Genetic Stability Analysis of In Vitro · Gel Electrophoresis • Electrophoresis is based on the...
Transcript of Genetic Stability Analysis of In Vitro · Gel Electrophoresis • Electrophoresis is based on the...

Genetic Stability Analysis of In Vitro and Cryopreserved Germplasm
Era Vaidya Malhotra
Scientist
Eighth International Training on In Vitro and Cryopreservation Approaches PGR Conservation

CRYOPRESERVATION
Long-term storage of viable biological resources at ultralow temperatures in
liquid nitrogen (−196 °C) under conditions that maintain tissue viability.
Each species has physiological and biochemical uniqueness, hence protocols
need to be optimised for individual characteristics.
During the development and/or improvement of a protocol, both cryogenic
and non-cryogenic factors need to be carefully balanced to support
acceptable levels of viability and recovery that satisfy fitness-for purpose
criteria.
Eighth International Training on In Vitro and Cryopreservation Approaches PGR Conservation

Concerns: Viability & Genetic Stability
It is important to verify that:
the storage protocol does not have any destabilizing effects the plants recovered and regenerated from cryopreserved germplasm are true-to-type
The importance is well recognised in several guidelines and standards for in vitro conservation best practices and in biorepositories and biobanks (Genebank Standards 1994; FAO 2012, 2013, 2014).
For genebank management it is essential to monitor sample viability and genetic integrity of materials during storage.
Concerns
Eighth International Training on In Vitro and Cryopreservation Approaches PGR Conservation

Re-introduction of plants; Conservation; Utilization- breeders,/commercial exploitation
CRYOINJURY Physical
Ice crystal damage Dehydration damage
Cellular Biochemical
Free radical attack Oxidative damage
Membrane damage
Genome Genetic/Epigenetic modifications
Mutation DNA methylation
Chromatin modulation
Transcriptome RNA modifications Alternative splicing
mRNA editing
Proteome Protein modifications
Phosphorylation Glycosylation Carboxylation
Metabolome Metabolite functions
Cell signalling Anabolism Catabolism
Genetic Stability Morphology
Histology Cytology
Biochemistry Molecular Biology
CRYOBIONOMICS Harding et al. 2009

CRYOBIONOMICS
Concept first presented in 2002 (Harding, 2002) to signify the reintroduction of species into the environment following cryostorage.
Biochemistry
4
Molecular biology
5
An interdisciplinary approach to assess possible cellular/biochemical damage due to
cryoinjury
Histology
2
Cytology
3
Phenotype
Thus, cryobionomics provides a conceptual framework to investigate the linkages between cryogenic and non-cryogenic stress factors
1

Possible events of cryopreservation process that lead to
cellular damage and genetic instability
(Martinez-Montero and Harding, 2015)

Issues of Genetic Stability
Patterns of organised shoot regeneration may be retarded in favour of callus formation which can often arise from wounded tissues as a result of cryoinjury.
Abnorm
al
gro
wth
Exposure to stresses such as water flux resulting from osmotic dehydration, desiccation and temperature oscillations during freezing/cooling and thawing/rewarming, can potentially change gene expression and metabolism.
Gene
expre
ssio
n
DNA methylation modifications leading to epigenetic changes (Kaity et al., 2008; Peredo et al., 2008; Adu-Gyamfi et al., 2016).
Epig
eneti
c
changes
Production of ROS, as evidenced by the detection of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, a marker for oxidative damage in DNA and detected in germplasm exposed to cryogenic treatments (Johnston et al. 2010 ). O
xid
ati
ve
stre
ss
Thus, it is vital that these effects are evaluated to ensure recovered material is identical to the donor plant before implementing such protocols in germplasm storage projects.

-
Morphological descriptors
Cytological Techniques •Polyploidy •Aneuploidy •Mitotic abnormalities
Molecular markers
DNA methylation patterns
Biochemical techniques
Chromosomal stability
Metabolite profiles
DNA sequence variation
Tools for stability assessment
Phenotypic variation
Epigenetic changes
Assessment of Genetic Stability

Phenotypic Characterization
• Using descriptors for a given species, to examine a large number of characters per plant.
• Most studies indicate a clear consensus of plants displaying morphological normality after cryopreservation
Cytological analysis
• Genome size • Gene content • Extent of repetitive sequences • Polyploidy/duplication events
Assessment of Genetic Stability
Musa Pisang Radjah, AAB (A Agrawal, unpublished data)
Rao et al, 1992

Biochemical Characterization
• Biochemical profiling of active ingredient/ secondary metabolite
• Techniques such as HPLC, UPLC or GC-MS may be used
• Comparisons made between the cryopreserved and in vitro grown plants post hardening
Molecular analysis
• Banding profiles compared • Markers with greater genome coverage
preferred • Expectation – monomorphic banding pattern • Percent similarity among the tested samples
recorded
Assessment of Genetic Stability
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
BC1 in vitro
BCJ in vitro
BCM in vitro
BCM ex vitro
Bac
osi
de
A (
μg/
g.d
w)
Treatments
Control
Cryopreserved
Sharma et al., 2013
M 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
E Malhotra, (unpublished data)

Molecular Markers
DNA sequences with a known location on a chromosome and associated with a particular gene or trait
• The use of molecular marker is based on naturally occurring DNA polymorphism
• A marker must be polymorphic i.e. it must exist in different forms so that the chromosome carrying the mutant gene can be distinguished from the chromosome carrying normal gene by the marker.

Molecular markers
Hybridisation based
RFLP
PCR based
Markers with specific sequences
SSR ISSR
Based on random or arbitrary sequences
RAPD AFLP
Molecular Markers

PCR: Basis of Molecular Biology Techniques
• Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a technique to amplify a DNA fragment to generate millions of its copies in an enzymatic reaction carried out in vitro.
• This technique was invented by Kary B. Mullis in 1983 and he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1993.
• PCR is a very simple and inexpensive technique for characterization, analysis and synthesis of specific fragments of DNA or RNA from virtually any living organism.

• PCR is based on the ability of DNA polymerase to add nucleotides to free 3' end of a DNA fragment in a template dependent manner under standard conditions.
• Initially, the DNA is denatured to separate out the two strands. To these single strands oligonucleotide primers bind at their complementary sequences.
• The Taq DNA polymerase, extracted from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus, then begins to add nucleotides to the 3' end of each primer and thereby extends the DNA strand, producing a new daughter strand.
• This cycle is then repeated a number of times to amplify the number of copies of that particular DNA fragment.

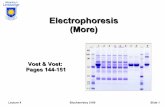
Gel Electrophoresis
• Electrophoresis is based on the principle of separating DNA molecules as per their mass in an applied electric field.
• DNA molecules have a negative charge and migrate towards the anode, under an electric field.
• The migration rate of the DNA is affected by the size of the DNA, agarose concentration and conformation of the DNA.
• Small molecules migrate faster and then bigger ones.
• Due to difference in the migration rate of various size DNA molecules in gel DNA fragments are separated based on sizes.
Anode
Cathode

Gel Electrophoresis
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Procedure

Gel Loading • Samples of DNA are mixed with the 6X sample
loading buffer (w/ tracking dye).
• This allows the samples to be seen when loading onto the gel, and increases the density of the samples, causing them to sink into the gel wells.
• 6X Loading Buffer:
Bromophenol Blue (for colour)
Glycerol (for weight)
• Samples are then carefully loaded into the wells, taking care not to puncture the gel with the pipette tip.
Gel Electrophoresis

Gel Staining • Gels are stained with Ethidium bromide, which binds
to DNA and fluoresces under UV light, allowing the visualization of DNA.
• Ethidium Bromide is an intercalating agent which resembles a DNA base pair. Due to its unique structure, it can easily intercalate into DNA strand.
• Ethidium bromide can be added to the gel and/or running buffer before the gel is run or the gel can be stained after it has run.
• Gels are photographed using a Gel documentation system
Gel Electrophoresis

Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA Markers (RAPD)
A very simple PCR-based technique developed in 1990 Single, short and arbitrary length primers used No previous knowledge of DNA sequence required Amplified products separated on agarose gels and visualized using Ethidium bromide staining Polymorphism between individuals visible as presence or absence of bands

SSRs- Simple Sequence Repeats (Microsatellite)
Based on the microsatellite repeats, i.e. short, tandemly repeated DNA stretches May be di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- or hexa-nucleotide repeat motifs, flanked by conserved DNA sequences Variation in the samples is reflected as length polymorphisms due to variation of the number of repeat motifs in the microsatellite. Two primers are designed complementary to the sequences flanking a specific microsatellite DNA sequence.
Mononucleotide SSR (T)8
TTTTTTTT Dinucleotide SSR (AG)6
AG AG AG AG AG AG Trinucleotide SSR (ATC)5
ATC ATC ATC ATC ATC Tetranucleotide SSR (GATC)4
GATC GATC GATC GATC

ISSRs- Inter Simple Sequence Repeats
Follow the principle of amplification of DNA fragments flanked by inversely oriented SSR motifs. Detection of DNA polymorphism depends on the abundance and variability of microsatellite repeats in the genome. This technique uses microsatellite repeat motifs as primers to amplify the inter simple sequence repeats of different sizes. The technique is simple, quick and needs no sequence information for primer synthesis.
M 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10

Studies on Genetic Stability of In Vitro Conserved Germplasm
• Taro – Colocassia esculenta • Conservation by in vitro corm
induction • Storage duration – 15 months • 22 morphological characters • 13 RAPD and 6 ISSR primers
• Turmeric – Curcuma longa • Conservation on low cost media • Subculture duration – 12 months • 22 morphological characters • 25 RAPD primers

Studies on Genetic Stability of In Vitro Conserved Germplasm
• Cardamom slow growth conservation on minimal media
• Subculture duration – 18 months • 20 RAPD and 13 ISSR primers • No significant reproducible
variation detected

Studies on Genetic Stability of Cryopreserved Germplasm
• Musa cv. Sommarani Monthan (AAB, Monthan subgroup) • Cryopreservation by vitrification • 12 agronomic characters • 9 SSR primers
• Dioscorea bulbifera • Cryopreservation by encapsulation
dehydration • Phenotypic characterization

• Musa ABB cv. ‘Karpura Chakkarakeli’
• Cryopreservation by droplet vitrification
• 11 phenotypic characters • 21 SSR primers
• Dioscorea rotundata • Vitrification and encapsulation
dehydration • 10 RAPD primers

0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
BC1 in vitro
BCJ in vitro
BCM in vitro
BCM ex vitro
Bac
osi
de
A (
μg/
g.d
w)
Treatments
Control
Cryopreserved
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 M 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 M 21 22 23 24
Studies on Genetic Stability of Cryopreserved Germplasm
• Bacopa monneri • Cryopreservation by vitrification • Biochemical profiling – HPLC • RAPD Primers

Studies on Genetic Stability of Cryopreserved Germplasm
Representative gel image showing amplification of (a) Allium chinense (IC 623458) with ISSR Primer UBC 873; (b): Allium tuberosum (IC 554562) with ISSR Primer IS6; M – Molecular weight marker, 1 – Mother Plant; 2,3,4 Tissue culture controls, 5 – LN control, 6,7,8 cryopreserved samples
• Stability analysis of cryopreserved Allium species
• 4 species tested • ISSR primers
CONTROL PLANTS LN REGENERANTS

Studies on Genetic Stability of Cryopreserved Germplasm
• Stability analysis of cryopreserved Musa cvs.
• 2 cvs.tested • EST - SSR primers
Percent frequency of occurrence of repeat motifs. a: mono-; b: di-; c: tri-; d: hexa-nucleotides
Total
examined
Total number
of identified
SSRs
Number of SSR
containing
sequences
Contigs 5387 526 474
Singletons 14839 1187 1012
Total 20226 1713 1486
Representative gel image showing amplification of Musa accessions with EST-SSR Primer E-P5 a) Musa AAB cv Pisang Rajdah: Musa ABB cv Pelipita:

Studies on Genetic Stability of Cryopreserved Germplasm
Frequency of repeat types
Gene ontology analysis
• 3152 Gentiana primer pairs designed • Primers tested for cross species
transferability • Being tested for stability analysis of
cryopreserved Gentiana kurroo germplasm

Acknowledgements
• All former and present Scientists of TCCU for sharing their experimental material for genetic stability analysis
• Present project team
• Dr Sangita Bansal
• Dr Gowthami R.
• Mr. Suresh Chand Mali
• Ms. Rishu Jain
Thank You