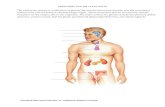
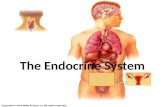
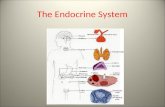
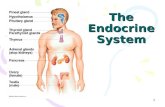
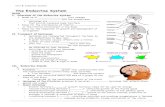
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. TWO GREAT CONTROLLING SYSTEMS Nervous System................ Endocrine System.
Endocrine System
-
Upload
rhys-moult -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
5 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Endocrine System

Topic 13Topic 13

The endocrine systemThe endocrine system
Content by Megan McDonald

HormonesHormonesA chemical substance produced by a
group of cells that is secreted into the blood stream to affect the function of other glands or organs in the body.

Target organsTarget organsOnly specific organs respond to
particular hormones

Hormone physiologyHormone physiology
Hormones alter cellular activity by changing
rate of metabolic processes of target cells.
usual metabolic process of target cells

Hormone classificationHormone classificationLipid solubleSteroid hormonesTwo thyroid hormones – T3 and
T4Nitric Oxide

Lipid soluble hormone Lipid soluble hormone actionaction Lipid soluble hormone diffuses
from blood, across the plasma membrane into a cell
If a target cell hormone binds to receptors in cytosol or nucleus and turns specific genes on or off
A new protein (often enzyme) is made
The protein alters the cells activity and causes the hormone response.

Hormone ClassificationHormone ClassificationWater solubleAmine hormonesPeptide and protein hormonesEicosanoid hormones.

Water soluble hormone Water soluble hormone actionaction Hormone binds to receptor on cell
membrane Binding causes ATP to convert to
cyclic AMP cAMP causes cellular proteins to
activate or deactivate, changing the cells activities.
After a short time cAMP is switched off by phosphodiestrase.

Pancreatic ActionPancreatic ActionSkip breakfastBlood sugar level lowAlpha cells of pancreatic islets
release glucagonGlucagon causes liver cells to
release glucose into blood, rapidly.
Blood sugar level rises.

Pancreatic actionPancreatic actionEat a doughnut for breakfast Blood sugar level lowBeta cells of pancreatic islets
release insulin.Insulin acts on various cells to
accelerate diffusion of glucose into the cells
Blood sugar levels return to normal.

Insulin actionInsulin actionGlucose diffuses into skeletal
muscle fibres.Slows formation of glucose from
fatty acids.Slows formation of glucose from
lactic acid and amino acids.

Endocrine glandsEndocrine glandsSecrete hormones into the blood
stream directlyDuctless

Exocrine glandsExocrine glandsSecrete their products into ducts Ducts open onto surface

Exocrine glandsExocrine glandsSudoriferous (sweat)Sebaceous (oil)SalivaryMucosal cellsLiverIntestinal glandsPancreasMammary glands

Activity 13.1Activity 13.1Colouring book.Qu 5. pg 182


Activity 13.2Activity 13.2Marieb workbook chapter 6Qu 4. p.181Qu. 6 p. 183Qu. 7 p. 183

Topic 16Topic 16
The reproductive The reproductive systemsystem

Male reproductive systemMale reproductive system
Internal structuresTestesDuctal systemUrethra

Male reproductive systemMale reproductive system
External structures (genitalia)PenisScrotum

Male reproductive systemMale reproductive system
Accessory glandsSeminal vesicleProstate glandBulbourethral gland


Male reproductive systemMale reproductive system
Fluid produced by male reproductive system containing -
SpermNutrientsMucosa
Semen

FunctionFunctionProduce sperm for delivery to the
female reproductive tract.Produce testosterone.

Sperm productionSperm productionBegins at pubertyContinues throughout lifeSpermatogenesis takes 64 -72
days


SpermSpermMade in testesDevelop in seminiferous tubules1 sperm fertilizes an ovum50 – 100 million sperm/millilitre
semen

TestosteroneDevelopment of male sexual
characteristicsControl of sperm maturationControl of sperm productionInfluences sexual behaviour

TestosteroneTestosteroneProduced in interstitial cells of
testes.Cells activated in puberty Luteinising hormone (LH) from
anterior pituitary gland.

TestosteroneTestosteroneStimulate development of
reproductive hormonesMale secondary sex
characteristics.

Secondary sex Secondary sex characteristicscharacteristicsEnlargement of larynx - deep voicePubic, axillary, chest and facial hairMuscular skeletal growth – wide
shoulders/narrow hips.Increased sebaceous gland secretionThickening of skin

Activity 16.2Activity 16.2Marieb workbook chapter 16Qu 9. p. 325

Female reproductive Female reproductive systemsystemInternal structuresVaginaUterusUterine (fallopian) tubesovaries

Female reproductive Female reproductive systemsystemExternal structures (Genitalia)
VulvaMons pubisLabiaClitorisUrethral and vaginal orificesBartholins glands


Activity 16.3Activity 16.3Marieb workbook chapter 16Qu 10. p. 325Qu 11. p. 326Qu 12. p. 327

FunctionFunctionProduction of ova (oocytes)Facilitate fertilisationFacilitate transportation, nuturing
of foetus

Ovarian cycleOvarian cycleOvarian follicles contain
immature ovaFSH released from Ant. Pituitary
glandFSH stimulates some immature
ova to mature each monthThis occurs for 30 – 40 years.

Ovarian cycleOvarian cycleOvulationMature follicle rupturesEgg released into peritoneal
cavityEgg swept into fallopian tube for
fertilisationFinishes at menopause (40-50
y.o)

Activity 16.4Activity 16.4Marieb workbook chapter 16Qu 16. p. 329

Menstrual cycleMenstrual cycle
When ova is unfertilisedEndometrial layer of uterus
breaks downExpelled via vaginaCyclical over 28 days (+/-)Occurs in response to hormones
in blood

Menstrual cycle – phase 1Menstrual cycle – phase 1Days 1 – 5Menstrual phaseFSH release by anterior pituitaryFollicle development beginsMenstrual flow 50-150ml
blood, tissue fluid, epithelial cells.Declining progesterone and oestrogen

Menstrual cycle – phase 1IMenstrual cycle – phase 1IDays 6 -14Proliferative phaseEndometrium is proliferating 4 -
10mmFollicle in ovary growing and
bulgingEstrogen production by mature
follicle increases.Ends in ovulation of (usually) one
ovum

Menstrual cycle – phase Menstrual cycle – phase 1II1IIDays 15 – 28Secretory phaseEndometrial glands secrete
glycogenEndometrium thickens to 12-
18mmCorpus luteum secretes
progesterone and estrogens

Mammary glandsMammary glandsModified sweat glands 15 -20 lobes radiating around
nippleProduce milk during lactationProduction stimulated by
prolactinRelease stimulated by oxytocin
from post. Pituitary and sucking action

Fertilisation & EmbryonicFertilisation & EmbryonicDevelopment Development

FertilisationFertilisationMale sperm + ovum = zygote
Usually occurs in distal fallopian tube

Embryonic developmentEmbryonic developmentDevelopment begins immediatelyImplants in endometrial layer of
uterusPlacenta forms

PlacentaPlacenta
SuppliesNutritionOxygenRemoves wasteProduces hormones

Embryonic developmentEmbryonic developmentProgresses rapidly for first 2
months9 weeks – Foetus40 week pregnancyConcludes with labour and
childbirth.

Activity 16.7Activity 16.7Marieb workbook chapter 16Qu 22. p. 333Qu 28. p. 335Qu 31. p. 336Qu 33. p. 336

Thank you!Thank you!