Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: DYSPEPSIA Primary Care Pathway: DYSPEPSIA Dec 2016 - Page 5/6 Flow...
Transcript of Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: DYSPEPSIA Primary Care Pathway: DYSPEPSIA Dec 2016 - Page 5/6 Flow...

Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: DYSPEPSIA Dec 2016 - Page 2/6
EnhancedPrimaryCarePathway:DYSPEPSIA
1.Focusedsummaryofdyspepsiarelevanttoprimarycare
Dyspepsia refers to a symptom complex of gastroduodenal origin, characterized by epigastric pain ordiscomfortthatmaybetriggeredbyeatingandmaybeaccompaniedbyasenseofabdominaldistentionor“bloating”andlossofappetite.TheRomeIIIcommitteeonfunctionalGIdisordersdefinesdyspepsiaasoneormoreofthefollowingsymptoms:
• Postprandialfullness(postprandialdistresssyndrome)• Epigastricpainorburning(epigastricpainsyndrome)• Earlysatiety
Othersymptomssuchasbelchingandnauseamayoccur.Thereisfrequentoverlapbetweendyspepsiaandheartburn,whichtypifiesgastroesophagealreflux(GERD).Irritablebowelsyndromealsooverlapswithfunctional dyspepsia, where the predominant symptom complex includes bloating and relief afterdefecation. Biliary tract pain should also be considered, the classic symptom description being post-prandial(worsewithfattymeals)deep-seatedrightupperquadrantpainthatbuildsoverseveralhoursandthendissipates.Dyspeptic symptoms in the general population are common: estimates as high as 30% of individualsexperiencedyspepticsymptoms,whilefewseekmedicalcare.Althoughthecausesofdyspepsiaincludeesophagitis,pepticulcerdisease,Helicobacterpyloriinfection,celiacdisease,andrarelyneoplasia,most patientswith dyspepsia have no organic disease, with a normal battery of investigationsincludingendoscopy.Themechanismofthissymptomcomplexis incompletelyunderstood,but likelyinvolvesvisceralhypersensitivity,alterationsingastricaccommodationandemptyingandalteredcentralpainprocessing.2.Checklisttoguideyourin-clinicreviewofthispatientwithdyspepsiasymptoms
o Absenceofredflagfeatures(weightloss,anemia,irondeficiency,dysphagia,vomiting,age>50ywithnewsymptoms)
o Negativeureabreathtest(mustbedoneoffPPI,H2-receptorantagonists,antacidsforminimumof3days,andoffallantibioticsforminimumof4weeks)
o Lifestylemodificationshavebeendiscussedandpatienthasincorporatedtheseintotheirinitialtreatmentplan(smallermeals,avoidanceofidentifiedfoodtriggers,appropriateweightloss,elevationofheadofbed,smokingcessation)
o PatientadherenttotrialofPPI(canstartoncedailythenescalatetotwicedaily,30minutesbeforebreakfastandsupperforminimumof8weeks)

Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: DYSPEPSIA Dec 2016 - Page 3/6
EnhancedPrimaryCarePathway:DYSPEPSIA3.Linkstoadditionalresourcesforphysiciansandpatients
CalgaryGIDivisionhttp://www.calgarygi.com
MyHealth.Alberta.cahttps://myhealth.alberta.ca/health/pages/conditions.aspx?Hwid=tm6322
CanadianDigestiveHealthFoundationhttp://www.cdhf.ca/en/disorders/details/id/20
UpToDate®–BeyondtheBasicsPatientInformation(freelyaccessible)http://www.uptodate.com/contents/upset-stomach-functional-dyspepsia-in-adults-beyond-the-basics?source=search_result&search=dyspepsia+patient+info&selectedTitle=2~150
AlbertaHealthyLivingProgramwww.ahs.ca/info/cdmcalgaryzone.asp
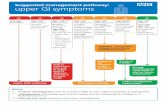
4.Clinicalflowdiagramwithexpandeddetail
This AHS Calgary Zone pathway incorporates the most current evidence-based clinical guidelines fordiagnosisandmanagementofdyspepsia,frombothGastroenterologyandPrimaryCareliterature:
Miwaetal.Evidence-basedclinicalpracticeguidelinesforfunctionaldyspepsia.JGastroenterol.50:125-39,2015
Ansarietal.Initialmanagementofdyspepsiainprimarycare:anevidence-basedapproach.BrJGenPract.63:498-9,2013
Diagnosis and treatment of chronic undiagnosed dyspepsia in adults. Toward Optimized Practicehttp://www.topalbertadoctors.org/cpgs/3294128
AmericanSocietyofGastrointestinalEndoscopyStandardsofPracticeCommittee.Theroleofendoscopyindyspepsia.GastrointestEndosc66:1071-5,2007
Thefollowingisabest-practiceclinicalpathwayformanagementofdyspepsiaintheprimarycaremedicalhome,whichincludesaflowdiagramandexpandedexplanationoftreatmentoptions:

Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: DYSPEPSIA Dec 2016 - Page 4/6

Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: DYSPEPSIA Dec 2016 - Page 5/6
FlowDiagram:DYSPEPSIADiagnosisandManagement-ExpandedDetail1. Establishthediagnosisofdyspepsiaasdefinedabovethroughhistoryandphysicalexamination,
excludingworrisomefeaturesorredflags.Inthepresenceofanyredflags,referraltoGastroenterologyforconsiderationofurgentendoscopicinvestigationisrecommended,eventhoughthepredictivevalueofthesefeaturesissomewhatlimited.
2. Reviewofthepatient’smedicationprofileshouldbeundertakentotrytoidentifyobviousculprits
suchasASA/NSAIDs/COX-2inhibitors,steroids,bisphosphonates,calciumchannelblockers,antibiotics,ironormagnesiumsupplements.Anyneworrecentlyprescribedmedication,overthecounterorherbal/naturalproductmaybeimplicatedasvirtuallyallmedicationscancauseGIupsetinsomepatients.
3. BaselineInvestigationsaimedatidentifyingconcerningfeaturesorclearetiologies:
• CBCandferritin• Anti-tissuetransglutaminasehas>95%sensitivitytoruleoutceliacdisease• ALT,ALP,GGT,andlipase,aimedatidentifyingahepatobiliaryorpancreaticsourceof
pain• Ifpainisconsistentwithbiliarycolicorliverenzymesorlipaseareabnormalorthereis
apalpableabdominalmass,obtainatrans-abdominalultrasound.• UpperGIseriesmaybeconsidered,butislowyieldforrelevantfindings,asis
endoscopy4. TestandtreatHelicobacterpyloribyureabreathtest(UBT).Thisstrategyisbasedonevidencethat
somedyspepticpatientsarecolonizedbyH.pyloriandwillhaveunderlyingpepticulcerdiseaseorgastritis.
• IftheUBTispositive,2016Canadianconsensusguidelinesnowrecommendquadrupletherapyregimens(seetablebelow).
• Tripletherapy(PPI+clarithromycin+amoxicillinormetronidazole)isnolongerrecommended,asstudiesofHpisolatesinCanadasuggest25-30%areresistanttometronidazoleand15-20%areresistanttoclarithromycin.
• Withtheexceptionoftherifabutin-basedregimen,alltreatmentsforHpshouldbe14daysduration.
• ALWAYSdiscusswithyourpatientthepossibleminororseriousadverseeffectsofantibiotics.SeeEnhancedPrimaryCarePathwayH.Pyloriforadditionaldetails,whichincludesusefulpatientinformationhandouts.
• Iffailsthirdlinetherapy,considerreferraltoGastroenterologyordiscussionviaSpecialistLinkbeforeproceedingtoRifabutin-basedtreatment.
5. Lifestylemodification.Therearefewstudiestosupportspecificdietaryrecommendations,buta
trialofvariousdietaryexclusionsundertheguidanceofanutritionistorregistereddieticianmaybehelpful,includingavoidanceoflactoseandfoodshighinfructose(FODMAPs).
6. Empiricanti-secretorymedicationtrial.IntheabsenceH.pyloriinfectionorcontinuedsymptoms
despitesuccessfulH.pylorieradication,atrialofstandarddosePPIfor4-8weeksmaybenefitsomepatients.PPIsarefavouredoverH2-receptorantagonists.Initialtherapyshouldbeoncedaily,30minbeforebreakfast.Ifthereisnosignificantsymptomaticimprovementafter4weeks,stepuptoBID

Enhanced Primary Care Pathway: DYSPEPSIA Dec 2016 - Page 6/6
dosingorswitchtoanotherPPI.Ifsymptomsarethencontrolled,itisadvisabletotitratedowntothelowesteffectivedose.
7. Trialofmotilityagents.Althoughdelayedgastricemptyingcanbedemonstratedin30-80%of
patientswithdyspepsia,gastricemptyingstudiesarenotpartofroutineinvestigationofdyspepsia.Prokineticagentsimprovegastricemptying,andsomepatientsmayfindclinicalbenefit.Domperidonecanbeusedinescalatingdoses,suggeststartingat5mgTID-AC,upto10mgPOQIDasa2-4weektrial.
Thereareinsufficientdatatorecommendtheroutineuseofbismuth,antacids,simethicone,misoprostol,anti-cholinergics,anti-spasmodics,TCAs,SSRIs,herbaltherapies,probioticsorpsychologicaltherapiesinfunctionaldyspepsia.However,thesetherapiesmaybeofbenefitinsomepatients,andthusatrialwithassessmentofresponsemaybereasonableandisunlikelytocauseharm.2016CanadianAssociationofGastroenterologyGuidelinesforTreatmentofH.pylori
First Round
CLAMET Quad for 14 days • PPI standard dose BID • Clarithromycin 500mg BID • Amoxicillin 1000mg BID • Metronidazole 500mg BID
OR
BMT Quad for 14 days • PPI standard dose BID • Bismuth subsalicylate 524mg QID • Metronidazole 375mg QID • Tetracycline 500mg BID
Second Round
• If CLAMET Quad was used as initial treatment, then use BMT Quad for second round • If BMT Quad was used as initial treatment, then use CLAMET Quad or consider Levo-Amox
Third Round Fourth Round
Levo-Amox for 14 days • PPI standard dose BID • Amoxicillin 1000mg BID • Levofloxacin 250 mg BID
Rif-Amox for 10 days • PPI standard dose BID • Rifabutin 150mg BID • Amoxicillin 1000mg BID
IMPORTANT: Rif-Amox should only be considered after failure or intolerance of other regimens. Rifabutin has rarely been associated with potentially serious myelotoxicity. The pros and cons of giving fourth-line therapy should be decided on a case-by-case basis.
Standard doses of PPIs are: omeprazole 20mg, rabeprazole 20mg, lansoprazole 30mg, pantoprazole 40mg, esomeprazole 40mg, and dexlansoprazole 30mg