Fluidized Bed versus Grate - ProcessEngFluidized Bed versus Grate – Two competitive Technologies...
Transcript of Fluidized Bed versus Grate - ProcessEngFluidized Bed versus Grate – Two competitive Technologies...
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 Sei1e 1
• Introduction
• Waste System Vienna
• Path of uncategorized waste
• Plant Spittelau
• Path of sewage sludge
• Plant Simmeringer Haide
• Fluidized Bed versus Grate
• Requirements for mechanical separation
• Construction and installation of „Wirbelschichtofen 4“
Topic:
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 2
One Company:
Two Business Area
Waste Disposal Services Energy Supply Services
Introduction
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 3
Flötzersteig:200.000 t/a uncategorized waste50 MWth
Spittelau:270.000 t/a uncategorized waste60 MWth
Simmeringer Haide:110.000 t/a hazardous waste 180.000 t/a sewage sludge40 MWth
Introduction
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page
paperUncategorized waste
prod
uct
whe
reho
ww
hat
glass metalplastic
Waste System Vienna (Separation)
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 5
wood2%
paper25%
metal4%
others18%
organics30%
glass7%
plastic11%
textiles3%
Fuel NCV Total Carbon Fossil Cin % to totalCarbon
biogenic C
[MJ/kg] [kg C/t FS]
55Uncategorized waste(Household waste)
8.810 184 45
in % to totalCarbon
C 195 ± 21 198 ± 10 184 ± 10Cl 4,8 ± 0,7 4,9 ± 1 4,6 ± 0,2Fe 28 ± 2 28 ± 2 27 ± 2Al 10,0 ± 1,2 11.2 ± 1,8 7.5 ± 0.6Pb 0,24 ± 0,05 0,33 ± 0,06 0,27 ± 0,03Zn 0,57 ± 0,07 0,61 ± 0,06 0,60 ± 0,05Cu 0,24 ± 0,05 0,31 ± 0,07 0,27 ± 0,02
Cd 0,0071 ± 0,0008 0,0068 ± 0,001 0,0057 ± 0,0005
Hg 0,0011 ± 0,00020,00084 ± 0,00011
0,00091 ± 0,0001
in mg/kg
2000 2001 2002
Waste System Vienna (Waste Composition)
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 6
Path of uncategorized Waste (Thermal Treatment)
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 7
38%
12%
49%
39%
14%
47%
39%
12%
49%
38%
12%
50%
44%
11%
45%
1998 1999 2000 2001 2002
873.842 938.604 935.849 964.754 988.184
seperation landfill incineration
Waste Treatment
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 8
Waste treatment in Vienna 1969 bis 2002
0100200300400500600700800900
1.000
1969
1971
1973
1975
1977
1979
1981
1983
1985
1987
1989
1991
1993
1995
1997
1999
2001
landfill sitewaste incinerationcompostingrecycling
in 1
.000
t
Waste Treatment
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 9
1
2
3
4
Waste bunker
Furnace feed chute
Firing grate
Furnace
5 Waste heat boiler
9
6
7
8
Slag discharger
Electrostatic precipitator
2-stage f lue gas scrubber
Fine dust separator
10 SCR-DeNOx facility
13
14
11
12
Stack
Feedw ater tank
Turbine generator
Heat exchanger bank
15 Electromagnet
16
17
18
19
Slag bunker
Scrap skip
Filter ash silo
Multi-stage recycling plant
20 Waste water treatment plant
21
Chamber f ilter press
22
23
24
Cleaned w ater tank
Sludge tank
Filter cake box
25 Receiving w ater
FreshwaterBasic process waterAcidic process waterSaturated steamFilter ash and slagHy droxide sludgeGy psum sludgeDistrict heating energy
Sodalye
Limeslurry
Fresh-water
Ammonia
3
1315
241716 25
1
Naturalgas
Lime slurryPrecipit. agents
11
G
7
18
21
10
9
Lime slurryPrecipit. agents
Lime slurryPrecipit. agents
23
2
12
14
22
88
6
19 2020
4
5
1
2
3
4
Waste bunker
Furnace feed chute
Firing grate
Furnace
5 Waste heat boiler
11
22
33
44
Waste bunker
Furnace feed chute
Firing grate
Furnace
55 Waste heat boiler
9
6
7
8
Slag discharger
Electrostatic precipitator
2-stage f lue gas scrubber
Fine dust separator
10 SCR-DeNOx facility
99
66
77
88
Slag discharger
Electrostatic precipitator
2-stage f lue gas scrubber
Fine dust separator
1010 SCR-DeNOx facility
13
14
11
12
Stack
Feedw ater tank
Turbine generator
Heat exchanger bank
15 Electromagnet
1313
1414
1111
1212
Stack
Feedw ater tank
Turbine generator
Heat exchanger bank
1515 Electromagnet
16
17
18
19
Slag bunker
Scrap skip
Filter ash silo
Multi-stage recycling plant
20 Waste water treatment plant
1616
1717
1818
1919
Slag bunker
Scrap skip
Filter ash silo
Multi-stage recycling plant
2020 Waste water treatment plant
21
Chamber f ilter press
22
23
24
Cleaned w ater tank
Sludge tank
Filter cake box
25 Receiving w ater
2121
Chamber f ilter press
2222
2323
2424
Cleaned w ater tank
Sludge tank
Filter cake box
2525 Receiving w ater
FreshwaterBasic process waterAcidic process waterSaturated steamFilter ash and slagHy droxide sludgeGy psum sludgeDistrict heating energy
FreshwaterBasic process waterAcidic process waterSaturated steamFilter ash and slagHy droxide sludgeGy psum sludgeDistrict heating energy
Sodalye
Limeslurry
Fresh-water
Ammonia
33
13131515
242417171616 2525
11
Naturalgas
Lime slurryPrecipit. agents
1111
GG
77
1818
2121
1010
99
Lime slurryPrecipit. agents
Lime slurryPrecipit. agents
2323
22
1212
1414
2222
8888
66
1919 20202020
44
55
Waste Incineration Plant Spittelau
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 10
Hazardous waste
Rotary kiln
District heat
Electrical power
AshSlag
Flue gas
Filter cake
sewage
Biological Treatment
Clean water
Hospital waste
Fluidized bed furnace
Flue gas treatment
Plant Simmeringer Haide
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 11
dm calorific value sulphurin % in kJ/kg dm in % dm
2002 33,74 17.029,60 0,57
min maxSb mg/kg dm 0,83 3,92 10,20 As mg/kg dm 0,88 2,39 6,51 Ba mg/kg dm 200,00 366,00 993,00 Be mg/kg dm < 1,7 < 2,5 < 3,1Fe mg/kg dm 36.960,00 56.711,00 87.280,00 Pb mg/kg dm 38,00 85,00 472,00 Cd mg/kg dm < 1,1 < 2,5 < 3,8Cr mg/kg dm 18,00 36,00 96,00 Co mg/kg dm 2,00 8,00 55,00 Cu mg/kg dm 154 191 270Mn mg/kg dm 76 127 260Ni mg/kg dm 12 38 151Hg mg/kg dm 0,3 1,27 4,5Ag mg/kg dm 5,7 15,3 38,3V mg/kg dm 6,8 14,4 33,6Zn mg/kg dm 392 766 2200Sn mg/kg dm 8,3 20,1 50,3
Sewage sludge composition
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 12
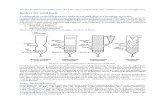
Fluidized bed Dust firingSolid state firing
FT = FA + FWFC carrying ForceFL lifting forceFW resisting powerFG gravity
Firing systems
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 13
Waste Flue gas
primary air slag
Waste Flue gas
Waste Flue gasWaste Flue gas
primary air slag
slagprimary air slagprimary air
Reverse FeedGrate
ForwardFeed Grate
Rollergrate
Counter directionFeed grate
Co Current furnace
Counter flow current f.
Medium current f.
low energy transfer with fire bed (for SRF)
Increase of drying zone
For waste with high moistness; high energy transfer with fire bed
Short drying und degasification zone (unburned gas streams)
For hardly burnable waste
Grate furnace
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 14
Stationary fluidized bed Circulating fluidized bed Rotating fluidized bed
Particle size independent •Precise Particle size required•Long residence time (burnout optimized)
•Ideal distribution•Long residence time (burnout optimized)•Steady temperature distribution
Flue gas
Waste
Secondary Air
Nozzle floorPrimary Air
Bottom Ash
Ash Hopper
Flue gas
Waste
Secondary Air
Secondary Air
Primary Air Bottom Ash
Cyclone
Deflector platesDeflector plates
Waste
Waste Waste
Nozzle floorGas Chamber
Fluidizing Air
Ash Air/ Sand Ash Air/ Sand
Fluidized bed furnace
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 15
•Steady temperature distribution as a result of vertical bed disposition
•Ideal exchange surface between reaction gas and small solid particles
•Perfect heat transfer between solid particles and reaction gas
•High heat transfer by use of heat exchange in the combustion chamber
•High flexibility performance according to input particle (low demand on separation)
•Ideal adaptability to waste composition
•Approved State of the art technology
•Quick start up and shut down phases
Grate Furnace Fluidized Bed Furnace
Advantages
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 16
•Solid particles are eroded in the Fluidized bed •Small particles are moved out of the combustion chamber by the flue gas which lead to an complicated dust recovery system•Danger of erosion in the combustion chamber of all components•Danger of dust contamination in the range of the heating surfaces •Bubbling in the fluidized bed might cause inefficient combustion
•Hardly controllable gas reactions in „drying and combustion“ zone•Small particles (dust) are transported by the flue gas •Combustion of fractions with high NCV should be avoided
Disadvantages
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 17
Grate firingStationary Fluidized Bed Circulating Fluidized
Bed
Fluidized Bed
Solid state
pneumaticdischarger
Heat transfercoefficient
Pressure loss
Bed height H
Fluidizing Initial point
Reactor velocity in m/s
Lost of pressure and heat transfer coefficient
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 18
Preperation and
splitting
Input: 1 Mg ar Household waste (Vienna)
Flue gas (dust)
Ferro metalls
Non ferro metalls
Over size fraction (> 250 mm) Solid recovered fuel (50 – 250 mm)
Reject (low NCV) fraction (< 50 mm) –
Preparation and splitting
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 19
waste bunker with 3 sectionsHousehold-, bulky-, sieving reject-
waste
crane
Walking FloorB200
Slat conveyorB210
ShredderB220
crane
Walking FloorB100
B110
ShredderB120
Pre crashedContainer loading
Sieving drumB250
Sieving drumB150
fraction < 50mm, Container loading
Sieving drumB280
Sieving drumB180
Over band magnetic separator B640
< 50 mm
< 50 mm
> 50 mm
> 250mm
mm, fraction > 50Container loading
line 1
fraction > 50mm, Container loading
line 2
< 250 mm < 250mm
> 50 mm
fraction > 250mm, Container loading
Over band magnetic separator B410
Eddy current separator B660
Ferro metals
Baling press B370
wrapping machine B380
fraction 50 -250mm, Container loading
fraction 50 -250mm, Container loading
fraction < 50 mm, Container loading
> 250mm
< 250 mm < 250mm
Slat conveyor
Magnetic drum separator B635
Magnetic drum separator B635
Over band magnetic separator B310
Non Ferro metals
Eddy current separator B310
Eddy current separator B330
Mechanical Treatment Plant Vienna
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 20
capacity standardized C S N W O H inert material NCVobservation periode kg/h in % in % in % in % in % in % in % in kJ/t
25.06.2003; 13:15 - 14:45 19.183 12.789 31,86% 0,001% 0,07% 30,07% 16,30% 5,00% 16,70% 13,3125.06.2003; 14:54 - 16:25 20.301 13.385 31,03% 0,001% 0,10% 22,26% 17,80% 5,00% 23,80% 13,0725.06.2003; 16:30 - 17:56 17.106 11.934 33,34% 0,001% 0,12% 35,12% 15,71% 5,00% 10,70% 13,7925.06.2003; 17:59 - 19:26 18.023 12.430 30,59% 0,001% 0,11% 39,86% 14,79% 5,00% 9,65% 12,8126.06.2003; 11:53 - 13:23 17.890 11.927 24,94% 0,001% 0,10% 21,29% 17,81% 5,00% 30,86% 10,9826.06.2003; 13:27 - 14:57 16.366 10.911 30,91% 0,001% 0,11% 33,94% 15,26% 5,00% 14,77% 13,02
12,83mean value
Pb Al Cd Hg
SRF (Input) 197,36 6183,44 5,51 0,31
slag 88,1 5454 1,2 0,1
ash 108,9 729,4 4,3 0,1
waste (Input 250 9000 6,25 0,88
slag 172 7946 0,52 0,22
ash 72,1 1054 5,6 0,36
SRF test
2002
online m
onitoring 2002
in g/t ar
SRF Composition
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 21
1. Waste bunker2. Feed chute3. Fluidized bed incinerator4. Boiler5. Economizer6. Electrostatic precipitator7. Heat exchanger bank 18. 2-stage flue gas scrubber9. Activated carbon filter10. SCR-DENOx facility11. Heat exchanging bank 212. Stack13. Primary air fan14. Secondary air fan15. Make up water pump16. Recycling air fan17. Scrubber pumps18. Flue gas fan19. Activated carbon transceiver20. Vibrating screen21. Solid residues22. Filter ash silo23. Demister unit24. Heat exchanger25. Waste water treatment
WSO 4 (Fluidized bed incineration)
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 22
Flue gas
Secondary Air „2“
Waste feeder
Secondary Air „1“
recirculation
Primary air
Discharger/cooler
Discharging systemVertical conveyorScreening system
Burner
Sandhopper
Sand valve
Rowitech process
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 23
Household waste
570.000
Splitting177.000 WSO476.00050-250 /42,8%
WIP 1+2
393.000
Bulky waste 50.000 1)(according to NCV)
20.000 x 1,5Flötzersteig
15.000 x 1,5Spittelau 450.000
7.000 over size> 250 / 4,0%
5.000Fe + nFe / 3,3%
Low NCV fraction 89.000
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 24
Construction of WSO4
-
Fluidized Bed versus Grate –Two competitive Technologies in a Waste System
IAE – FBC Workshop 24.05.04 page 25
•For a complete thermal treatment of the total household and bulky waste in Vienna the capacity of Spittelau and Flötzersteig is not sufficient•By splitting the waste the target of no land filling of household waste might be achieved•Perfect treatment of sewage sludge and solid recovered fuel from the Splittingplant by the operation of the fluidized bed incinerator 4
Summary
IntroductionIntroductionWaste System Vienna (Separation)Waste System Vienna (Waste Composition)Path of uncategorized Waste (Thermal Treatment)Waste TreatmentWaste TreatmentWaste Incineration Plant SpittelauPlant Simmeringer HaideSewage sludge compositionFiring systemsGrate furnaceFluidized bed furnaceAdvantagesDisadvantagesLost of pressure and heat transfer coefficientPreparation and splittingMechanical Treatment Plant ViennaSRF CompositionWSO 4 (Fluidized bed incineration)Rowitech processTwo competetive Technologies in a Waste SystemConstruction of WSO4Summary