Finals Lectures
Transcript of Finals Lectures
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
1/24
Dealing with Counterproductive People
Chapter 12
Learning Objectives:
1. Understand the nature of the influenceprocess;
2. Acquire insights into how to confront andcriticize counter productive (or difficult)people;
3. Appreciate the role of recognition and
affection in dealing with counter productivepeople.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
2/24
Dealing with Counterproductive People
A. The influence process:
Five concepts to consider in trying to influence or
change people:
1. It is an emotional process;
2. Recognize your motives;
3. All change is self-change;
4. Change is uncomfortable;
5. Responsibility for change should be shared.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
3/24
Dealing with Counter Productive People (Cont)
B. Confronting and criticizing the difficult person
Confrontation techniques:
1. Attempt to relax during the session;
2. Quickly get to the core topic;
3. Avoid being apologetic or defensive;
4. Be non-hostile in your confrontation;
5. Confront job-related behavior;
6. Show that you care.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
4/24
Dealing with Counter Productive People (Cont)
B. Confronting and criticizing the difficult person (cont)
Suggestions for constructive criticism:
1. Be sensitive to the setting;
2. Base the criticism on objective facts;
3. Express your criticism in terms of a common goal;
4. Avoid playing boss;
5. When criticizing your boss, relate to your work performance.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
5/24
Dealing with Counter Productive People (Cont)
C. Giving recognition and affection
Counter productive people are sometimes seeking
attention. By giving them recognition and
attention, their counter productive behavior
sometimes decreases.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
6/24
Working within a group
Chapter 13
Learning Objectives:
1. Understand the importance of groups;
2. Understand the difference between aformal and informal group;
3. Explain some advantages and disadvantagesof group effort;
4. Understand how decisions are made and
problems solved by groups.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
7/24
Working within a group
A group is a collection of people who interact with each
other, are aware of each other, and are working toward some
common purpose.
I. Why are groups important?
Building blocks of a larger organization;
To accomplish a task.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
8/24
Working within a group (cont)
II. Formal versus Informal Groups
A formal group is one deliberatelyformed by an organization to accomplish
specific tasks and achieve objectives.
An informal group is one that evolvesnaturally in an organization to take careof peoples desire for friendship and
companionship.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
9/24
Working within a group (cont)
Advantages of group effort:
1. Assistance in solving problems;
2. Economic power;3. Feeling of safety;
4. Satisfaction of psychological needs;
5. Reduction of tension;
6. Increased job satisfaction.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
10/24
Working within a group (cont)
Disadvantages of group effort:
1. Pressures toward conformity;
2. Pressures toward mediocre or averageperformance;
3. Avoidance of individual responsibility;
4. Breeding of conflict.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
11/24
Working within a group (cont)
III. Group decision making and problem solving:
Types of group decision making:
Consultativethe group leader consults with members beforemaking a decision.
Democraticthe problem is turned over to the group and theydelegated the authority to arrive at a decision themselves.
Consensusthe leader shares the problem with the subordinatesand together they generate and evaluate alternatives to reach ona solution.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
12/24
Working within a group (cont)
Advantages of groupdecision making:
1. A greater variety of
alternatives andsolution is considered.
2. Helpful in gainingacceptance and
commitment.
Potential problems withgroup decisions:
1. Individual dominance.
2. Group think.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
13/24
Working within a group (cont)
IV. Group Brainstorming:
A method or way of generating multiple
alternatives for solving a problem.
Rules for effective brainstorming session:
1. Group size: five to seven people;
2. No criticism allowed;
3. Encourage freewheeling (unrestrictive);
4. Quantity and variety are very important;5. Encourage combinations and improvements;
6. Take notes during the session;
7. Edit the alternatives generated to avoid duplication.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
14/24
Leading and Influencing Others
Chapter 14
Learning Objectives:
1. Understand the meaning of leadership and
power;2. Be aware of some of the potential satisfactions
and frustrations in being a leader;
3. Identify the characteristics and behaviors ofeffective leaders;
4. To describe three key leadership styles.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
15/24
Leading and Influencing People
I. What is leadership? How does it differ from Management and Supervision?
Leadershipis the process of influencing the activities of an individual or a
group toward reaching a goal in a given situation. It can be exercised by a
person whether or not he has the official job title of manager or supervisor.
Managementis a process of working with and through other individualsand groups to accomplish organizational goals in a changing environment.
Supervisionis essentially a first-level management. It involves overseeing
the work of others with a particular emphasis on leadership.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
16/24
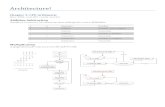
Conceptual Framework of Management
ManagerINPUTS uses
Organizational
Resources:
Human
Financial
Material
Information
through
Functions of
Management: Planning
Organizing
Leading
Controlling
Effectivelyand
Efficiently
ATTAIN
The goals and
objectives of the
organization in a
changing
environment
OUTPUTS/
SOCIAL
RESPONSIBILITY
in order to
Produced Goods
Render ServicesProfit
The organizations
obligation to benefit
society aside from
profits (Eco, legal,ethical, discretionary)
F E E D B A C K
THE MANAGEMENT PROCESS
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
17/24
Management Skills
Human Skills orInterpersonal
Skills
ConceptualSkills Technical Skills
TOP MANAGEMENT
MIDDLE MANAGEMENT
BOTTOM MANAGEMENT
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
18/24
Leading and Influencing People (cont)
Satisfaction of leaders:
1. Feeling of power and prestige;
2. Chance to help others;
3. High income;4. Respect and status;
5. Good opportunities foradvancement;
6. Feeling of being in on things;
7. Chance to control money.
Frustration of leaders:
1. Too much casual overtime;
2. Too many headaches;
3. Not enough authority tocarry out responsibilities;
4. Loneliness;
5. Too many personnelproblems;
6. Too much paper works;
7. Too much politics.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
19/24
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
20/24
Leading and Influencing People (cont)
Two Types of power:
1. Position Powerwhen power stems from the formalposition occupied.
Three subtypes of position power:
a) Legitimate poweris the legitimate right of theleader to make certain types of requests.
b) Reward powerrefers to the leaders control over
rewards valued by the subordinate.
c) Coercive powerrefers to the leaders control overpunishments.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
21/24
Leading and Influencing People (cont)
Two Types of power (cont):
2. Personal Powerwhen power stems from your
personal characteristics.
Two subtypes of personal power:
a) Expert poweris the leaders knowledge relevant
to the job at hand perceived by subordinates.
b) Referent power or Charismatic powerrefers to
loyalty to the leader and the subordinates desire
to please that person.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
22/24
Leading and Influencing People (cont)
III. Characteristics and behaviors of effective leaders
1. Human relation skills;
2. Technical competence;
3. Self-confidence;
4. Motivation and energy;
5. Problem solving ability;
6. Sensitivity to people;
7. Need for achievement;
8. Need for power;
9. Stability of performance;
10. High expectations for subordinates;
11. Good work habits;
12. Ability to size up people and situations.
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
23/24
Leading and Influencing People (cont)
Three key leadership styles:
1. Autocratic leadership (boss-centered) - attempt to
retain most of the authority.
2. Participative leadership (consultative and democratic
styles)shares decision making with members of the
group.
3. Free-rein leadership (subordinate-centered style)
referred to as laissez-faire (allow them to do).
-
8/13/2019 Finals Lectures
24/24
End of Presentation