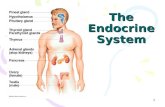
Chapter 9 Endocrine system – cells, tissues, or organs that secrete hormones
Endocrine System. I. Endocrine system A. Endocrine tissues & organs are found throughout the body...
-
Upload
michael-dorsey -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
2
Transcript of Endocrine System. I. Endocrine system A. Endocrine tissues & organs are found throughout the body...

Endocrine System

I. Endocrine system
• A. Endocrine tissues & organs are found throughout the body some along organs part of other systems others found along glands
• B. Hormones are the molecules that are secreted by this system into extracellular fluid, circulate in the blood and communicate regulatory messages throughout the body.– 1. Each hormone has specific receptors in the body that
can regulate reproduction, development, metabolism, growth & behavior


II. Intercellular Communication
• A. There are 2 main criteria that classify how signals are transmitted between cells: the type of secreting cell & the route taken by the signal in reaching its target.

• 1. Endocrine Signaling – hormones secreted into extracellular fluid by endocrine cells & reach target by flowing through blood stream

• 2. Local regulators – secrete molecules that act over short distances & reach target cells solely by diffusion.• Ex. Paracrine – signaling target cells that lie near
secreting cell Autocrine – signaling cells are the secreted cell
itself

• 3. Synaptic & Neuroendocrine Signaling – allow for signaling through nervous system by neurons– a. Neurotransmitters – signaling at synapses– b. Neurohormones – molecules that are secreted by
special neurons into the bloodstream (Ex. ADH)

• 4. Pheromones – chemicals released into the external environment– a. commination within own species

III. Classes of Hormones
• A. Hormones vary by size & chemical properties since there are 3 chemical classes of hormones including:– 1. Polypeptides – 2 polypeptides chains (insulin)– 2. Steroids – composed of lipids, 4 fused carbon rings
(cortisol)– 3. Amines – one single amino acid (tyrosine/trptophan)
• B. The chemical make-up of the hormone explains how the hormone targets the cell; polypeptides & amines are water soluble so they can not pass through the cell membrane unlike steroids that are lipid soluble



IV. Cellular Response Pathways
• A. How a hormone causes a response are different between water-soluble & lipid-soluble hormones.– 1. Water-soluble hormones – are secreted by exocytosis
& travel through the blood stream & bind to cell-surface protein receptors. • a. can cause changes in transcription by signal transduction
(extracellular chemical causing intercellular response) Ex. epinephrine

• 2. Lipid-soluble hormones – diffuse out across a membrane of endocrine cells, they bind to transport proteins that keep them soluble in the blood stream and then diffuse into target cells
– a. change in gene expression

V. Effects of Hormones• A. Hormones can cause more than one type of
response in your body since target cells can vary in their response to a particular molecule with different receptors.– 1. Epinepherine – mediating body’s response to stress• Triggers glycogen breakdown in liver• Increased blood flow to major skeletal muscles• Decreased blood flow to digestive tract


VI. Signaling by Local Regulators
• A. There are several chemical compounds function as local regulators (Paracrine &Autocrine)– 1. Growth factor – stimulate cell proliferation– 2. Nitric oxide – helps regulate the oxygen levels by
activating enzymes that relax muscles– 3. Prostaglandins – stimulate muscle contraction in the
uterus, promote fever & inflammation, blood clotting

VII. Regulatory Pathways
• A. Two basic types of organization– 1. Simple endocrine pathway – endocrine cells respond
directly to internal or environment stimulus by secreting a hormone into blood stream• Ex. Stomach contents enter duodenum - pancrease
– 2. Simple neuroendocrine pathway – stimulates is received by sensory neuron, stimulates neurosecretory cell then secretes a neurohormone which diffuses into the bloodstreamand travels to target cells• Ex. Suckling stimulates hypothalamus then trigger oxytocin
from pituitary gland

Negative vs. Positive

IIX. Control of Blood Glucose• A. Controlled by 2 antagonistic hormones that operate in a
simple endocrine pathway & regulated by negative feedback– 1. Insulin – triggers uptake of glucose from the blood, slows down
glycogen breakdown– 2. Glucagon – promotes the release of glucose into the blood
from energy stores, such as liver glycogen, • B. Both are released by the pancreas into the circulatory
system– Alpha cells – make glucagon– Beta cells – make insulinDiabetes mellitus: deficiency of insulin or a decreased
response to insulin in target cells. Fat becomes main energy source – acidic metabolites form lowering blood pH