Endocrine system
-
Upload
geraldine-d-reyes -
Category
Education
-
view
1.117 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Endocrine system

ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Prepared by: Geraldine D. Reyes
Jerome De Jesus


Endocrine system
• Endocrine and Nervous systems together constitute the two
great regulatory systems of the body.
• Endocrine System is made up of tissues or organs
called endocrine glands, which secrete chemicals directly into the
bloodstream. ( The chemical secretions are called HORMONES )
• ENDOCRINE CELLS are glandular secretory cells that
release their secretions internally rather than on an epitelial surface.
• HORMONES are chemical messengers that are released in
one tissue and transported by bloodstream to reach target cells in
their tissues.

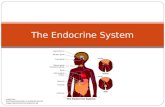
COMPONENTS OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
• HYPOTHALAMUS
• PINEAL GLAND
• PITUITARY GLAND
• THYROID GLAND
• THYMUS
• PARATHYROID GLANDS
• ADRENAL GLANDS
• GONADS
• PANCREAS

HYPOTHALAMUS
• Primary link between Endocrine and Nervous systems.
• Portion of diencephalon that includes the mamilary bodies, infundibulum and part of hypophysis.
• HYPOTHALAMUS regulate activities of nervous and endocrine systems in three ways:
1. Acts as an endocrine organ ( release hormones ADH and OXYTOCIN )
2. Secretes REGULATORY HORMONES ( releasing hormones or inhibiting hormones )
3. Control endocrine cells in adrenal medullae.
PITUITARY GLAND
• Also know as HYPOPHYSIS
• Small oval gland seated in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone
• The infundibulum conects it to the floor of the hypothalamus.
• Consists of two lobes ( anterior and posterior )

PINEAL GLAND
• Lies in the roof of the thalamus ( third ventricle ). Under the posterior end of the corpus callosum.
• It contains neurons, glial cells and secretory cells that synthesize the hormone MELATONIN ( PINEALOCYTES
are the cells that secrete melatonin )
THYROID GLAND
• Lies anterior to the trachea and just below the thyroid cartilage, which forms most of the anterior surface of
the larynx.
• Has two lobes ( bow tie or butterfly shape ) united by a slender connection ( the isthmus )
PARATHYROID GLANDS
• There are two pairs of parathyroids embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
• Each one is isolated from thyroid by the Parathyroid capsule.
• There are two different types of cells within the parathyroid glands ( chief cells and oxyphil cells )
• The CHIEF CELLS produces parathyroid hormone ( PARATHORMONE )
• Parathormone stimulates osteoclasts, inhibits osteoblasts, increases intestinal absorption, and reduces urinary
excretion of calcium ions.

THE THYMUS
• Is embedded in the mediastinum, usually posterior to the sternum.
• The gland is organized in two lobes separated by a septae. Each lobe consists of a dense outer CORTEX and a central
MEDULLA.
• The CORTEX consists of epithelial cells that secrete the thymic hormones ( thymosins ) which play a key role in
development and maintenance of inmunological defenses.
• The MEDULLA has the thymic corpuscles ( Hassall´s corpuscles ) surrounded by lymphocytes. Function:unknow.
ADRENAL GLANDS
• Also know as SUPRARENAL glands.
• Lie along the superior borders of the kidneys.
• Has a pyramid-shaped glands.
• The adrenals can be subdivided on histological grounds into an outer cortex and an inner medulla.
PANCREAS
• Contains exocrine and endocrine cells populations.
• Endocrine cells are found within the pancreatic islets ( ISLETS OF LANGERHANS )
• Alpha cells secrete glucagon
• Beta cells produce insulin

GONADS
• TESTES – male gonads ( 2 ), located in the scrotum.
• Each testicle is made up seminiferous tubules which produce spermatozoa. Between
the tubules are the INTERSTITIAL CELLS that secrete steroid hormones know
asANDROGENS, notably TESTOSTERONE.
TESTOSTERONE promotes production of functional sperm, mantains the secretory glands of
the male reproductive tract, and determines secondary sexual characteristics.
• OVARIES – female sex organs, located in the pelvic cavity.
• Follicle cells in the ovaries produce steroid ESTROGENS while eggs are developing.
After ovulation the cells reorganize into a corpus luteum that produces PROGESTERONE.
If a pregnancy occurs, the placenta will gradually develop endocrine functions of its ow

Function of Endocrine System-
The endocrine systems consists of hormones and glands. The hormones
are the chemical messengers of the body that travel down to the
various body parts concerned transferring information. There are many
hormones secreted by the endocrine system, and each individual type
of hormone affects only those body cells that have a genetic program
that allows them to react only to those hormones that are related to
them. The hormones influence the body to react according to the
changes in the balance of fluids and minerals in blood, stress, infection,
etc. Let us understand more on how does the endocrine system
function.