy
Assist in thyroidfunction and bonegrowth byosteoblasts
Increase resilience in bone,teeth, gums,joint, tendon,liga
and skin
Promote healing by regulating collagen
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scrotumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scrotumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beardhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Axillary_hairhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Axillary_hairhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estradiolhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sertoli_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-4http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inhibinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sertoli_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle_stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=20http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=20http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovarian_folliclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corpus_luteumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Progesteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theca_internahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theca_internahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnancyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnancyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-colostate-5http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterine_lininghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterine_lininghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cervix#Cervical_mucushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cervix#Cervical_mucushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immune_systemhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immune_systemhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_embryohttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_embryohttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-colostate-5http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Labor_(childbirth)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Labor_(childbirth)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epidermal_growth_factor-1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epidermal_growth_factor-1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-GeorgiaPhysiology-6http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spasmhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spasmhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bronchihttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mucushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inflammationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gall-bladderhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gall-bladderhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-7http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloodhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloodhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zinchttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Copperhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_(biology)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxygenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resiliencehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teethhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gingivahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jointhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tendonhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tendonhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ligamenthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_skinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Collagenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scrotumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beardhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Axillary_hairhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estradiolhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sertoli_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosishttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-4http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inhibinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sertoli_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle_stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=20http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ovarian_folliclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corpus_luteumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Progesteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theca_internahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theca_internahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnancyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-colostate-5http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterine_lininghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cervix#Cervical_mucushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immune_systemhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_embryohttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-colostate-5http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Labor_(childbirth)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epidermal_growth_factor-1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-GeorgiaPhysiology-6http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spasmhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bronchihttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mucushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inflammationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gall-bladderhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-7http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloodhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zinchttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Copperhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_(biology)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxygenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thyroidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resiliencehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teethhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gingivahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jointhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tendonhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ligamenthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_skinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Collagen -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
11/15
Provide nerve function and healing by regulating myelin
Preventendometrial cancerby regulating effects of estrog
Androstenedione Theca cells Substrate forestrogen
Estrogens (mainly estradiol) Granulosa
cells
Structural:
Promote formation of female secondary sex characteristic
Accelerate heightgrowth
Accelerate metabolism(burn fat)
Reducemuscle mass
Stimulate endometrial growth
Increase uterine growth
Maintain blood vesselsand skin
Reducebone resorption, increase bone formation
Protein synthesis:
Increase hepatic production of binding proteins
Coagulation:
Increase circulating leveloffactors2, 7,9,10, antithrombinIII,plasminogen
Increase platelet adhesiveness
Increase HDL,triglyceride,height growth
Decrease LDL, fat deposition
Fluid balance:
Regulate salt (sodium) and water retention
Increase growth hormone
Increase cortisol,SHBG
Gastrointestinal tract:
Reduce bowel motility
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Myelinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endometrial_cancerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endometrial_cancerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endometrial_cancerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androstenedionehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theca_internahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estrogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estrogenshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estradiolhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secondary_sex_characteristicshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heighthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heighthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metabolismhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metabolismhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endometriumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_vesselhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_vesselhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bone_resorptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bone_resorptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coagulationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coagulationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coagulation_factorhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coagulation_factorhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factor_IIhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factor_VIIhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factor_IXhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factor_IXhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factor_Xhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factor_Xhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antithrombinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antithrombinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plasminogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Platelethttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High-density_lipoproteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High-density_lipoproteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceridehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceridehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heighthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Low-density_lipoproteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fathttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cortisolhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SHBGhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SHBGhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Myelinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endometrial_cancerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androstenedionehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theca_internahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estrogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estrogenshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estradiolhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secondary_sex_characteristicshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heighthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metabolismhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endometriumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_vesselhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bone_resorptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coagulationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coagulation_factorhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factor_IIhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factor_VIIhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factor_IXhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factor_Xhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antithrombinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plasminogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Platelethttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High-density_lipoproteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceridehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heighthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Low-density_lipoproteinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fathttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodiumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Growth_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cortisolhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SHBG -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
12/15
Increase cholesterol in bile
Melanin:
Increase pheomelanin, reduceeumelanin
Cancer:
Support hormone-sensitivebreast cancers[9](Suppression
production in the body of estrogen is a treatment for these can
Lung function:
Promote lung function by supporting alveoli.[10]
InhibinGranulosa
cellsInhibit production ofFSHfrom anterior pituitary
[edit]Placenta (when pregnant)
Secreted hormone Abbreviation From cells Effect
Progesterone (Primarily)
Supportpregnancy[6]:
Inhibit immune response,
towards the fetus.
Decrease uterine smooth
musclecontractility[6]
Inhibit lactation
Inhibit onset oflabor.
Supportfetalproduction
ofadrenalmineralo- and
glucosteroids.
Other effects on mother similar to
ovarian follicle-progesterone
Estrogens (mainly Estriol)
(Also Primarily)
Effects on mother similar to ovarian
follicle estrogen
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pheomelaninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eumelaninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eumelaninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Hormone-sensitive&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Breast_cancerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Breast_cancerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-8http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-8http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alveolihttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alveolihttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-9http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inhibinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle_stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle_stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=21http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=21http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Placentahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnanthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Progesteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnancyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnancyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnancyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-colostate-5http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immune_systemhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fetushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-colostate-5http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Labor_(childbirth)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Labor_(childbirth)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fetalhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fetalhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fetalhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenalhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenalhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estrogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estriolhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pheomelaninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eumelaninhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Hormone-sensitive&action=edit&redlink=1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Breast_cancerhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-8http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alveolihttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-9http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inhibinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granulosa_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle_stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anterior_pituitaryhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=21http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Placentahttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnanthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Progesteronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnancyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-colostate-5http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immune_systemhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fetushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smooth_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-colostate-5http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Labor_(childbirth)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fetalhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenalhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estrogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estriol -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
13/15
Human chorionic
gonadotropinHCG Syncytiotrophoblast
promote maintenance ofcorpus
luteum during beginning ofpregnancy
Inhibit immune response, towards
thehuman embryo.
Human placental lactogen HPL Syncytiotrophoblast
increase production ofinsulinandIGF-1
increaseinsulin
resistanceand carbohydrate intolerance
Inhibin Fetal Trophoblasts suppress FSH
[edit]Uterus (whenpregnant)
Secreted hormone Abbreviation From cells Effect
Prolactin PRL Decidual cells milk production in mammary glands
Relaxin Decidual cells Unclear in humans and animals
[edit]Calcium regulation
[edit]Parathyroid
Secreted hormone Abbreviation From cells Effect
Parathyroid PTH Parathyroid Calcium:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_chorionic_gonadotropinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_chorionic_gonadotropinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syncytiotrophoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corpus_luteumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corpus_luteumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corpus_luteumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnancyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immune_systemhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_embryohttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_embryohttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_embryohttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_placental_lactogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syncytiotrophoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IGF-1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IGF-1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbohydratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inhibinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trophoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle_stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=22http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=22http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnanthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnanthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decidual_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mammary_glandshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relaxinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decidual_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=23http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=23http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=24http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=24http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_chief_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calciumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Endocrine_caclcium_en.svghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Endocrine_caclcium_en.svghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_chorionic_gonadotropinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_chorionic_gonadotropinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syncytiotrophoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corpus_luteumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corpus_luteumhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnancyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immune_systemhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_embryohttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_placental_lactogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syncytiotrophoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IGF-1http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbohydratehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inhibinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trophoblasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Follicle_stimulating_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=22http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uterushttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pregnanthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prolactinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decidual_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mammary_glandshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relaxinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decidual_cellshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=23http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=24http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroidhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_chief_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcium -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
14/15
hormone chief cell
Stimulates Ca2+ release from bone,
thereby increasing blood Ca2+
Stimulates osteoclasts, thus breaking
down bone
Stimulates Ca2+ reabsorption in kidney
Stimulates activated vitamin
D production in kidney
Phosphate:
Stimulates PO3-4 release from bones,
thereby increasing blood PO3-4.
Inhibits PO3-4 reabsorption in kidney,
so more PO3-4 is excreted
Overall, small net drop in serum PO3-4.
[edit]Skin
Secreted hormone From cells Effect
Calcidiol(25-
hydroxyvitamin D3)Inactive form ofvitamin D3
[edit]Miscellaneous
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_chief_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoclasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoclasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kidneyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_Dhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_Dhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kidneyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=25http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=25http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_skinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcidiolhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcidiolhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_D3http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_D3http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_D3http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=26http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=26http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Endocrine_miscelaneous_en.svghttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_hormonehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_chief_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parathyroid_chief_cellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osteoclasthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kidneyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_Dhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_Dhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kidneyhttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=25http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_skinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcidiolhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_D3http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=26 -
8/3/2019 Glands of the Endocrine System
15/15
[edit]Heart
Secreted hormone Abbreviation From cells Effect
Atrial-natriuretic
peptideANP
Cardiac
myocytes
Reduce blood pressure by:
reducing systemicvascular resistance,
reducing blood water, sodium andfats
Brain natriuretic
peptideBNP
Cardiac
myocytes
(To a lesser degree than ANP) reduceblood
pressure by:
reducing systemicvascular resistance,
reducing blood water, sodium andfats
[edit]Bone Marrow
Secreted hormone From cells Effect
Thrombopoietin liver and kidney cells stimulates megakaryocytes to produce platelets[3]
[edit]Adipose tissue
Secreted hormone From cells Effect
Leptin (Primarily) Adipocytesdecrease ofappetiteand increase
ofmetabolism.
Estrogens[11] (mainlyEstrone) Adipocytes
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=27http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=27http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hearthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atrial-natriuretic_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atrial-natriuretic_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systemic_circulationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vascular_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vascular_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vascular_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_fatshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_fatshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain_natriuretic_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain_natriuretic_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systemic_circulationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vascular_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vascular_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vascular_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_fatshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_fatshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=28http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=28http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bone_Marrowhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thrombopoietinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Megakaryocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plateletshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-Kaushansky2006-2http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=29http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=29http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipose_tissuehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leptinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Appetitehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Appetitehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metabolismhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estrogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estrogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-10http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Endocrine_miscelaneous_en.svghttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=27http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hearthttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atrial-natriuretic_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atrial-natriuretic_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systemic_circulationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vascular_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_fatshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain_natriuretic_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brain_natriuretic_peptidehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiac_musclehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_pressurehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systemic_circulationhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vascular_resistancehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blood_fatshttp://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=28http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bone_Marrowhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thrombopoietinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Megakaryocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plateletshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-Kaushansky2006-2http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Endocrine_system&action=edit§ion=29http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipose_tissuehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leptinhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocytehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Appetitehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metabolismhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estrogenhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocrine_system#cite_note-10http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Estronehttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocyte